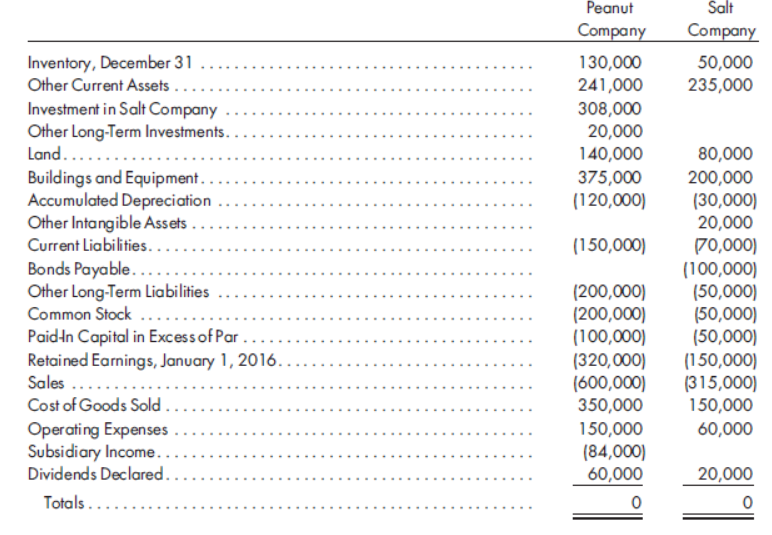
Peanut Salt Company Company Inventory, December 31 .... Other Current Assets ... Investment in Salt Company Other Long-Term Investments.. Land..... 130,000 241,000 50,000 235,000 308,000 20,000 140,000 80,000 Buildings and Equipment. Accumulated Depreciation Other Intangible Assets Current Liabilities.... Bonds Payable..... Other Long-Term Liabilities Common Stock .... Paidin Capital in Excessof Par .. Retained Earnings, January 1, 2016. Sales . Cost of Goods Sold . Operating Expenses Subsidiary Income.. Dividends Declared.. Totals .... 375,000 200,000 (30,000) 20,000 70,000) (100,000) (50,000) (50,000) (50,000) (150,000) (315,000) 150,000 60,000 (120,000) (150,000) (200,000) (200,000) (100,000) (320,000) (600,000) 350,000 150,000 (84,000) 60,000 20,000
On January 1, 2015, Peanut Company acquired 80% of the common stock of Salt Company for $200,000. On this date, Salt had total owners’ equity of $200,000 (including
Any excess of cost over book value is attributable to inventory (worth $12,500 more than cost), to equipment (worth $25,000 more than book value), and to
The following
Complete the worksheet for consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2016. Include the necessary determination and distribution of excess schedule and income distribution schedules.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 7 images







