P3C.1 At 10K Cpm (Hg(s)) = 4.64 J K¯¹ mol¹. Between 10 K and the melting point of Hg(s), 234.3 K, heat capacity measurements indicate that the entropy increases by 57.74 J K ¹ mol ¹. The standard enthalpy of fusion of Hg(s) is 2322 Jmol-¹ at 234.3 K. Between the melting point and 298.0 K, heat capacity measurements indicate that the entropy increases by 6.85 J K¹ mol™¹. Determine the Third-Law standard molar entropy of Hg(1) at 298 K. P3C.2 The measurements described in Problem P3C.1 were extended to 343.9 K, the normal boiling point of Hg(1). Between the melting point and the boiling point, heat capacity measurements indicate that the entropy increases by 10.83 JK¯¹ mol¯¹. The standard enthalpy of vaporization of Hg(1) is 60.50 kJ mol¹ at 343.9 K. Determine the Third-Law standard molar entropy of Hg(g) at 343.9K (you will need some of the data from Problem P3C.1).
P3C.1 At 10K Cpm (Hg(s)) = 4.64 J K¯¹ mol¹. Between 10 K and the melting point of Hg(s), 234.3 K, heat capacity measurements indicate that the entropy increases by 57.74 J K ¹ mol ¹. The standard enthalpy of fusion of Hg(s) is 2322 Jmol-¹ at 234.3 K. Between the melting point and 298.0 K, heat capacity measurements indicate that the entropy increases by 6.85 J K¹ mol™¹. Determine the Third-Law standard molar entropy of Hg(1) at 298 K. P3C.2 The measurements described in Problem P3C.1 were extended to 343.9 K, the normal boiling point of Hg(1). Between the melting point and the boiling point, heat capacity measurements indicate that the entropy increases by 10.83 JK¯¹ mol¯¹. The standard enthalpy of vaporization of Hg(1) is 60.50 kJ mol¹ at 343.9 K. Determine the Third-Law standard molar entropy of Hg(g) at 343.9K (you will need some of the data from Problem P3C.1).
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter6: Thermochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 68E: In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 1.60 g NH4NO3 is mixed with 75.0 g water at an initial temperature of...
Related questions
Question
Please answer P3C.2. Question P3C.1 is just posted for reference.
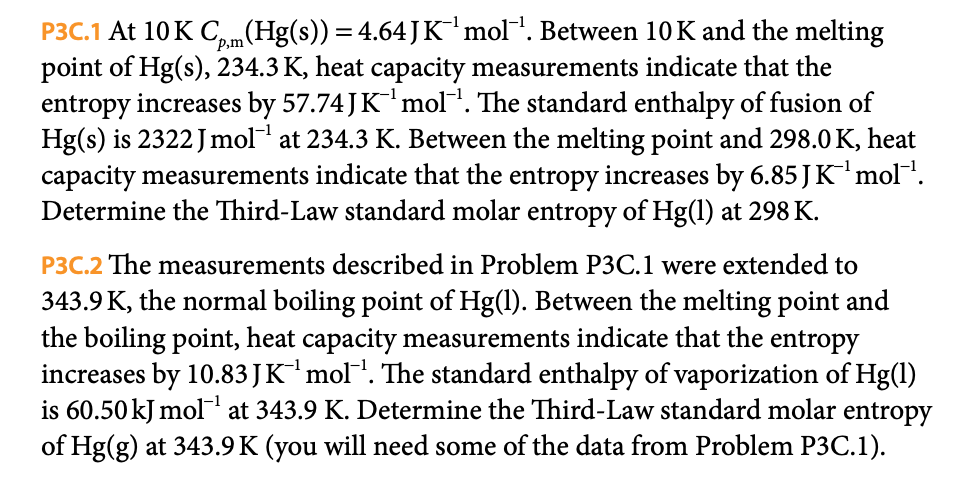
Transcribed Image Text:P3C.1 At 10K Cpm (Hg(s)) = 4.64 J K¯¹ mol¹. Between 10 K and the melting
point of Hg(s), 234.3 K, heat capacity measurements indicate that the
entropy increases by 57.74 J K ¹ mol ¹. The standard enthalpy of fusion of
Hg(s) is 2322 Jmol-¹ at 234.3 K. Between the melting point and 298.0 K, heat
capacity measurements indicate that the entropy increases by 6.85 J K¹ mol™¹.
Determine the Third-Law standard molar entropy of Hg(1) at 298 K.
P3C.2 The measurements described in Problem P3C.1 were extended to
343.9 K, the normal boiling point of Hg(1). Between the melting point and
the boiling point, heat capacity measurements indicate that the entropy
increases by 10.83 JK¯¹ mol¯¹. The standard enthalpy of vaporization of Hg(1)
is 60.50 kJ mol¹ at 343.9 K. Determine the Third-Law standard molar entropy
of Hg(g) at 343.9K (you will need some of the data from Problem P3C.1).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning