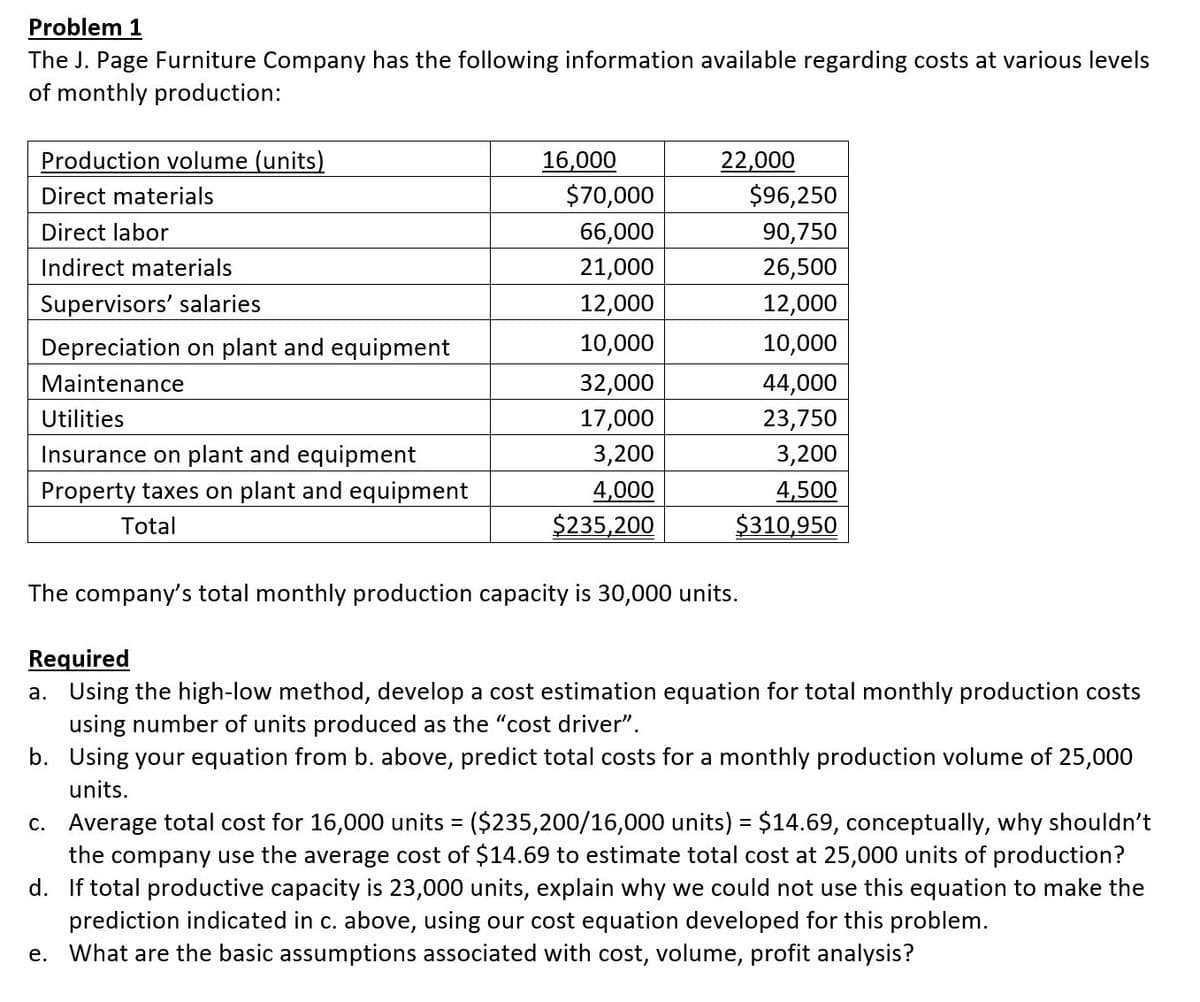
Problem 1 The J. Page Furniture Company has the following information available regarding costs at various levels of monthly production: Production volume (units) 16,000 22,000 $70,000 66,000 21,000 12,000 $96,250 90,750 26,500 12,000 Direct materials Direct labor Indirect materials Supervisors' salaries Depreciation on plant and equipment 10,000 10,000 44,000 23,750 3,200 Maintenance 32,000 17,000 3,200 Utilities Insurance on plant and equipment Property taxes on plant and equipment 4,000 4,500 Total $235,200 $310,950 The company's total monthly production capacity is 30,000 units. Required a. Using the high-low method, develop a cost estimation equation for total monthly production costs using number of units produced as the "cost driver". b. Using your equation from b. above, predict total costs for a monthly production volume of 25,000 units. c. Average total cost for 16,000 units = ($235,200/16,000 units) = $14.69, conceptually, why shouldn't the company use the average cost of $14.69 to estimate total cost at 25,000 units of production? d. If total productive capacity is 23,000 units, explain why we could not use this equation to make the %3D prediction indicated in c. above, using our cost equation developed for this problem. e. What are the basic assumptions associated with cost, volume, profit analysis?
The Effect Of Prepaid Taxes On Assets And Liabilities
Many businesses estimate tax liability and make payments throughout the year (often quarterly). When a company overestimates its tax liability, this results in the business paying a prepaid tax. Prepaid taxes will be reversed within one year but can result in prepaid assets and liabilities.
Final Accounts
Financial accounting is one of the branches of accounting in which the transactions arising in the business over a particular period are recorded.
Ledger Posting
A ledger is an account that provides information on all the transactions that have taken place during a particular period. It is also known as General Ledger. For example, your bank account statement is a general ledger that gives information about the amount paid/debited or received/ credited from your bank account over some time.
Trial Balance and Final Accounts
In accounting we start with recording transaction with journal entries then we make separate ledger account for each type of transaction. It is very necessary to check and verify that the transaction transferred to ledgers from the journal are accurately recorded or not. Trial balance helps in this. Trial balance helps to check the accuracy of posting the ledger accounts. It helps the accountant to assist in preparing final accounts. It also helps the accountant to check whether all the debits and credits of items are recorded and posted accurately. Like in a balance sheet debit and credit side should be equal, similarly in trial balance debit balance and credit balance should tally.
Adjustment Entries
At the end of every accounting period Adjustment Entries are made in order to adjust the accounts precisely replicate the expenses and revenue of the current period. It is also known as end of period adjustment. It can also be referred as financial reporting that corrects the errors made previously in the accounting period. The basic characteristics of every adjustment entry is that it affects at least one real account and one nominal account.
please answer last 3 questions
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps









