PO 5Aug-9781118486894-97811193 X O File | C:/Users/HP/Downloads/5Aug-9781118486894-9781119394112-Physics%20by%20David%20Young,%20Shane%20Stadler.pdf 43 of 994 A) Read aloud Draw O Erase ++ Problems 23 41. The displacement vector A has scalar components of A, = 80.0 m and A, = 60.0 m. The displacement vector B has a scalar component of B. = 60.0 m and a magnitude of B = 75.0 m. The displacement vector C has a magnitude of C = 100.0 m and is directed at an angle of 36.9° above the +x axis. Two of these vectors are equal. Determine which two, and support your choice with a calculation. FA 20.0° F 20.0 (a) (Ь) *42. Go Two racing boats set out from the same dock and speed away at the same constant speed of 101 km/h for half an hour (0.500 h), the blue boat headed 25.0° south of west, and the green boat headed 37.0° south of west. During this half hour (a) how much farther west does the blue boat travel, compared to the green boat, and (b) how much farther south does the green boat travel, compared to the blue boat? Express your answers in km. Problem 48 49. Displacement vector A points due east and has a magnitude of 2.00 km. Displacement vector B points due north and has a magnitude of 3.75 km. Displacement vector C points due west and has a magnitude of 2.50 km. Displacement vector D points due south and has a magnitude of 3.00 km. Fir the magnitude and direction (relative to due west) of the *43. ssm mmh The magnitude of the force vector F is 82.3 newtons. The x component of this vector is directed along the +x axis and has a magni- tude of 74.6 newtons. The y component points along the +y axis. (a) Find the direction of F relative to the +x axis. (b) Find the component of F along the +y axis. resultant vector A + B + C + D. 50. Multiple-Concept Example 9 provides background pertinent to this problem. The magnitudes of the four displacement vectors shown in the drawing are A = 16.0 m, B = 11.0 m, C = 12.0 m, and D = 26.0 m. De- **44. The drawing shows a force vector that has a magnitude of 475 new- tons. Find the (a) x, (b) y, and (c) z components of the vector. termine the magnitude and directional angle for the resultant that occurs when these vectors are added together. +y 54.0° 20.0 35.0 +x 50.0* 33.0° Section 1.8 Addition of Vectors by Means of Components 45. ssm Consult Multiple-Concept Example 9 in preparation for this problem. A golfer, putting on a green, requires three strokes to “hole the ball." During the first putt, the ball rolls 5.0 m due east. For the second putt, the ball travels 2.1 m at an angle of 20.0° north of east. The third putt is 0.50 m due north. What displacement (magnitude and direction relative to due east) would have been needed to “hole the ball" on the verv first nutt? 51. mmh On a safari, a team of naturalists sets out toward a research station located 4.8 km away in a direction 42° north of east. After trav- eling in a straight line for 2.4 km, they stop and discover that they have been traveling 22° north of east, because their guide misread his compass. What are (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction (relative to due east) of 17:19 O Type here to search O G 4)) ENG 14-08-2020
PO 5Aug-9781118486894-97811193 X O File | C:/Users/HP/Downloads/5Aug-9781118486894-9781119394112-Physics%20by%20David%20Young,%20Shane%20Stadler.pdf 43 of 994 A) Read aloud Draw O Erase ++ Problems 23 41. The displacement vector A has scalar components of A, = 80.0 m and A, = 60.0 m. The displacement vector B has a scalar component of B. = 60.0 m and a magnitude of B = 75.0 m. The displacement vector C has a magnitude of C = 100.0 m and is directed at an angle of 36.9° above the +x axis. Two of these vectors are equal. Determine which two, and support your choice with a calculation. FA 20.0° F 20.0 (a) (Ь) *42. Go Two racing boats set out from the same dock and speed away at the same constant speed of 101 km/h for half an hour (0.500 h), the blue boat headed 25.0° south of west, and the green boat headed 37.0° south of west. During this half hour (a) how much farther west does the blue boat travel, compared to the green boat, and (b) how much farther south does the green boat travel, compared to the blue boat? Express your answers in km. Problem 48 49. Displacement vector A points due east and has a magnitude of 2.00 km. Displacement vector B points due north and has a magnitude of 3.75 km. Displacement vector C points due west and has a magnitude of 2.50 km. Displacement vector D points due south and has a magnitude of 3.00 km. Fir the magnitude and direction (relative to due west) of the *43. ssm mmh The magnitude of the force vector F is 82.3 newtons. The x component of this vector is directed along the +x axis and has a magni- tude of 74.6 newtons. The y component points along the +y axis. (a) Find the direction of F relative to the +x axis. (b) Find the component of F along the +y axis. resultant vector A + B + C + D. 50. Multiple-Concept Example 9 provides background pertinent to this problem. The magnitudes of the four displacement vectors shown in the drawing are A = 16.0 m, B = 11.0 m, C = 12.0 m, and D = 26.0 m. De- **44. The drawing shows a force vector that has a magnitude of 475 new- tons. Find the (a) x, (b) y, and (c) z components of the vector. termine the magnitude and directional angle for the resultant that occurs when these vectors are added together. +y 54.0° 20.0 35.0 +x 50.0* 33.0° Section 1.8 Addition of Vectors by Means of Components 45. ssm Consult Multiple-Concept Example 9 in preparation for this problem. A golfer, putting on a green, requires three strokes to “hole the ball." During the first putt, the ball rolls 5.0 m due east. For the second putt, the ball travels 2.1 m at an angle of 20.0° north of east. The third putt is 0.50 m due north. What displacement (magnitude and direction relative to due east) would have been needed to “hole the ball" on the verv first nutt? 51. mmh On a safari, a team of naturalists sets out toward a research station located 4.8 km away in a direction 42° north of east. After trav- eling in a straight line for 2.4 km, they stop and discover that they have been traveling 22° north of east, because their guide misread his compass. What are (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction (relative to due east) of 17:19 O Type here to search O G 4)) ENG 14-08-2020
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter3: Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.62AP: After a ball rolls off the edge of a horizontal table at time t = 0, its velocity as a function of...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:PO 5Aug-9781118486894-97811193 X
O File | C:/Users/HP/Downloads/5Aug-9781118486894-9781119394112-Physics%20by%20David%20Young,%20Shane%20Stadler.pdf
43
of 994
A) Read aloud
Draw
O Erase
++
Problems
23
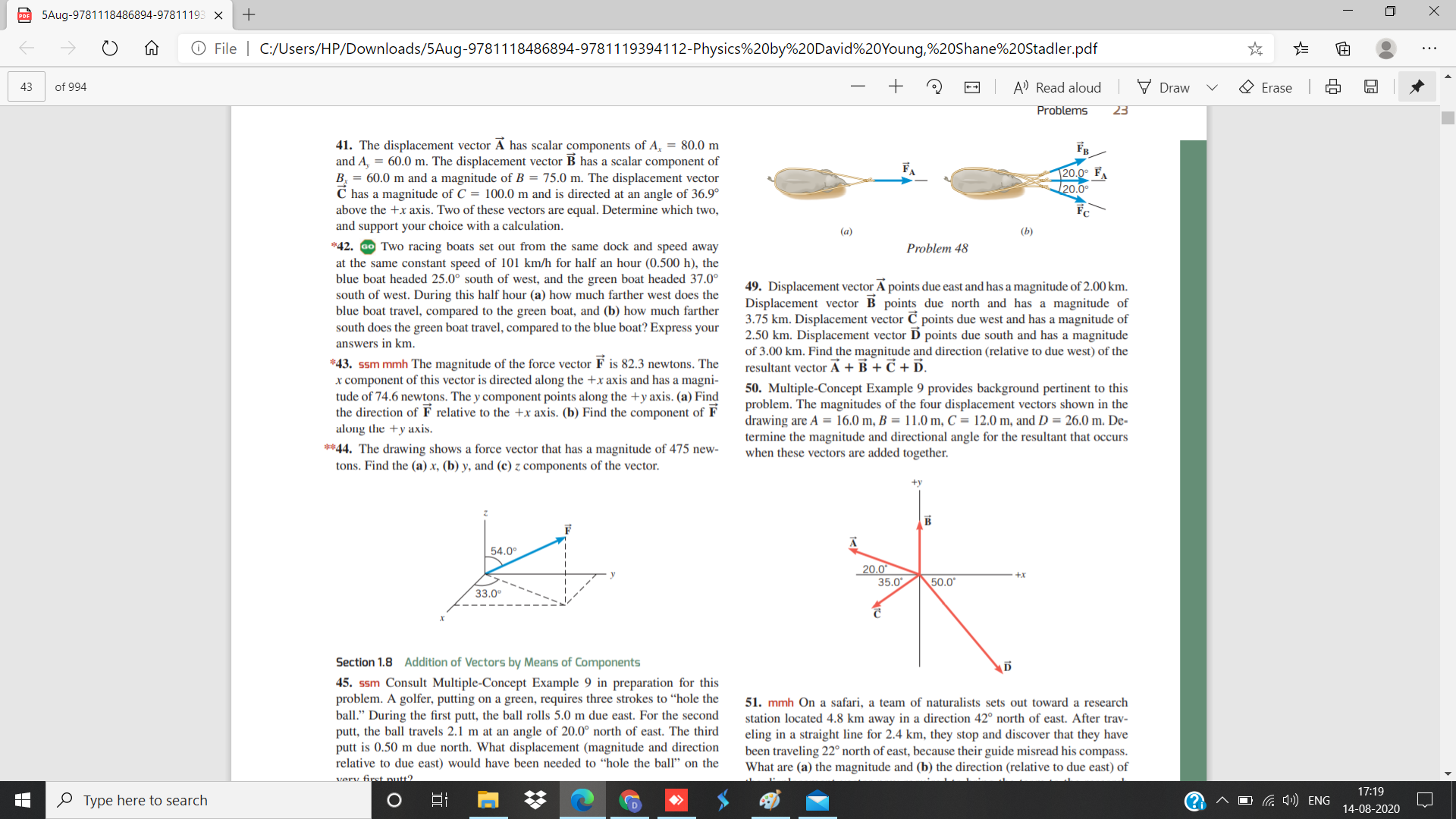
41. The displacement vector A has scalar components of A, = 80.0 m
and A, = 60.0 m. The displacement vector B has a scalar component of
B. = 60.0 m and a magnitude of B = 75.0 m. The displacement vector
C has a magnitude of C = 100.0 m and is directed at an angle of 36.9°
above the +x axis. Two of these vectors are equal. Determine which two,
and support your choice with a calculation.
FA
20.0° F
20.0
(a)
(Ь)
*42. Go Two racing boats set out from the same dock and speed away
at the same constant speed of 101 km/h for half an hour (0.500 h), the
blue boat headed 25.0° south of west, and the green boat headed 37.0°
south of west. During this half hour (a) how much farther west does the
blue boat travel, compared to the green boat, and (b) how much farther
south does the green boat travel, compared to the blue boat? Express your
answers in km.
Problem 48
49. Displacement vector A points due east and has a magnitude of 2.00 km.
Displacement vector B points due north and has a magnitude of
3.75 km. Displacement vector C points due west and has a magnitude of
2.50 km. Displacement vector D points due south and has a magnitude
of 3.00 km. Fir
the magnitude and direction (relative to due west) of the
*43. ssm mmh The magnitude of the force vector F is 82.3 newtons. The
x component of this vector is directed along the +x axis and has a magni-
tude of 74.6 newtons. The y component points along the +y axis. (a) Find
the direction of F relative to the +x axis. (b) Find the component of F
along the +y axis.
resultant vector A + B + C + D.
50. Multiple-Concept Example 9 provides background pertinent to this
problem. The magnitudes of the four displacement vectors shown in the
drawing are A = 16.0 m, B = 11.0 m, C = 12.0 m, and D = 26.0 m. De-
**44. The drawing shows a force vector that has a magnitude of 475 new-
tons. Find the (a) x, (b) y, and (c) z components of the vector.
termine the magnitude and directional angle for the resultant that occurs
when these vectors are added together.
+y
54.0°
20.0
35.0
+x
50.0*
33.0°
Section 1.8 Addition of Vectors by Means of Components
45. ssm Consult Multiple-Concept Example 9 in preparation for this
problem. A golfer, putting on a green, requires three strokes to “hole the
ball." During the first putt, the ball rolls 5.0 m due east. For the second
putt, the ball travels 2.1 m at an angle of 20.0° north of east. The third
putt is 0.50 m due north. What displacement (magnitude and direction
relative to due east) would have been needed to “hole the ball" on the
verv first nutt?
51. mmh On a safari, a team of naturalists sets out toward a research
station located 4.8 km away in a direction 42° north of east. After trav-
eling in a straight line for 2.4 km, they stop and discover that they have
been traveling 22° north of east, because their guide misread his compass.
What are (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction (relative to due east) of
17:19
O Type here to search
O G 4)) ENG
14-08-2020
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University