Catalysis and Enzymatic Reactions
Catalysis is the kind of chemical reaction in which the rate (speed) of a reaction is enhanced by the catalyst which is not consumed during the process of reaction and afterward it is removed when the catalyst is not used to make up the impurity in the product. The enzymatic reaction is the reaction that is catalyzed via enzymes.
Lock And Key Model
The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity, based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate. This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific substrate can only fit into the particular active site of the enzyme. This is significant in understanding the intermolecular interaction between proteins and plays a vital role in drug interaction.
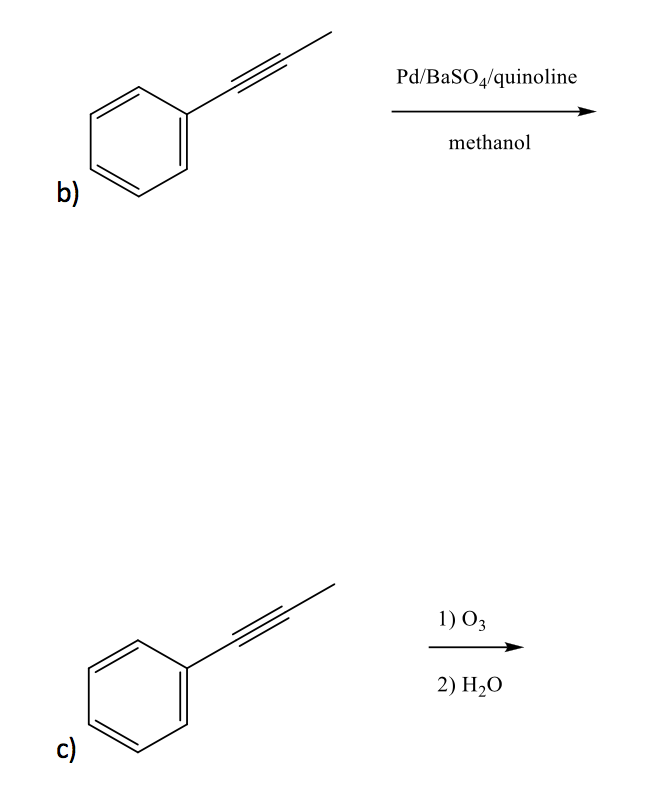
Draw the major product of each reaction below.

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images


