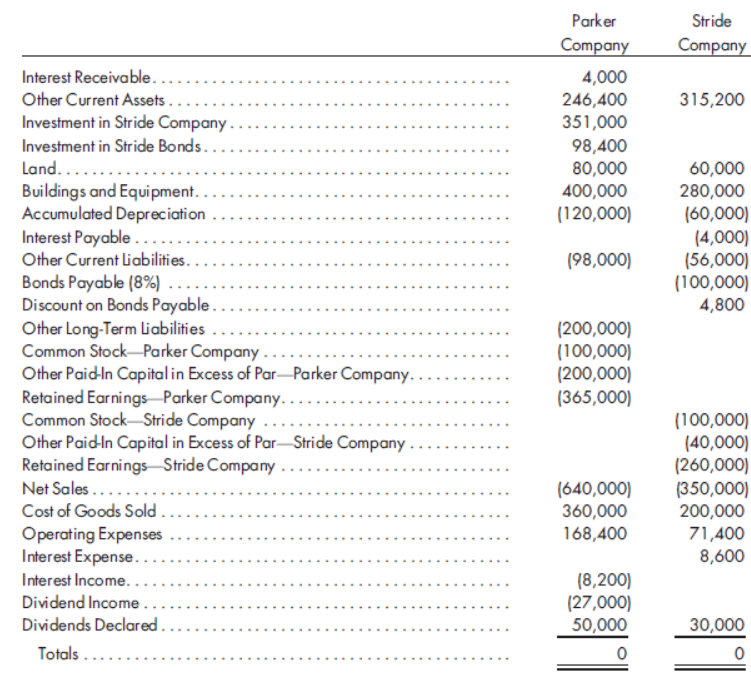
Parker Stride Company Company Interest Receivable... 4,000 Other Current Assets . 246,400 351,000 315,200 Investment in Stride Company.. Investment in Stride Bonds.. Land...... Buildings and Equipment. Accumulated Depreciation Interest Payable .... Other Current liabilities.. 98,400 80,000 400,000 (120,000) 60,000 280,000 (60,000) (4,000) (56,000) (100,000) 4,800 ... (98,000) Bonds Payable (8%) Discount on Bonds Payable.... Other Long-Term Liabilities. Common Stock-Parker Company Other Paid-In Capitalin Excess of Par-Parker Company. Retained Earnings Parker Company. Common Stock-Stride Company Other Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Stride Company . Retained Earnings Stride Company Net Sales ..... Cost of Goods Sold . (200,000) (100,000) (200,000) (365,000) (100,000) (40,000) (260,000) (350,000) 200,000 71,400 8,600 ... (640,000) 360,000 Operating Expenses Interest Expense.. Interest Income.. Dividend Income. Dividends Declared. 168,400 (8,200) (27,000) 50,000 30,000 Totals.
On January 1, 2015, Parker Company acquired 90% of the common stock of Stride Company for $351,000.
On this date, Stride had common stock, other paid-in capital in excess of par, and
On January 1, 2015, Stride sold $100,000 par value of 10-year, 8% bonds for $94,000. The bonds pay interest semiannually on January 1 and July 1 of each year. On December 31, 2015, Parker purchased all of Stride’s bonds for $98,200. The bonds are still held on December 31, 2016. Both companies correctly recorded all entries relative to bonds and interest, using straight-line amortization for premium or discount.
The
Prepare the worksheet necessary to produce the consolidated financial statements of Parker and its subsidiary Stride for the year ended December 31, 2016. Round all computations to the nearest dollar.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 7 images









