Problem 1 1200 K Consider a heat engine in contact with a hot and cold reservoir, as shown. If 1000 joules of energy are input from the hot reservoir: 1000 J (a) What is the maximum amount of work that can be done? Explain. (b) How much energy in the form of heat is exhausted to the cold reservoir? Explain. (c) Assume the heat engine and the two reservoirs are isolated from the rest of the universe. Calculate the change in entropy of this isolated system during one cycle of operation. Explain. 400 K
Problem 1 1200 K Consider a heat engine in contact with a hot and cold reservoir, as shown. If 1000 joules of energy are input from the hot reservoir: 1000 J (a) What is the maximum amount of work that can be done? Explain. (b) How much energy in the form of heat is exhausted to the cold reservoir? Explain. (c) Assume the heat engine and the two reservoirs are isolated from the rest of the universe. Calculate the change in entropy of this isolated system during one cycle of operation. Explain. 400 K
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
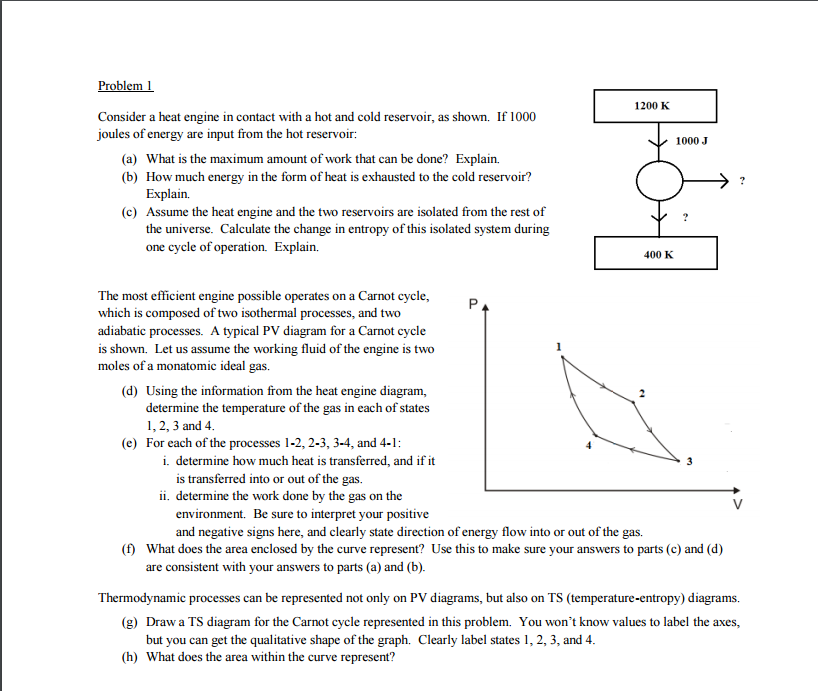
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1
1200 K
Consider a heat engine in contact with a hot and cold reservoir, as shown. If 1000
joules of energy are input from the hot reservoir:
1000 J
(a) What is the maximum amount of work that can be done? Explain.
(b) How much energy in the form of heat is exhausted to the cold reservoir?
Explain,
(c) Assume the heat engine and the two reservoirs are isolated from the rest of
the universe. Calculate the change in entropy of this isolated system during
one cycle of operation. Explain.
400 K
The most efficient engine possible operates on a Carnot cycle,
which is composed of two isothermal processes, and two
adiabatic processes. A typical PV diagram for a Carnot cycle
is shown. Let us assume the working fluid of the engine is two
moles of a monatomic ideal gas.
(d) Using the information from the heat engine diagram,
determine the temperature of the gas in each of states
1, 2, 3 and 4.
(e) For each of the processes 1-2, 2-3, 3-4, and 4-1:
i. determine how much heat is transferred, and if it
is transferred into or out of the gas.
3
ii. determine the work done by the gas on the
environment. Be sure to interpret your positive
and negative signs here, and clearly state direction of energy flow into or out of the gas.
(f) What does the area enclosed by the curve represent? Use this to make sure your answers to parts (c) and (d)
are consistent with your answers to parts (a) and (b).
Thermodynamic processes can be represented not only on PV diagrams, but also on TS (temperature-entropy) diagrams.
(g) Draw a TS diagram for the Carnot cycle represented in this problem. You won't know values to label the axes,
but you can get the qualitative shape of the graph. Clearly label states 1, 2, 3, and 4.
(h) What does the area within the curve represent?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY