Persons having Raynaud's syndrome are apt to suffer a sudden impairment of blood circulation in fingers and toes. In an experiment to study the extent of this impairment, each subject immersed a forefinger in vater and the resulting heat output (cal/cm/min) vas measured. For m = 9 subjects with the syndrome, the average heat output was x = 0.62, and for n = 9 nonsufferers, the average output was 2.06. Let u and uz denote the true average heat outputs for the sufferers and nonsufferers, respectively. Assume that the two distributions of heat output are normal with a, = 0.1 and c, =n= What is the probability of a type II error vwhen the actual difference between , and uz is u - iz = -1.1? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) Assuming that m = n, what sample sizes are required ensure that 6 = 0.1 when u - uz = -1.1? (Round your answver up to the nearest whole number.)
Persons having Raynaud's syndrome are apt to suffer a sudden impairment of blood circulation in fingers and toes. In an experiment to study the extent of this impairment, each subject immersed a forefinger in vater and the resulting heat output (cal/cm/min) vas measured. For m = 9 subjects with the syndrome, the average heat output was x = 0.62, and for n = 9 nonsufferers, the average output was 2.06. Let u and uz denote the true average heat outputs for the sufferers and nonsufferers, respectively. Assume that the two distributions of heat output are normal with a, = 0.1 and c, =n= What is the probability of a type II error vwhen the actual difference between , and uz is u - iz = -1.1? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) Assuming that m = n, what sample sizes are required ensure that 6 = 0.1 when u - uz = -1.1? (Round your answver up to the nearest whole number.)
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section5.6: Exponential And Logarithmic Equations
Problem 64E
Related questions
Question
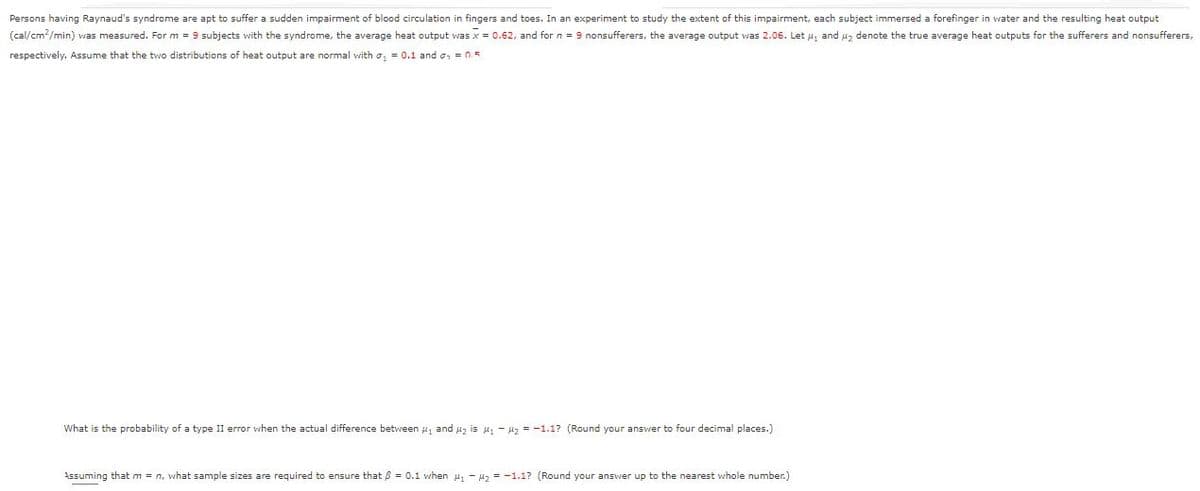
Transcribed Image Text:Persons having Raynaud's syndrome are apt to suffer a sudden impairment of blood circulation in fingers and toes. In an experiment to study the extent of this impairment, each subject immersed a forefinger in water and the resulting heat output
(cal/cm?/min) was measured. For m = 9 subjects with the syndrome, the average heat output was x = 0.62, and for n = 9 nonsufferers, the average output was 2.06. Let u, and u, denote the true average heat outputs for the sufferers and nonsufferers,
respectively. Assume that the two distributions of heat output are normal with o, = 0.1 and o, = 0.5
What is the probability of a type II error vhen the actual difference between u, and uz is u, - uz = -1.1? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
Assuming that m = n, what sample sizes are required to ensure that B = 0.1 when u1 - H2 = -1.1? (Round your answer up to the nearest whole number.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning