Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter15: Solutions Of Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 15.130QE: A solution is made by dissolving 15.0 g sodium hydroxide in approximately 450 mL water. The solution...
Related questions
Question
Please help with on the guide questions section below.
Thank you.

Transcribed Image Text:6:18
Drive
Experiment 4 pH and buffers
Materials needed
Red Cabbage
Purified water
5 different glasses/jars
Sprite (40 mL)
dropper/syringe
Baking soda ( 2 teaspoon) NaHCO3
Lemon juice/ calamansi juice/ vinegar (choose one)
Concentrated lye ( liquid sosa) drainage cleaner
Procedure:
1. Boil Red cabbage in 700 mL water. Make sure
to cut the leaves into small pieces to maximize
the amount of indicator in solution. This will
serve as your pH indicator
2. Let the solution cool and transfer 100mL each
to a jar
3. Label the containers with the proper label, A ,
B, C, D. Add 1 teaspoon of baking soda and 20
mL of sprite in the mixture into container B and
C. Stir it well.
4. In container A, add 1 mL dropwise of lemon
juice or any acid. Stir wellI. Observe the
changes in color.
5. In container B, add 1 ml of lemon juice or any
acid. Observe the changes in color. Add
another 1 mL of lemon juice
6. In container D, add 1 mL of concentrated lye.
Stir well. Observe the changes in color.
7. In container C, add 1 mL of concentrated lye.
Stir well. Observe the changes in color
Container
Observations after
1 ml of substance
of lemon juice is
Observations
1 ml of substa
of concentrate
added
is added
A
Color ohangod
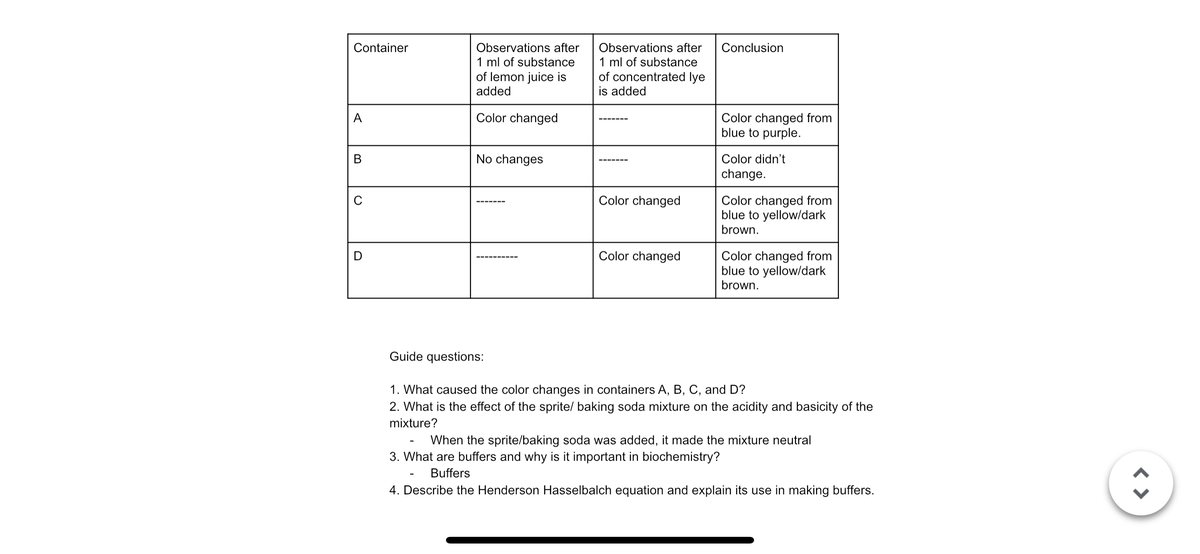
Transcribed Image Text:Container
Observations after
1 ml of substance
of lemon juice is
Observations after
1 ml of substance
of concentrated lye
is added
Conclusion
added
Color changed
Color changed from
blue to purple.
В
No changes
Color didn't
change.
C
Color changed
Color changed from
blue to yellow/dark
brown.
D
Color changed
Color changed from
blue to yellow/dark
brown.
Guide questions:
1. What caused the color changes in containers A, B, C, and D?
2. What is the effect of the sprite/ baking soda mixture on the acidity and basicity of the
mixture?
When the sprite/baking soda was added, it made the mixture neutral
3. What are buffers and why is it important in biochemistry?
Buffers
4. Describe the Henderson Hasselbalch equation and explain its use in making buffers.
< >
A.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning