An experiment to compare the tension bond strength of polymer latex modified mortar (Portland cement mortar to which polymer latex emulsions have been added during mixing) to that of unmodified mortar resulted in x = 18.13 kgf/cm? for the modified mortar (m = 42) and y = 16.85 kgf/cm? for the unmodified mortar (n = 32). Let u, and u, be the true average tension bond strengths for the modified and unmodified mortars, respectively. Assume that the bond strength distributions are both normal. (a) Assuming that o, = 1.6 and o, = 1.3, test Ho: 4, - u, = 0 versus H: u, - Hz >0 at level 0.01. Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) 2= 3.80 p-value = 0.0001 State the conclusion in the problem context. O Fail to reject Hg. The data suggests that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0. O Fail to reject H. The data does not suggest that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds from 0. O Reject Hg. The data suggests that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0. O Reject Ha. The data does not suggest that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0. (b) Compute the probability of a type II error for the test of part (a) when u, - H, = 1. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) 0.2611 (c) Suppose the investigator decided to use a level 0.05 test and wished = 0.10 when , - H, = 1. If m = 42, what value of n is necessary? (Round your answer up to the nearest whole number.) n= 28
An experiment to compare the tension bond strength of polymer latex modified mortar (Portland cement mortar to which polymer latex emulsions have been added during mixing) to that of unmodified mortar resulted in x = 18.13 kgf/cm? for the modified mortar (m = 42) and y = 16.85 kgf/cm? for the unmodified mortar (n = 32). Let u, and u, be the true average tension bond strengths for the modified and unmodified mortars, respectively. Assume that the bond strength distributions are both normal. (a) Assuming that o, = 1.6 and o, = 1.3, test Ho: 4, - u, = 0 versus H: u, - Hz >0 at level 0.01. Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) 2= 3.80 p-value = 0.0001 State the conclusion in the problem context. O Fail to reject Hg. The data suggests that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0. O Fail to reject H. The data does not suggest that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds from 0. O Reject Hg. The data suggests that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0. O Reject Ha. The data does not suggest that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0. (b) Compute the probability of a type II error for the test of part (a) when u, - H, = 1. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) 0.2611 (c) Suppose the investigator decided to use a level 0.05 test and wished = 0.10 when , - H, = 1. If m = 42, what value of n is necessary? (Round your answer up to the nearest whole number.) n= 28
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter2: Equations And Inequalities
Section2.7: More On Inequalities
Problem 44E
Related questions
Question
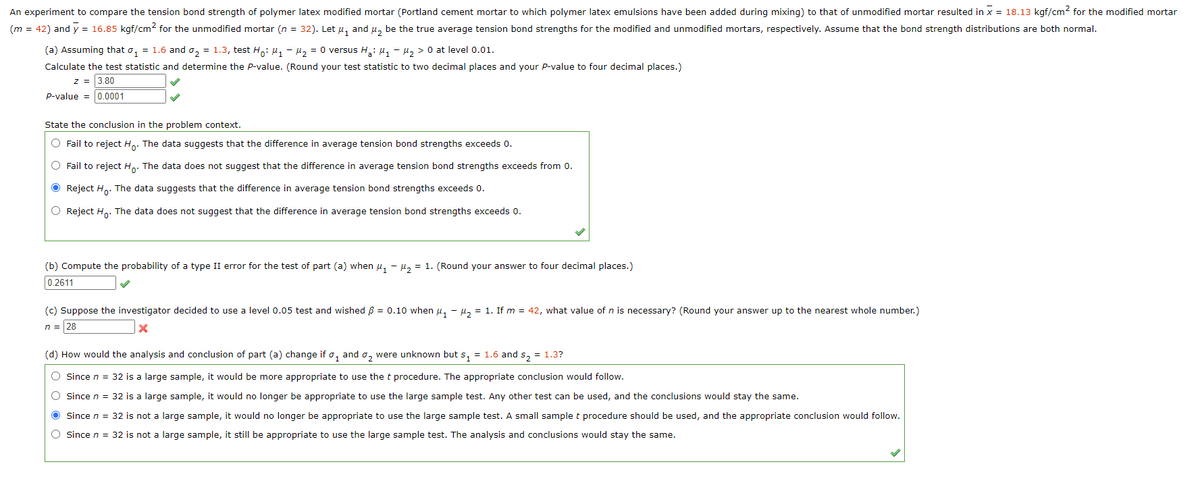
Transcribed Image Text:An experiment to compare the tension bond strength of polymer latex modified mortar (Portland cement mortar to which polymer latex emulsions have been added during mixing) to that of unmodified mortar resulted in x = 18.13 kgf/cm? for the modified mortar
(m = 42) and y = 16.85 kgf/cm2 for the unmodified mortar (n = 32). Let u, and u, be the true average tension bond strengths for the modified and unmodified mortars, respectively. Assume that the bond strength distributions are both normal.
(a) Assuming that o, = 1.6 and o, = 1.3, test Ho: 4, - H, = 0 versus H: u, - µ, > 0 at level 0.01.
Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your p-value to four decimal places.)
z = 3.80
P-value = 0.0001
State the conclusion in the problem context.
O Fail to reject H,. The data suggests that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0.
O Fail to reject Ho: The data does not suggest that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds from 0.
O Reject Ho: The data suggests that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0.
O Reject H,. The data does not suggest that the difference in average tension bond strengths exceeds 0.
(b) Compute the probability of a type II error for the test of part (a) when u, - µ, = 1. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
0.2611
(c) Suppose the investigator decided to use a level 0.05 test and wished B = 0.10 when u, - µ, = 1. If m = 42, what value of n is necessary? (Round your answer up to the nearest whole number.)
n = 28
(d) How would the analysis and conclusion of part (a) change if o, and o, were unknown but s, = 1.6 and s, = 1.3?
O Since n = 32 is a large sample, it would be more appropriate to use the t procedure. The appropriate conclusion would follow.
O Since n = 32 is a large sample, it would no longer be appropriate to use the large sample test. Any other test can be used, and the conclusions would stay the same.
O since n = 32 is not a large sample, it would no longer be appropriate to use the large sample test. A small sample t procedure should be used, and the appropriate conclusion would follow.
O Since n = 32 is not a large sample, it still be appropriate to use the large sample test. The analysis and conclusions would stay the same.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage