Next, imagine the rather than sliding down the hill, the skier holds onto a rope that is connected to a tree at the top of the hill, and that the force of the rope holds the skier in place. How would you modify your force diagram now? Hint: The rope is parallel to the surface of the hill. Show that the net force is zero, again by using the parallelogram rule to show that any 2 forces add up to exactly cancel the 3rd force. Note that tension force is always along the direction of the rope but is not drawn equal to the length of the rope. What must be true for an object in equilibrium is that vector sum of the forces in any and every direction must equal zero. Though, we only need to show that along our chosen coordinate axes. Here it is okay to use the "usual" x- and y- directions
Next, imagine the rather than sliding down the hill, the skier holds onto a rope that is connected to a tree at the top of the hill, and that the force of the rope holds the skier in place. How would you modify your force diagram now? Hint: The rope is parallel to the surface of the hill. Show that the net force is zero, again by using the parallelogram rule to show that any 2 forces add up to exactly cancel the 3rd force. Note that tension force is always along the direction of the rope but is not drawn equal to the length of the rope. What must be true for an object in equilibrium is that vector sum of the forces in any and every direction must equal zero. Though, we only need to show that along our chosen coordinate axes. Here it is okay to use the "usual" x- and y- directions
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter5: Newton's Law Of Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 85AP: Two boxes, A and B, are at rest Box A is on level ground, while box B rests on an inclined plane...
Related questions
Question
2. Next, imagine the rather than sliding down the hill, the skier holds onto a rope that is connected to a tree at the top of the hill, and that the force of the rope holds the skier in place. How would you modify your force diagram now?
Hint:
The rope is parallel to the surface of the hill. Show that the net force is zero, again by using the parallelogram rule to show that any 2 forces add up to exactly cancel the 3rd force. Note that tension force is always along the direction of the rope but is not drawn equal to the length of the rope. What must be true for an object in equilibrium is that vector sum of the forces in any and every direction must equal zero. Though, we only need to show that along our chosen coordinate axes. Here it is okay to use the "usual" x- and y- directions
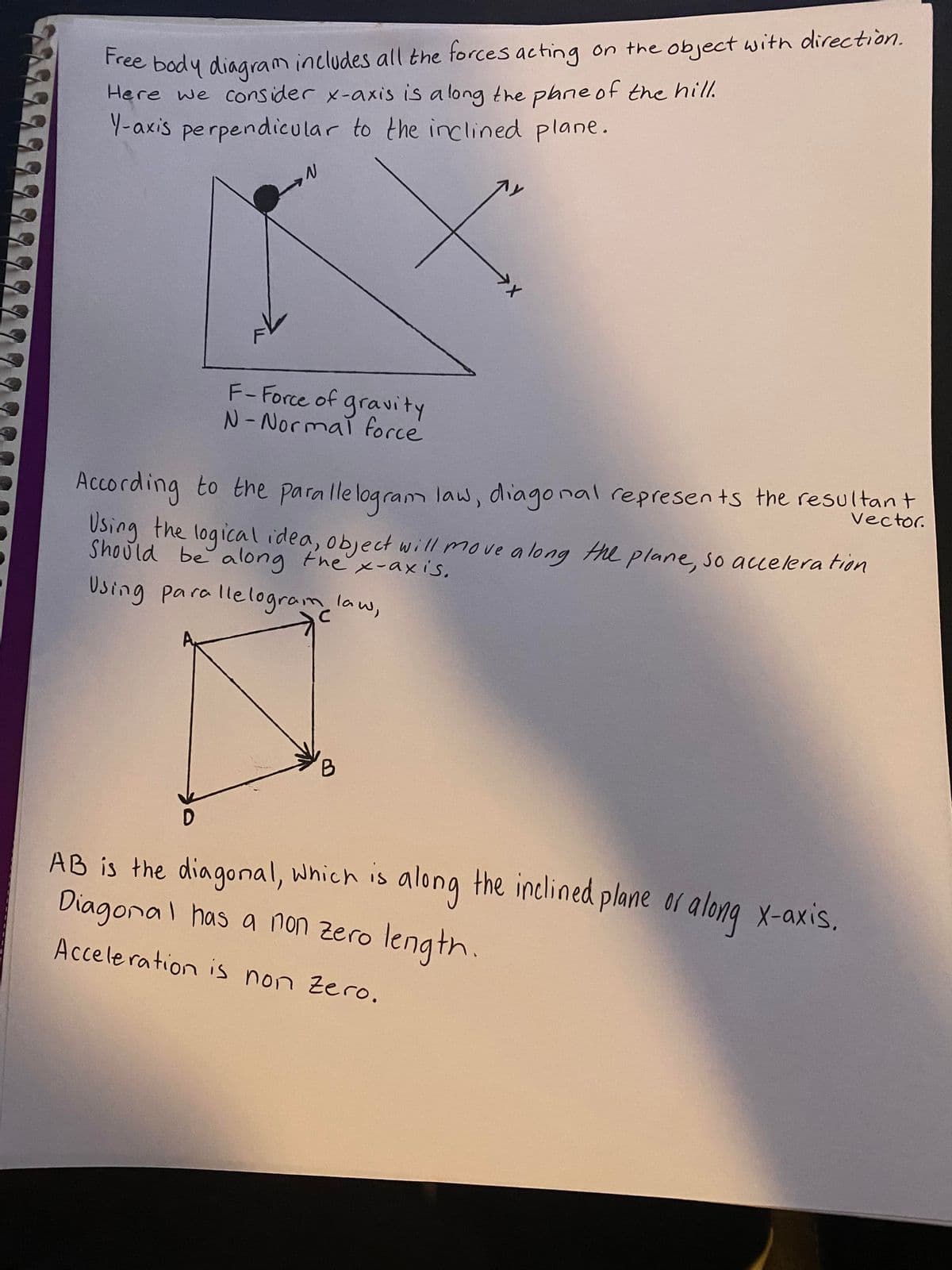
Transcribed Image Text:Tree body diagram includes all the forces acting on the object with direction.
Here we consider x-axis is a long the pane of the hil.
Y-axis perpendicular to the inclined plane.
F-Force of gravity
N-Normai force
Vector.
According to the parallelogranm law, diago nal represen ts the resultant
Using the logical idea, object will move a long HL plane, so accelera tion
Should be along thex-axis,
Using para llelogram law,
AB is the diagonal, which is along the inclined plane or along x-axis.
Diagonal has a non zero
length.
Accele ration is non Zero.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill