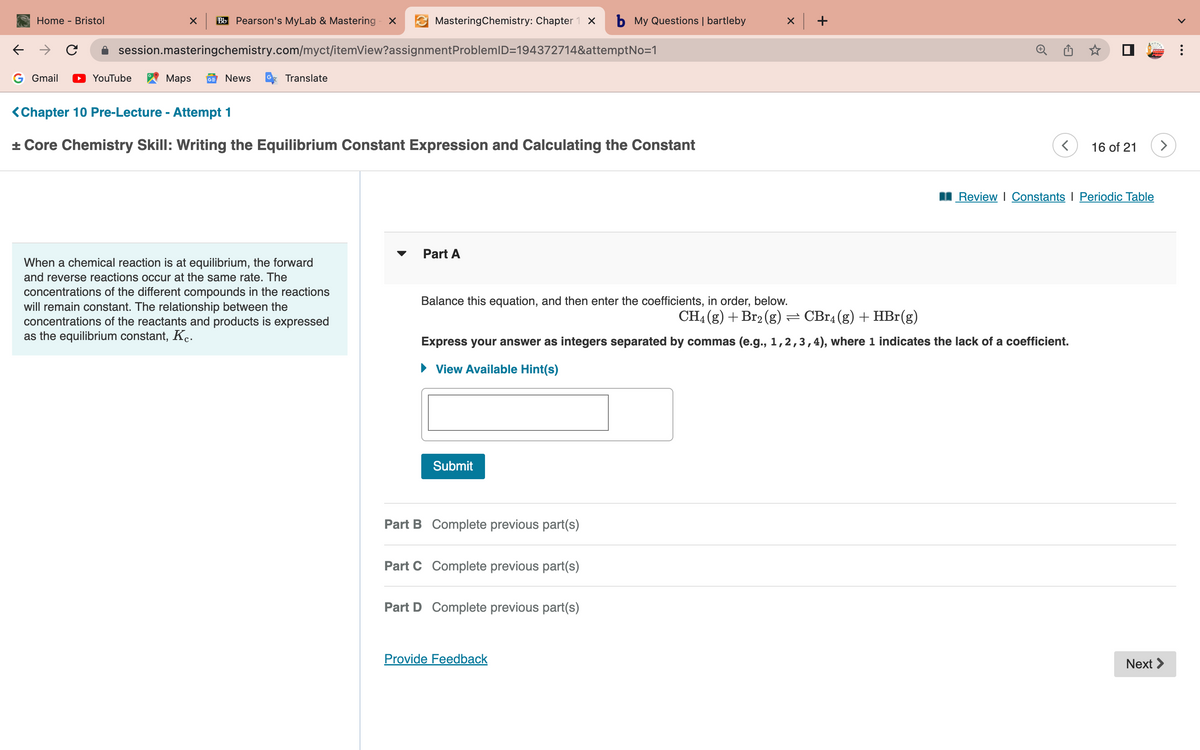
▾ Part A Balance this equation, and then enter the coefficients, in order, below. CH4 (g) + Br₂(g) = CBr4(g) + HBr(g) Express your answer as integers separated by commas (e.g., 1, 2, 3, 4), where 1 indicates the lack of a coefficient. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Submit
▾ Part A Balance this equation, and then enter the coefficients, in order, below. CH4 (g) + Br₂(g) = CBr4(g) + HBr(g) Express your answer as integers separated by commas (e.g., 1, 2, 3, 4), where 1 indicates the lack of a coefficient. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Submit
Chapter7: Statistical Data Treatment And Evaluation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.9QAP
Related questions
Question
PRE) question 16
please answer and show work thank you
Transcribed Image Text:←
Home - Bristol
G Gmail
с
X Bb Pearson's MyLab & Mastering - X
YouTube
session.masteringchemistry.com/myct/itemView?assignment
Maps GE News
Translate
MasteringChemistry: Chapter 1 X b My Questions | bartleby
ProblemID=194372714&attemptNo=1
<Chapter 10 Pre-Lecture - Attempt 1
+ Core Chemistry Skill: Writing the Equilibrium Constant Expression and Calculating the Constant
When a chemical reaction is at equilibrium, the forward
and reverse reactions occur at the same rate. The
concentrations of the different compounds in the reactions
will remain constant. The relationship between the
concentrations of the reactants and products is expressed
as the equilibrium constant, Kc.
▼
Part A
Balance this equation, and then enter the coefficients, in order, below.
Submit
Part B Complete previous part(s)
Part C Complete previous part(s)
X
CH4 (g) + Br₂(g) ⇒ CBr4 (g) + HBr(g)
Express your answer as integers separated by commas (e.g., 1,2,3,4), where 1 indicates the lack of a coefficient.
► View Available Hint(s)
Part D Complete previous part(s)
Provide Feedback
+
<
16 of 21
Review Constants | Periodic Table
>
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
