Practice/Exercises: Solve the following problems. 1. Consider the normal distribution of IQs with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 16. What percent of IQs are a. greater than 95? b. less than 120? c. between 90 and 110? 2. A normal distribution of scores has a mean of 120 and a standard deviation of 20. What score separates the top 40% of the scores from the rest?
Practice/Exercises: Solve the following problems. 1. Consider the normal distribution of IQs with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 16. What percent of IQs are a. greater than 95? b. less than 120? c. between 90 and 110? 2. A normal distribution of scores has a mean of 120 and a standard deviation of 20. What score separates the top 40% of the scores from the rest?
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.3: Measures Of Spread
Problem 26PFA
Related questions
Question
Note: Please follow the steps in the given lesson and sketch the normal curve

Transcribed Image Text:Practice/Exercises: Solve the following problems.
1. Consider the normal distribution of IQs with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 16. What percent of
IQs are
a. greater than 95?
b. less than 120?
c.
between 90 and 110?
2. A normal distribution of scores has a mean of 120 and a standard deviation of 20. What score
separates the top 40% of the scores from the rest?
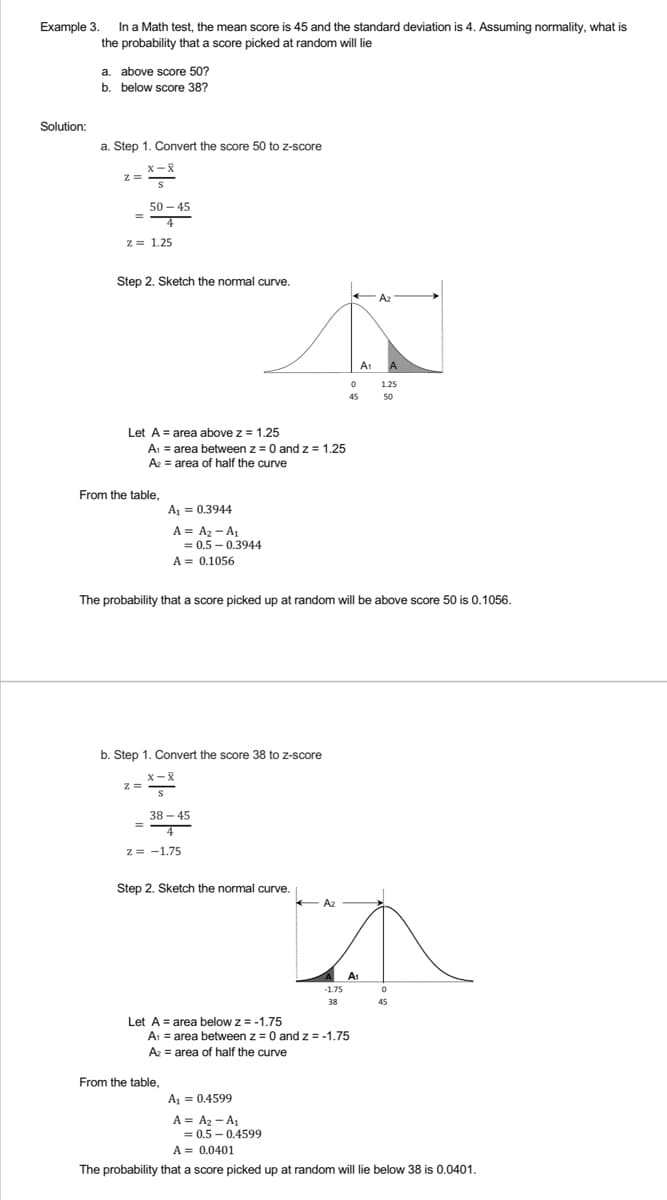
Transcribed Image Text:Example 3.
Solution:
In a Math test, the mean score is 45 and the standard deviation is 4. Assuming normality, what is
the probability that a score picked at random will lie
a. above score 50?
b. below score 38?
a. Step 1. Convert the score 50 to z-score
X-X
Z =
=
50-45
4
z = 1.25
Step 2. Sketch the normal curve.
0
45
Let A area above z = 1.25
A₁ = area between z = 0 and z = 1.25
A₂ = area of half the curve
From the table,
A₁ = 0.3944
A = A₂-A₁
= 0.5-0.3944
A = 0.1056
The probability that a score picked up at random will be above score 50 is 0.1056.
b. Step 1. Convert the score 38 to z-score
Z=
X-X
S
38-45
=
2= -1.75
Step 2. Sketch the normal curve.
-1.75
38
Let A = area below z = -1.75
A₁ = area between z = 0 and z = -1.75
A₂ = area of half the curve
From the table,
A₁ = 0.4599
A = A₂-A₁
= 0.5-0.4599
A = 0.0401
The probability that a score picked up at random will lie below 38 is 0.0401.
← A₂
A1
A1
A2
A
1.25
50
0
45
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill