Now, suppose that the public fully anticipates the Fed's decision to decrease the money supply. Assume the public also believes that the Fed is firmly committed to carrying out this policy. According to rational expectations theory, when the economy is in long-run equilibrium, a fully anticipated decrease in the money supply will cause the economy to move on the previous Phillips curve graph. In this case, rational expectations theory predicts that the fully anticipated decrease in the money supply will have the immediate effect of in the inflation rate and in the unemployment rate.
Now, suppose that the public fully anticipates the Fed's decision to decrease the money supply. Assume the public also believes that the Fed is firmly committed to carrying out this policy. According to rational expectations theory, when the economy is in long-run equilibrium, a fully anticipated decrease in the money supply will cause the economy to move on the previous Phillips curve graph. In this case, rational expectations theory predicts that the fully anticipated decrease in the money supply will have the immediate effect of in the inflation rate and in the unemployment rate.
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337091985
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter17: The Short-run Trade-off Between Inflation And Unemployment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PA
Related questions
Question
Just need an answer for the red bracket question please, thanks.
Solutions for the bottom question are as follows:
from A to B to C then back to B, From A to B and then back to A, from A to B, From A to B to C, from A to C
An increase, a decrease, no change,
An increase, decrease, no change.
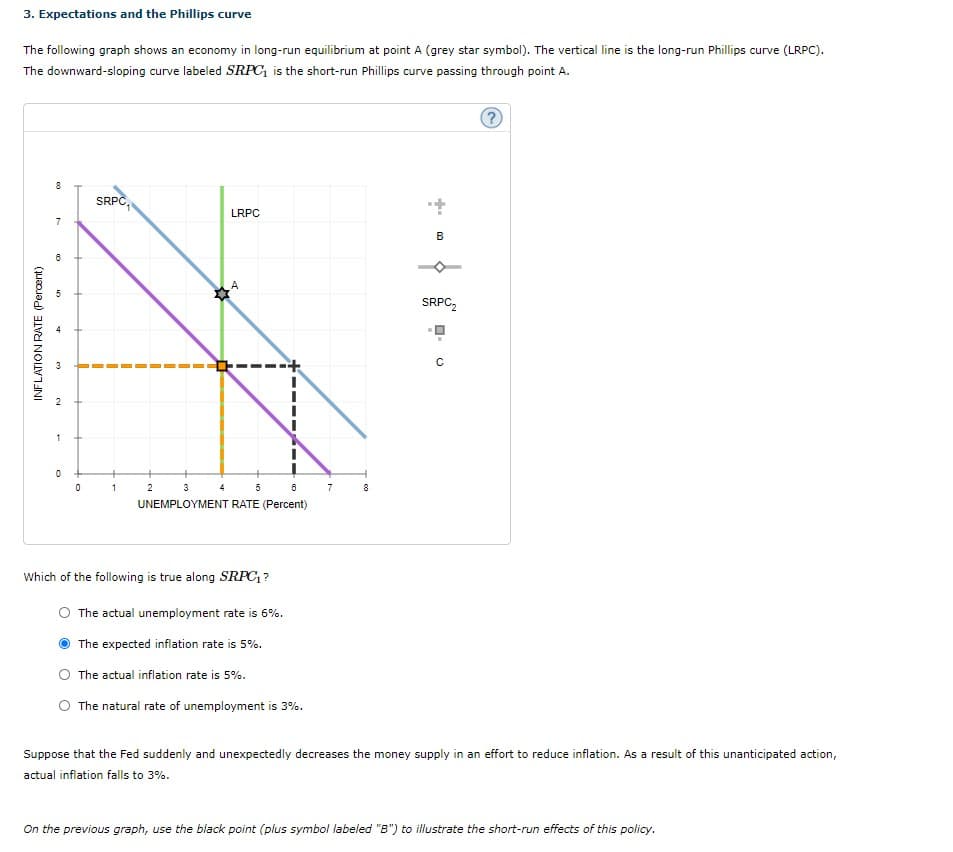
Transcribed Image Text:3. Expectations and the Phillips curve
The following graph shows an economy in long-run equilibrium at point A (grey star symbol). The vertical line is the long-run Phillips curve (LRPC).
The downward-sloping curve labeled SRPC, is the short-run Phillips curve passing through point A.
SRPC
LRPC
7
SRPC,
3
2
1
2
3
5 6
4
7
8
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (Percent)
Which of the following is true along SRPC, ?
The actual unemployment rate is 6%.
The expected inflation rate is 5%.
The actual inflation rate is 5%.
The natural rate of unemployment is 3%.
Suppose that the Fed suddenly and unexpectedly decreases the money supply in an effort to reduce inflation. As a result of this unanticipated action,
actual inflation falls to 3%.
On the previous graph, use the black point (plus symbol labeled "B") to illustrate the short-run effects of this policy.
INFLATION RATE (Percent)
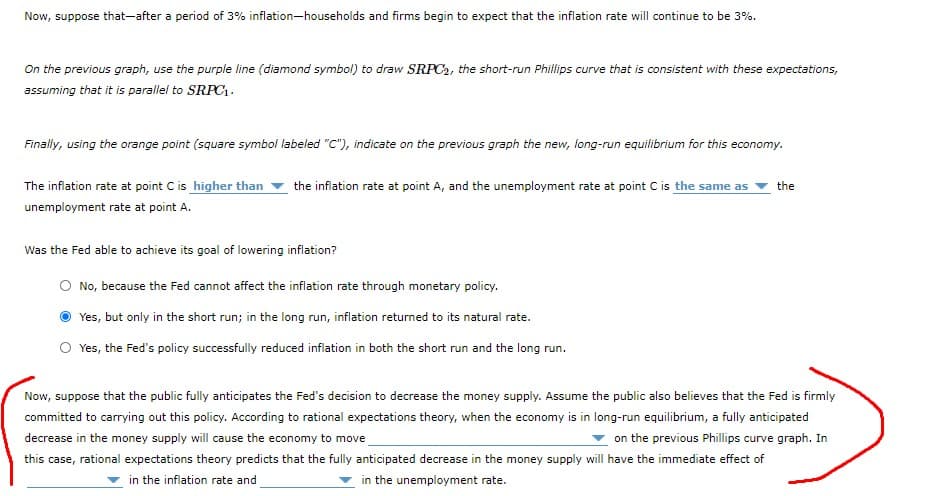
Transcribed Image Text:Now, suppose that-after a period of 3% inflation-households and firms begin to expect that the inflation rate will continue to be 3%.
On the previous graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to draw SRPC2, the short-run Phillips curve that is consistent with these expectations,
assuming that it is parallel to SRPC.
Finaly, using the orange point (square symbol labeled "C"), indicate on the previous graph the new, long-run equilibrium for this economy.
The inflation rate at point Cis higher than
the inflation rate at point A, and the unemployment rate at point C is the same as
the
unemployment rate at point A.
Was the Fed able to achieve its goal of lowering inflation?
O No, because the Fed cannot affect the inflation rate through monetary policy.
Yes, but only in the short run; in the long run, inflation returned to its natural rate.
Yes, the Fed's policy successfully reduced inflation in both the short run and the long run.
Now, suppose that the public fully anticipates the Fed's decision to decrease the money supply. Assume the public also believes that the Fed is firmly
committed to carrying out this policy. According to rational expectations theory, when the economy is in long-run equilibrium, a fully anticipated
decrease in the money supply will cause the economy to move
on the previous Phillips curve graph. In
this case, rational expectations theory predicts that the fully anticipated decrease in the money supply will have the immediate effect of
in the inflation rate and
in the unemployment rate.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
