oke DR LIV y=Y3 y=Y₂ Y₁=0 = Because of the foamy nature of the fluid, its density is significantly less than the density of water. We'll assume that the density of the foam is p = 430.0 kg/m³. The height of the coke bottle is y2 0.306 meters, and the maximum height reached by the foam is y3 = 1.546 meters. We'll do our analysis using absolute pressure, and so we conclude that at the places where the fluid touches air (y2 and y3) it has the same pressure as the air, namely 101300 Pascals. We will furthermore, treat the bottle as a "tank" so that the fluid velocity at the bottom of the bottle is zero. Finally, we note that the opening of the bottle is circular with a radius of 0.014 meters. Determine all the following: The absolute pressure at the bottom of the coke bottle: P = The velocity of the fluid as it exits the bottle: v₂ = The mass rate of flow (kg/sec) leaving the bottle: m/s kg/sec Pascals
oke DR LIV y=Y3 y=Y₂ Y₁=0 = Because of the foamy nature of the fluid, its density is significantly less than the density of water. We'll assume that the density of the foam is p = 430.0 kg/m³. The height of the coke bottle is y2 0.306 meters, and the maximum height reached by the foam is y3 = 1.546 meters. We'll do our analysis using absolute pressure, and so we conclude that at the places where the fluid touches air (y2 and y3) it has the same pressure as the air, namely 101300 Pascals. We will furthermore, treat the bottle as a "tank" so that the fluid velocity at the bottom of the bottle is zero. Finally, we note that the opening of the bottle is circular with a radius of 0.014 meters. Determine all the following: The absolute pressure at the bottom of the coke bottle: P = The velocity of the fluid as it exits the bottle: v₂ = The mass rate of flow (kg/sec) leaving the bottle: m/s kg/sec Pascals
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
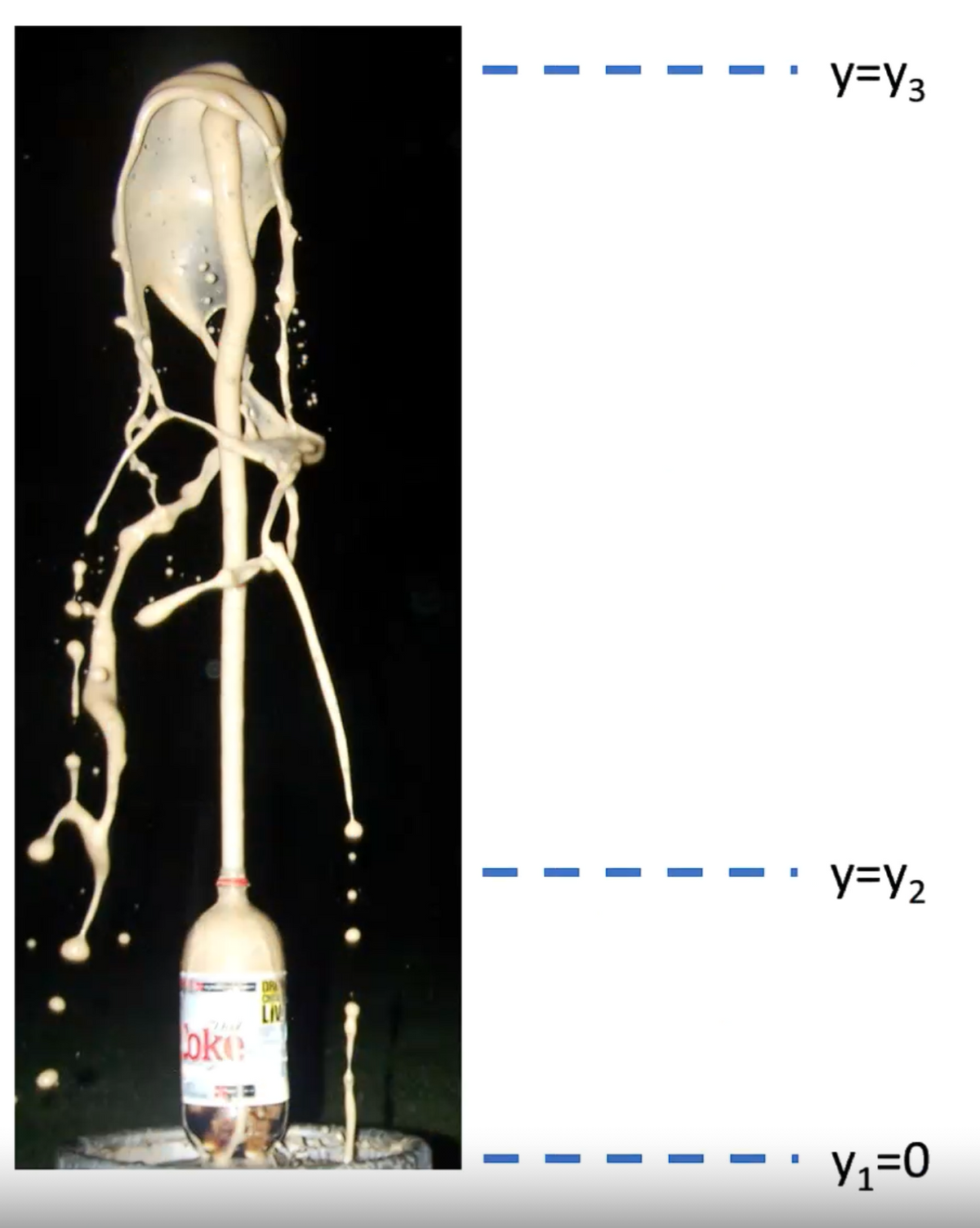
Transcribed Image Text:oke
DR
LIV
y=Y3
y=Y₂
Y₁=0

Transcribed Image Text:=
Because of the foamy nature of the fluid, its density is significantly less than the density of water. We'll assume that the
density of the foam is p = 430.0 kg/m³. The height of the coke bottle is y2 0.306 meters, and the maximum height
reached by the foam is y3 = 1.546 meters. We'll do our analysis using absolute pressure, and so we conclude that at the
places where the fluid touches air (y2 and y3) it has the same pressure as the air, namely 101300 Pascals. We will
furthermore, treat the bottle as a "tank" so that the fluid velocity at the bottom of the bottle is zero. Finally, we note that the
opening of the bottle is circular with a radius of 0.014 meters.
Determine all the following:
The absolute pressure at the bottom of the coke bottle: P =
The velocity of the fluid as it exits the bottle: v₂ =
The mass rate of flow (kg/sec) leaving the bottle:
m/s
kg/sec
Pascals
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The