Part A ReviewI Constants Periodic Table In researching the forces that act on flying birds scientists studied the motion of cockatiels' bodies as they fly in horizontal flight. As the birds beat their wings, their bodies move up and down. (Figure 1) shows the vertical acceleration of a cockatiel's body during one wing beat, consisting of an upstroke followed by a downstroke If the bird's mass is 82 g, what is the maximum net vertical force exerted on the bird? Express your answer with the appropriate units. F-2.95 SubmitPn Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Figure 1 of 1 Part B "y (m/s2) 50 The bird is held in level flight due to the force exerted on it by the air as the bird beats its wings. What is the maximum value of this force due to the air? Note that the bird's weight, the force of gravity acting on it, is calculated using w mg, a result that will be justified in Chapter 5 Express your answer with the appropriate units. 0 I-t (s) 0.02 0.06 0.08 0.10 50 (FairxValue Units Upstroke Downstroke Submit Request Answer
Part A ReviewI Constants Periodic Table In researching the forces that act on flying birds scientists studied the motion of cockatiels' bodies as they fly in horizontal flight. As the birds beat their wings, their bodies move up and down. (Figure 1) shows the vertical acceleration of a cockatiel's body during one wing beat, consisting of an upstroke followed by a downstroke If the bird's mass is 82 g, what is the maximum net vertical force exerted on the bird? Express your answer with the appropriate units. F-2.95 SubmitPn Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Figure 1 of 1 Part B "y (m/s2) 50 The bird is held in level flight due to the force exerted on it by the air as the bird beats its wings. What is the maximum value of this force due to the air? Note that the bird's weight, the force of gravity acting on it, is calculated using w mg, a result that will be justified in Chapter 5 Express your answer with the appropriate units. 0 I-t (s) 0.02 0.06 0.08 0.10 50 (FairxValue Units Upstroke Downstroke Submit Request Answer
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter5: Displacement And Force In Two Dimensions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 72A
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
If the bird's mass is 82 g, what is the maximum net vertical force exerted on the bird?
Can someone help me solve these two questions? I thought it was a direct plug into f=ma.
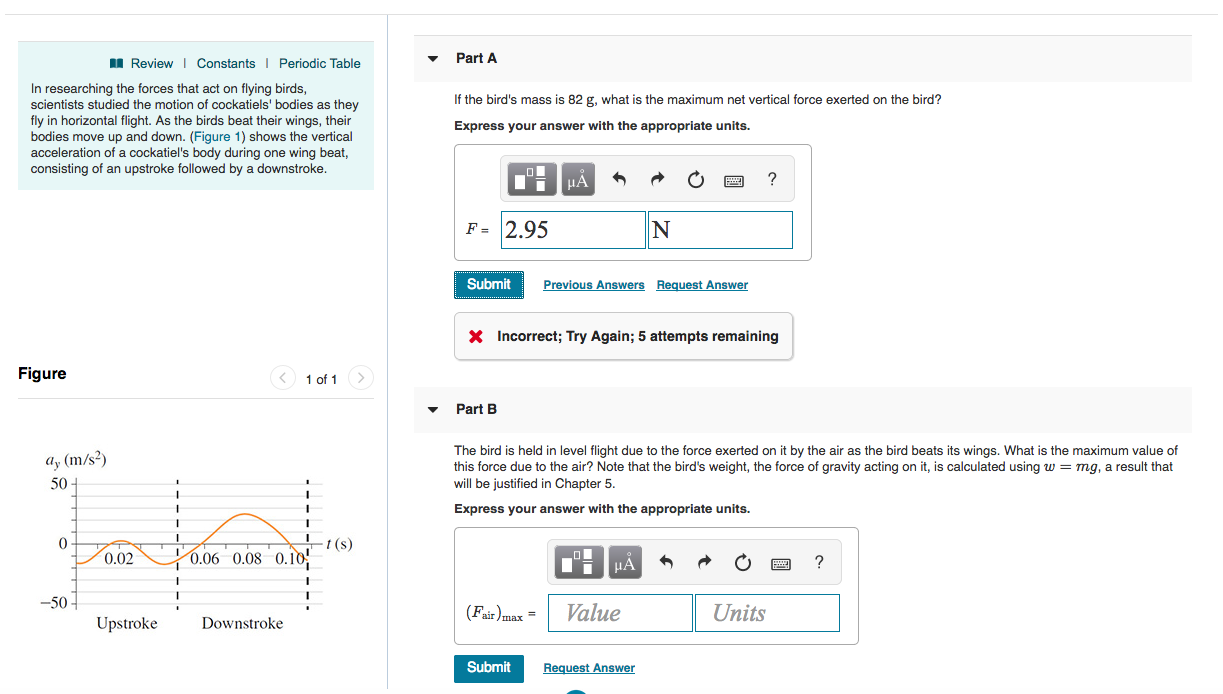
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
ReviewI Constants
Periodic Table
In researching the forces that act on flying birds
scientists studied the motion of cockatiels' bodies as they
fly in horizontal flight. As the birds beat their wings, their
bodies move up and down. (Figure 1) shows the vertical
acceleration of a cockatiel's body during one wing beat,
consisting of an upstroke followed by a downstroke
If the bird's mass is 82 g, what is the maximum net vertical force exerted on the bird?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
F-2.95
SubmitPn
Previous Answers
Request Answer
X
Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
Figure
1 of 1
Part B
"y (m/s2)
50
The bird is held in level flight due to the force exerted on it by the air as the bird beats its wings. What is the maximum value of
this force due to the air? Note that the bird's weight, the force of gravity acting on it, is calculated using w mg, a result that
will be justified in Chapter 5
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
0
I-t (s)
0.02
0.06 0.08 0.10
50
(FairxValue
Units
Upstroke
Downstroke
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:
9781305079137
Author:
James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning