Part 1: Make a three part process drawing (like a cartoon strip) to demonstrate Mendel's Principle of Segregation. Use two parents with homologous chromosomes marked with alleles “A” and “a”. Circle and label these three action parts of the Principle of Segregation: a) parents are diploid, b) alleles separate to form haploid gametes (indicate when this happens), and c) gametes from each parent combine at random to form diploid offspring Part 2: Use the cross Aa x Aa and a Punnett square to demonstrate Mendel's Principle of Segregation. Circle and label these three action parts of the Principle of Segregation: a) parents are diploid, b) alleles separate to form haploid gametes and c) gametes from each parent combine at random to form diploid offspring. Part 3: Use homologous chromosomes marked with alleles “A” and “a” and a second pair of homologs marked with alleles "B" and "b". to demonstrate Mendel's Principle of Independent Assortment in cells in Meiosis. Indicate what phase this happens in meiosis.
Part 1: Make a three part process drawing (like a cartoon strip) to demonstrate Mendel's Principle of Segregation. Use two parents with homologous chromosomes marked with alleles “A” and “a”. Circle and label these three action parts of the Principle of Segregation: a) parents are diploid, b) alleles separate to form haploid gametes (indicate when this happens), and c) gametes from each parent combine at random to form diploid offspring Part 2: Use the cross Aa x Aa and a Punnett square to demonstrate Mendel's Principle of Segregation. Circle and label these three action parts of the Principle of Segregation: a) parents are diploid, b) alleles separate to form haploid gametes and c) gametes from each parent combine at random to form diploid offspring. Part 3: Use homologous chromosomes marked with alleles “A” and “a” and a second pair of homologs marked with alleles "B" and "b". to demonstrate Mendel's Principle of Independent Assortment in cells in Meiosis. Indicate what phase this happens in meiosis.
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter3: Transmission Of Genes From Generation To Generation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18QP: More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of Independent Assortment Determine the possible...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
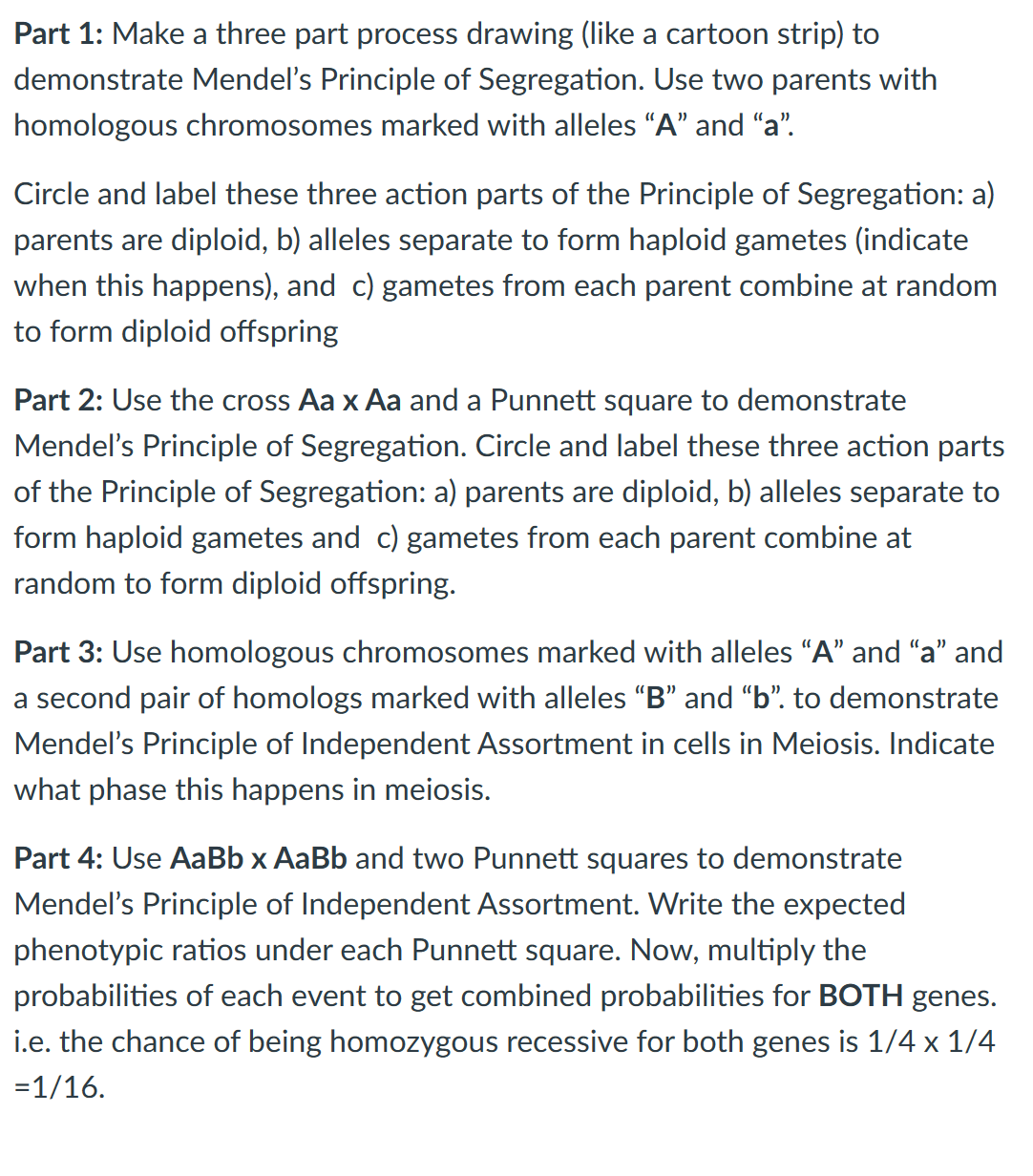
Transcribed Image Text:Part 1: Make a three part process drawing (like a cartoon strip) to
demonstrate Mendel's Principle of Segregation. Use two parents with
homologous chromosomes marked with alleles "A" and "a".
Circle and label these three action parts of the Principle of Segregation: a)
parents are diploid, b) alleles separate to form haploid gametes (indicate
when this happens), and c) gametes from each parent combine at random
to form diploid offspring
Part 2: Use the cross Aa x Aa and a Punnett square to demonstrate
Mendel's Principle of Segregation. Circle and label these three action parts
of the Principle of Segregation: a) parents are diploid, b) alleles separate to
form haploid gametes and c) gametes from each parent combine at
random to form diploid offspring.
Part 3: Use homologous chromosomes marked with alleles "A" and "a" and
a second pair of homologs marked with alleles "B" and "b". to demonstrate
Mendel's Principle of Independent Assortment in cells in Meiosis. Indicate
what phase this happens in meiosis.
Part 4: Use AaBb x AaBb and two Punnett squares to demonstrate
Mendel's Principle of Independent Assortment. Write the expected
phenotypic ratios under each Punnett square. Now, multiply the
probabilities of each event to get combined probabilities for BOTH genes.
i.e. the chance of being homozygous recessive for both genes is 1/4 x 1/4
=1/16.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168116
Author:
Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:
OpenStax College