Part D Find the equation for the block's position ænew(t) in the new coordinate system. Express your answer in terms of L, xinit » w (Greek letter omega), and t. • View Available Hint(s)
Part D Find the equation for the block's position ænew(t) in the new coordinate system. Express your answer in terms of L, xinit » w (Greek letter omega), and t. • View Available Hint(s)
Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
5th Edition
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Chapter7: Hamilton's Principle-lagrangian And Hamiltonian Dynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.21P
Related questions
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:nstants I Perlodic Table
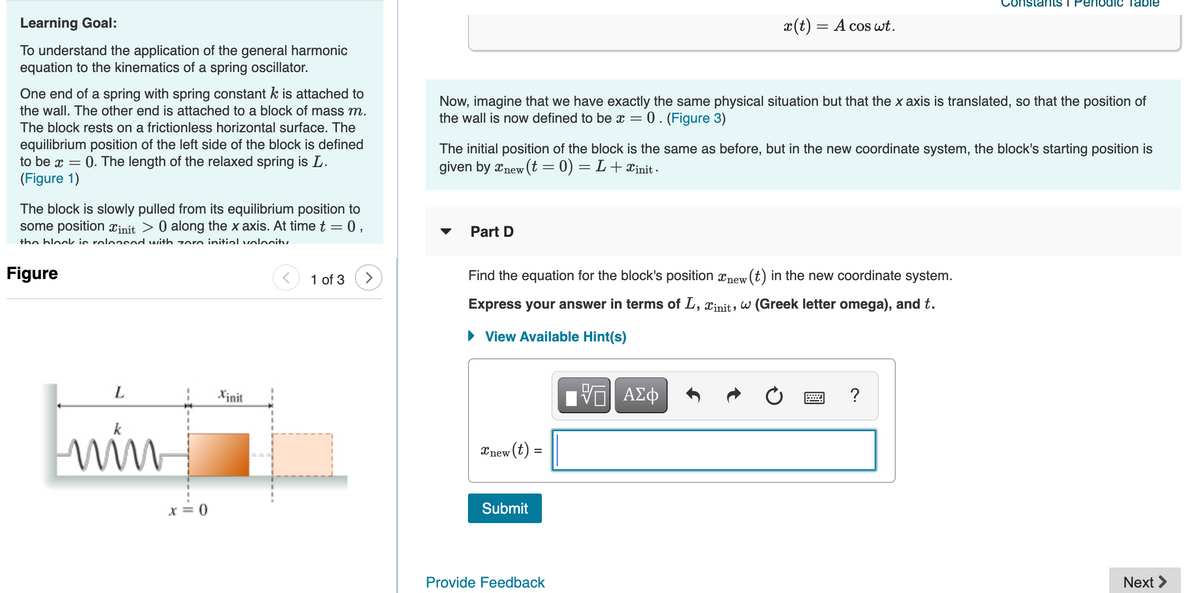
Learning Goal:
x(t) = A cos wt.
To understand the application of the general harmonic
equation to the kinematics of a spring oscillator.
One end of a spring with spring constant k is attached to
Now, imagine that we have exactly the same physical situation but that the x axis is translated, so that the position of
the wall is now defined to be x = 0. (Figure 3)
the wall. The other end is attached to a block of mass m.
The block rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. The
equilibrium position of the left side of the block is defined
to be x =
The initial position of the block is the same as before, but in the new coordinate system, the block's starting position is
0. The length of the relaxed spring is L.
given by xnew (t = 0) = L+xinit -
(Figure 1)
The block is slowly pulled from its equilibrium position to
some position xinit > 0 along the x axis. At time t = 0,
Part D
the block ie releasod with zoro initialvelocitu
Figure
1 of 3
>
Find the equation for the block's position xnew (t) in the new coordinate system.
Express your answer in terms of L, xinit, w (Greek letter omega), and t.
• View Available Hint(s)
L
Xinit
ΑΣφ
?
win
Xnew (t) =
x = 0
Submit
Provide Feedback
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University