o Bo m1 m2 Figure P7.6 Problems 66 and 67. 67. * Again consider the track and carts in Figure P7.66 with m, = 10 kg and m, = 20 kg, but this time the carts stick together after the collision. (a) Find the height h from which cart 1 would need to start to make sure that both carts complete the loop without leaving the track. (b) Find the height needed if instead the
o Bo m1 m2 Figure P7.6 Problems 66 and 67. 67. * Again consider the track and carts in Figure P7.66 with m, = 10 kg and m, = 20 kg, but this time the carts stick together after the collision. (a) Find the height h from which cart 1 would need to start to make sure that both carts complete the loop without leaving the track. (b) Find the height needed if instead the
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter9: Linear Momentum And Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.59P: Figure P9.59a shows an overhead view of the configuration of two pucks of mass In on frictionless...
Related questions
Question
100%
The problem 67a is attached. I received the wrong solution already once. Please use the equation sheet attached and start with an equation on this sheet and show all algebra and conversion of formula and ALL steps. Please do not use U for velocity. Use V and subscript. I know the final answer and I know most steps but I need help with pulling it together. Please show all work. Final answer is 5.6m. Please help me get to this answer. I believe FnetdeltaT=deltaMA needs to be used first.
Transcribed Image Text:Figure P7.65
vom
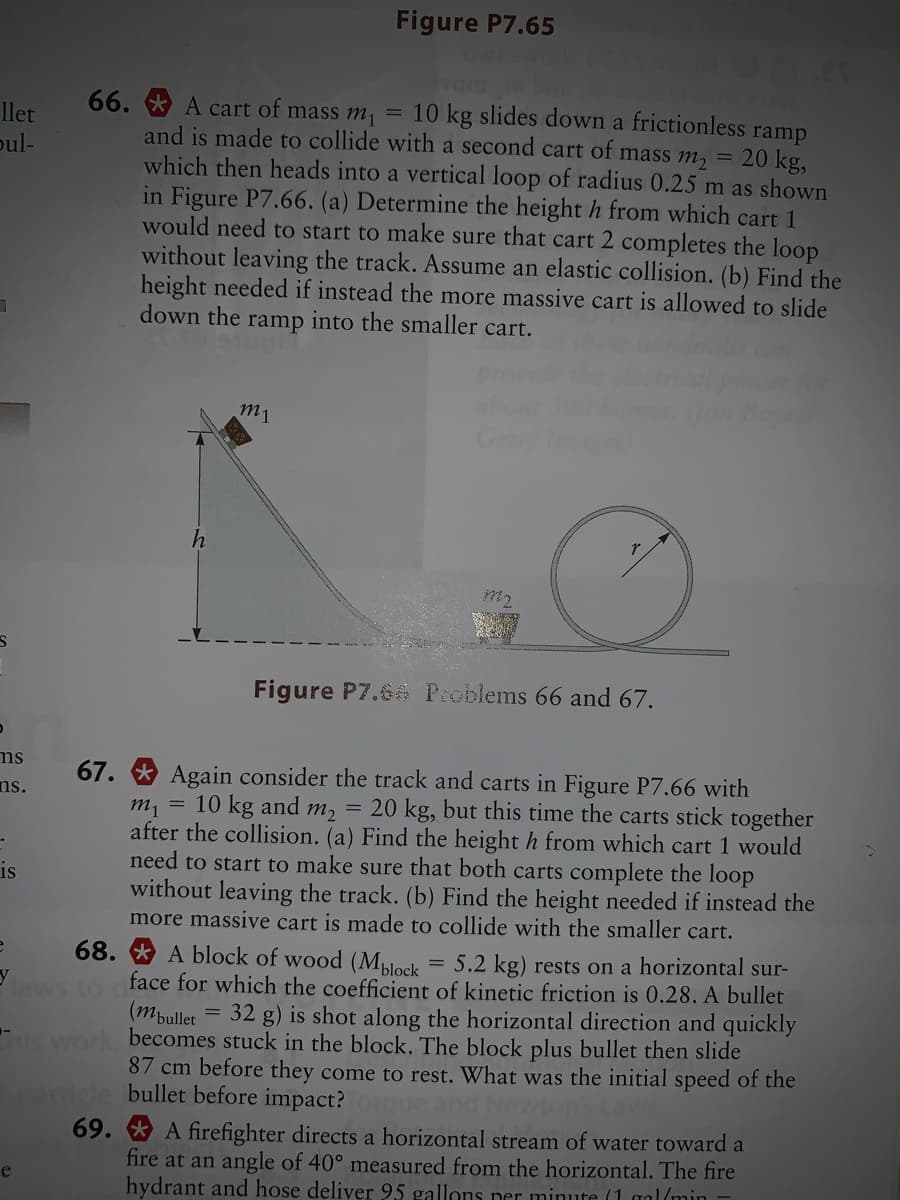
66. * A cart of mass m, = 10 kg slides down a frictionless ramp
and is made to collide with a second cart of mass m, = 20 kg,
which then heads into a vertical loop of radius 0.25 m as shown
in Figure P7.66. (a) Determine the height h from which cart 1
would need to start to make sure that cart 2 completes the loop
without leaving the track. Assume an elastic collision. (b) Find the
height needed if instead the more massive cart is allowed to slide
into the smaller cart.
llet
pul-
down the
ramp
m1
m2
Figure P7.6 Problems 66 and 67.
ms
Again consider the track and carts in Figure P7.66 with
m, = 10 kg and m, = 20 kg, but this time the carts stick together
after the collision. (a) Find the height h from which cart 1 would
need to start to make sure that both carts complet
without leaving the track. (b) Find the height needed if instead the
more massive cart is made to collide with the smaller cart.
67.
ns.
the loop
is
68. * A block of wood (Mblock
face for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.28. A bullet
(mpullet
becomes stuck in the block. The block plus bullet then slide
87 cm before they come to rest. What was the initial speed of the
bullet before impact?
5.2 kg) rests on a horizontal sur-
32 g) is shot along the horizontal direction and quickly
69.
A firefighter directs a horizontal stream of water toward a
fire at an angle of 40° measured from the horizontal. The fire
hydrant and hose deliver 95 gallons per minute (1 gal(min
e

Transcribed Image Text:pr
Physics 103 Equation Sheet
Patm = 1.01 x 10S N/m?
Mearth = 5.98 x 1024 kg
g = 9.8 m/s? = 32 ft/s?
k = 1.38 x 1023 J/K
G=6.67 x 1011 Nm?/kg?
O = 5.67 x 108 W/m?K
Pwater = 1.0 x 10³ kg/m3
Pair = 1.29 kg/m3
Pseawater = 1.03 x 10' kg/m?
Pice = 0.92 x 103 kg/m3
Piron = 7.87 x 10³ kg/m3
Paluminum = 2.7 x 10 kg/m?
orc
nj
rr
es
sin e = opp/hyp
cos e = adj/hyp
tan e = opp/adj
a? + b? = c?
-b ± vb2 – 4ac
2a
or
Ax
v =
At
Av
a =
At
v? = vo? + 2a(x-xo)
at
Δω
W =
a =
Δε
lir
X = Xo + Vọt + ½ at?
V = Vo + at
m
EF = ma
ET = la
T= Fr sin e
Fg = w = mg
Gm,m2
F, =
10
Fr S uN
ac = v/r
Fb = pVsubg
Fsp = -kAx
r2
ki
V1A1 = V2A2=AV/At
P1+pgh;+½ pv;?= P2+pgh2+½ pv;?
p = m/V
Vave = (AP r)/8nL
P = Po+ pgh
P = F/A
i
DE
IE
P = W/At
FAt = Ap
W = FAr cos e
Wnet = AKE
PEg = mgh
PEsp = % k Ax?
KE1 + PE1 = KE2 + PE2 – Wnc
KE = % mv?
p = mv
E = mc?
Momentum
T2 - T1
= KA
L
= o£A(T – T†)
t
AS =
Q = mL
AU = Q-W
R=L/K
Q = mc AT
PV = NkT
KEave = 3/2 kT
thermeff = 1-Tc/TH
W = PAV
Cannot Start with mese but hey are anes to build to using above
Fret o MA =MAV/AT
Must start withh
Fnet AT- Amv
AP - Amv- FnetOT
equahon above he line
on top and buld from
there showing all Steps.
and manixlation' of formclas.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning