Mutations of haplosufficient genes are recessive Homozygous wild type Heterozygote Homozygous recessive mutant +/m m/m +/+ Protein Functional Functional Nonfunctional MRNA and Chromosome Chromosome MRNA Protein Functional Nonfunctional Nonfunctional be distinguished from the heterozygote; that is, at the phenotypic level, A/A = A/a. As mentioned earlier, phenylketonuria (PKU) and many other single-gene human diseases are fully recessive, whereas their wild-type alleles are dominant. Other single-gene diseases such as achondroplasia are fully dominant, whereas, in those cases, the wild-type allele is recessive. How can these dominance relations FIGURE 6-1 In the heterozygote, even though the mutated copy of the gene pro- duces nonfunctional protein, the wild-type copy generates enough functional protein to produce the wild-type phenotype. E E
Mutations of haplosufficient genes are recessive Homozygous wild type Heterozygote Homozygous recessive mutant +/m m/m +/+ Protein Functional Functional Nonfunctional MRNA and Chromosome Chromosome MRNA Protein Functional Nonfunctional Nonfunctional be distinguished from the heterozygote; that is, at the phenotypic level, A/A = A/a. As mentioned earlier, phenylketonuria (PKU) and many other single-gene human diseases are fully recessive, whereas their wild-type alleles are dominant. Other single-gene diseases such as achondroplasia are fully dominant, whereas, in those cases, the wild-type allele is recessive. How can these dominance relations FIGURE 6-1 In the heterozygote, even though the mutated copy of the gene pro- duces nonfunctional protein, the wild-type copy generates enough functional protein to produce the wild-type phenotype. E E
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter10: From Proteins To Phenotypes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2CS: A couple was referred for genetic counseling because they wanted to know the chances of having a...
Related questions
Question
In Figure 6-1,
a. what do the yellow stars represent?
b. explain in your own words why the heterozygote is
functionally wild type
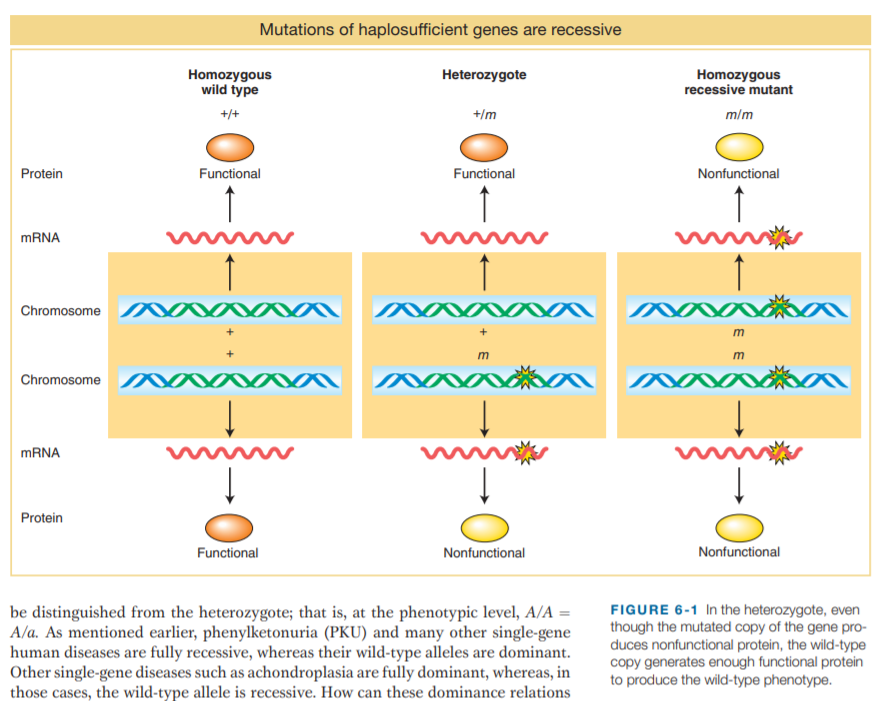
Transcribed Image Text:Mutations of haplosufficient genes are recessive
Homozygous
wild type
Heterozygote
Homozygous
recessive mutant
+/m
m/m
+/+
Protein
Functional
Functional
Nonfunctional
MRNA
and
Chromosome
Chromosome
MRNA
Protein
Functional
Nonfunctional
Nonfunctional
be distinguished from the heterozygote; that is, at the phenotypic level, A/A =
A/a. As mentioned earlier, phenylketonuria (PKU) and many other single-gene
human diseases are fully recessive, whereas their wild-type alleles are dominant.
Other single-gene diseases such as achondroplasia are fully dominant, whereas, in
those cases, the wild-type allele is recessive. How can these dominance relations
FIGURE 6-1 In the heterozygote, even
though the mutated copy of the gene pro-
duces nonfunctional protein, the wild-type
copy generates enough functional protein
to produce the wild-type phenotype.
E E
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning