Part A What is the standard Gibbs free energy for this reaction? Assume the commonly used standard reference temperature of 298 K Express your answer as an integer and include the appropriate units. ▸ View Available Hint(s) μA AG-89 kJ Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining ▾ Part B What is the Gibbs free energy for this reaction at 5975 K? Assume that AH and AS do not change with temperature. Express your answer to two decimal places and include the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) D HA ? 1
Part A What is the standard Gibbs free energy for this reaction? Assume the commonly used standard reference temperature of 298 K Express your answer as an integer and include the appropriate units. ▸ View Available Hint(s) μA AG-89 kJ Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining ▾ Part B What is the Gibbs free energy for this reaction at 5975 K? Assume that AH and AS do not change with temperature. Express your answer to two decimal places and include the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) D HA ? 1
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter16: Thermodynamics: Directionality Of Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 83QRT: Another step in the metabolism of glucose, which occurs after the formation of glucose6-phosphate,...
Related questions
Question
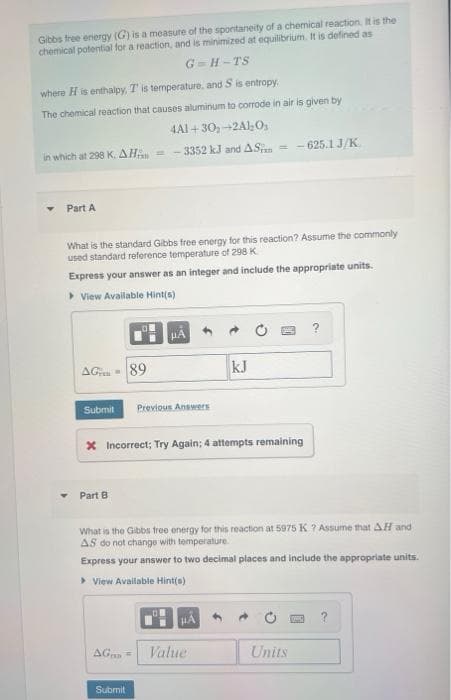
Transcribed Image Text:Gibbs free energy (G) is a measure of the spontaneity of a chemical reaction. It is the
chemical potential for a reaction, and is minimized at equilibrium. It is defined as
G=H-TS
where H is enthalpy, T' is temperature, and S is entropy.
The chemical reaction that causes aluminum to corrode in air is given by
4A1+30₂-2Al₂O₁
in which at 298 K, AH =
-3352 kJ and AS = -625.1J/K
Part A
What is the standard Gibbs free energy for this reaction? Assume the commonly
used standard reference temperature of 298 K
Express your answer as an integer and include the appropriate units.
▸ View Available Hint(s)
μA
AG - 89
kJ
Submit Previous Answers
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Part B
What is the Gibbs free energy for this reaction at 5975 K? Assume that AH and
AS do not change with temperature.
Express your answer to two decimal places and include the appropriate units.
> View Available Hint(s)
?
AG= Value
Units
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning