Mott ." cometer, which we can analyze later in Chap. 7. A small ball of diameter D and density p, falls through a tube of test liquid (p. µ). The fall velocity V is calculated by the time to fall a measured distance. The formula for calculating the viscosity of the fluid is discusses a simple falling-ball vis- (Po – p)gD² 18 V This result is limited by the requirement that the Reynolds number (pVD/u) be less than 1.0. Suppose a steel ball (SG = 7.87) of diameter 2.2 mm falls in SAE 25W oil (SG = 0.88) at 20°C. The measured fall velocity is 8.4 cm/s. (a) What is the viscosity of the oil, in kg/m-s? (b) Is the Reynolds num- ber small enough for a valid estimate?
Mott ." cometer, which we can analyze later in Chap. 7. A small ball of diameter D and density p, falls through a tube of test liquid (p. µ). The fall velocity V is calculated by the time to fall a measured distance. The formula for calculating the viscosity of the fluid is discusses a simple falling-ball vis- (Po – p)gD² 18 V This result is limited by the requirement that the Reynolds number (pVD/u) be less than 1.0. Suppose a steel ball (SG = 7.87) of diameter 2.2 mm falls in SAE 25W oil (SG = 0.88) at 20°C. The measured fall velocity is 8.4 cm/s. (a) What is the viscosity of the oil, in kg/m-s? (b) Is the Reynolds num- ber small enough for a valid estimate?
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter5: Analysis Of Convection Heat Transfer
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.9P: When a sphere falls freely through a homogeneous fluid, it reaches a terminal velocity at which the...
Related questions
Question
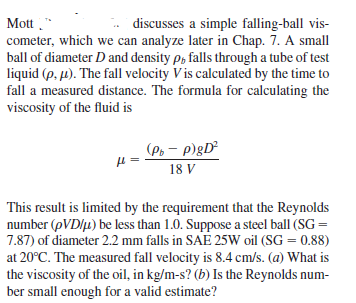
Transcribed Image Text:Mott ."
cometer, which we can analyze later in Chap. 7. A small
ball of diameter D and density p, falls through a tube of test
liquid (p. µ). The fall velocity V is calculated by the time to
fall a measured distance. The formula for calculating the
viscosity of the fluid is
discusses a simple falling-ball vis-
(Po – p)gD²
18 V
This result is limited by the requirement that the Reynolds
number (pVD/u) be less than 1.0. Suppose a steel ball (SG =
7.87) of diameter 2.2 mm falls in SAE 25W oil (SG = 0.88)
at 20°C. The measured fall velocity is 8.4 cm/s. (a) What is
the viscosity of the oil, in kg/m-s? (b) Is the Reynolds num-
ber small enough for a valid estimate?
Expert Solution
Step 1
The data given is,
- The specific gravity of steel ball, SGb = 7.87
- The diameter of the steel ball, D = 2.2 mm = 0.0022 m
- Fall velocity, V = 8.4 cm/s = 0.084 m/s
- The specific gravity of oil, SG = 0.88
Step 2
The formula employed with the problem to calculate viscosity is as follows,
The density of ball and oil will be given as follows,
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning