Price Level OOOO Aggregate Demand price level; GDP; decreases price level; consumption; decreases price level; investment; decreases price level; GDP; increases GDP
Price Level OOOO Aggregate Demand price level; GDP; decreases price level; consumption; decreases price level; investment; decreases price level; GDP; increases GDP
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
33. Refer to Figure 4. As the_____decreases, the amount of ____demanded by all sectors of the economy_____
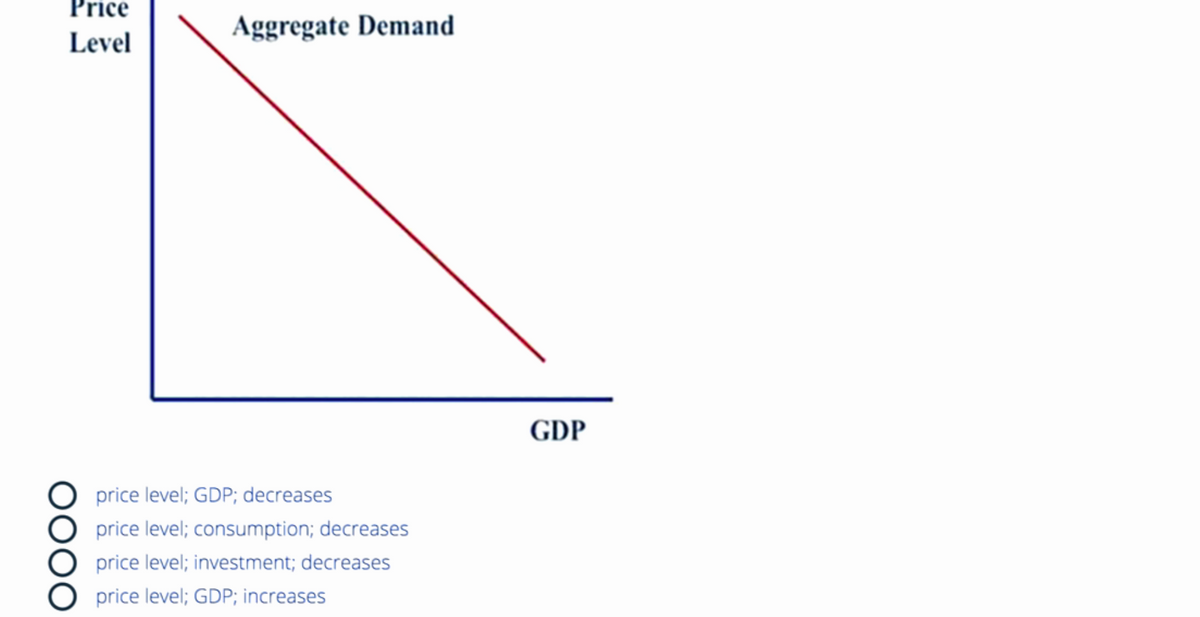
Transcribed Image Text:Price
Level
OOOO
Aggregate Demand
price level; GDP; decreases
price level; consumption; decreases
price level; investment; decreases
price level; GDP; increases
GDP
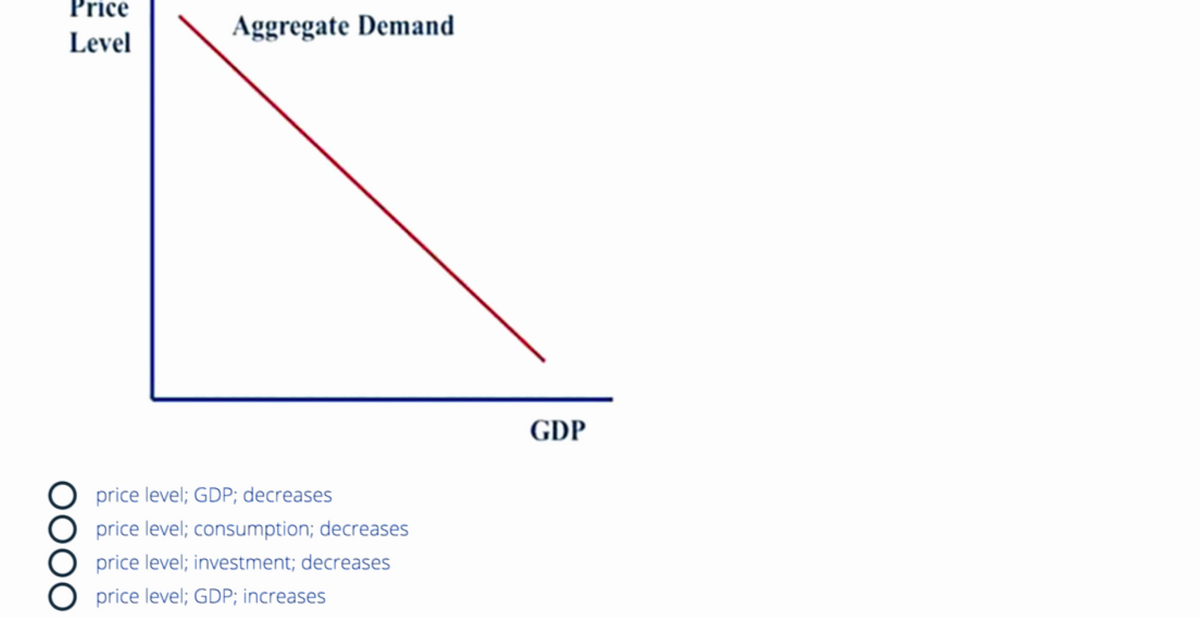
Transcribed Image Text:Price
Level
OOOO
Aggregate Demand
price level; GDP; decreases
price level; consumption; decreases
price level; investment; decreases
price level; GDP; increases
GDP
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education