Practice 1. solve for the Efficiency of the Given Company aple Company Statement of Financial Position as of December 31, 2014 ASSETS LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY Cash P 120,000.00 Accounts Payable P 70,000.00 Marketable Securities P 35,000.00 Short-term notes P 55,000.00 Accounts Receivable P 45,000.00 Current Liabilities P 125,000.00 Inventories P 130,000.00 Long-term debt P 2,700,000.00 Current Assets P 330,000.00 Total Liabilities P 2,825,000.00 Equipment P 2,970,000.00 Common stock P 500,000.00 Buildings P 1,600,000.00 Retained earnings P 1,575,000.00 Fixed Assets P 4,570,000.00 Stockholders' equity P 2,075,000.00 Total Assets P 4,900,000.00 Total liabilities and equity P 4,900,000.00 Sample Company Statement of Financial Performance for the Year Ended December 31, 2014 Sales Revenue P 2,000,000.00 Cost of Sales/Service P (1,300,000.00) Gross Margin P 700,000.00 Operating Expenes P (199,000.00) Operating Profit P 501,000.00 Other Income P 5,000.00 Other Expenses P (2,800.00) Net Income before Tax P 503,200.00 P (150,960.00) Income Tax P 352,240.00 Net Income after Tax
Practice 1. solve for the Efficiency of the Given Company aple Company Statement of Financial Position as of December 31, 2014 ASSETS LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY Cash P 120,000.00 Accounts Payable P 70,000.00 Marketable Securities P 35,000.00 Short-term notes P 55,000.00 Accounts Receivable P 45,000.00 Current Liabilities P 125,000.00 Inventories P 130,000.00 Long-term debt P 2,700,000.00 Current Assets P 330,000.00 Total Liabilities P 2,825,000.00 Equipment P 2,970,000.00 Common stock P 500,000.00 Buildings P 1,600,000.00 Retained earnings P 1,575,000.00 Fixed Assets P 4,570,000.00 Stockholders' equity P 2,075,000.00 Total Assets P 4,900,000.00 Total liabilities and equity P 4,900,000.00 Sample Company Statement of Financial Performance for the Year Ended December 31, 2014 Sales Revenue P 2,000,000.00 Cost of Sales/Service P (1,300,000.00) Gross Margin P 700,000.00 Operating Expenes P (199,000.00) Operating Profit P 501,000.00 Other Income P 5,000.00 Other Expenses P (2,800.00) Net Income before Tax P 503,200.00 P (150,960.00) Income Tax P 352,240.00 Net Income after Tax
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285190907
Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Chapter12: Valuation: Cash-flow Based Approaches
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2EIC
Related questions
Question
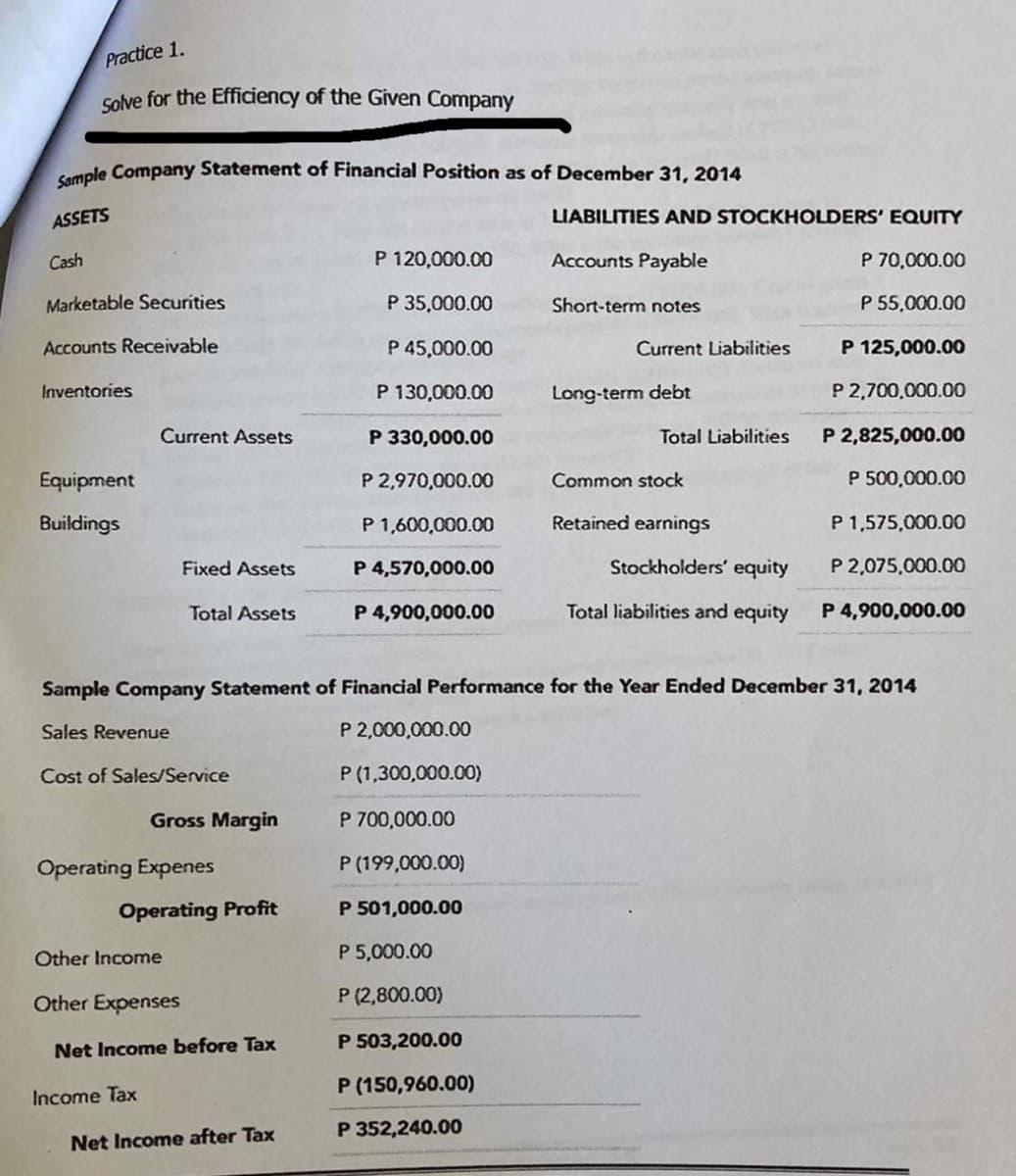
Transcribed Image Text:Practice 1.
Solve for the Efficiency of the Given Company
Cample Company Statement of Financial Position as of December 31, 2014
ASSETS
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
Cash
P 120,000.00
Accounts Payable
P 70,000.00
Marketable Securities
P 35,000.00
Short-term notes
P 55,000.00
Accounts Receivable
P 45,000.00
Current Liabilities
P 125,000.00
Inventories
P 130,000.00
Long-term debt
P 2,700,000.00
Current Assets
P 330,000.00
Total Liabilities
P 2,825,000.00
Equipment
P 2,970,000.00
Common stock
P 500,000.00
Buildings
P 1,600,000.00
Retained earnings
P 1,575,000.00
Fixed Assets
P 4,570,000.00
Stockholders' equity
P 2,075,000.00
Total Assets
P 4,900,000.00
Total liabilities and equity
P 4,900,000.00
Sample Company Statement of Financial Performance for the Year Ended December 31, 2014
Sales Revenue
P 2,000,000.00
Cost of Sales/Service
P (1,300,000.00)
Gross Margin
P 700,000.00
Operating Expenes
P (199,000.00)
Operating Profit
P 501,000.00
Other Income
P 5,000.00
Other Expenses
P (2,800.00)
Net Income before Tax
P 503,200.00
P (150,960.00)
Income Tax
P 352,240.00
Net Income after Tax

Transcribed Image Text:GIVEN FORMULAS:
Sales
Accounts receivable turnover =
Accounts Receivable
365
Average collection period =
Accounts Receivable Turnover
Cost of goods sold
Inventory turnover =
Inventory
365
Average age of inventory =
Inventory Turnover
Purchases
Accounts payable turnover =
Inventory
365
Average payment period =
Accounts Payable Turnover
Operating Cycle = Average Collection Period + Average Age of Inventory
Cash Conversion Cycle = Average collection period + Average age of inventory -Average age of payables
OR
Cash Conversion Cycle = Operating Cycle -Average Age of Payables
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis…
Finance
ISBN:
9781285190907
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis…
Finance
ISBN:
9781285190907
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning