Problem 2 ots 1-D Heat Transfer with Convection. The solid material is subjected to a temperature differential that can be described using the mixed boundary conditions. Use four identical elements to determine the steady-state temperature distribution through the solid. Both ends of the surface are subjected to heat loss by convection (Nodes 1 and 5). Assume the cross-sectional area is the same for all elements, A=0.01 m?. Insulated, 1-d heat transfer in x-dir Gas 1: h1=2000 W/(m²K) Gas 2: hs=5000w/(m²K) T1°=110°C=383.15 K Solid surface: T5°=81°C=354.15 K +x k=150 W/(m K) 0.1 m
Problem 2 ots 1-D Heat Transfer with Convection. The solid material is subjected to a temperature differential that can be described using the mixed boundary conditions. Use four identical elements to determine the steady-state temperature distribution through the solid. Both ends of the surface are subjected to heat loss by convection (Nodes 1 and 5). Assume the cross-sectional area is the same for all elements, A=0.01 m?. Insulated, 1-d heat transfer in x-dir Gas 1: h1=2000 W/(m²K) Gas 2: hs=5000w/(m²K) T1°=110°C=383.15 K Solid surface: T5°=81°C=354.15 K +x k=150 W/(m K) 0.1 m
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter2: Steady Heat Conduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.43P: 2.43 A turbine blade 6.3 cm long, with cross-sectional area and perimeter , is made of stainless...
Related questions
Question
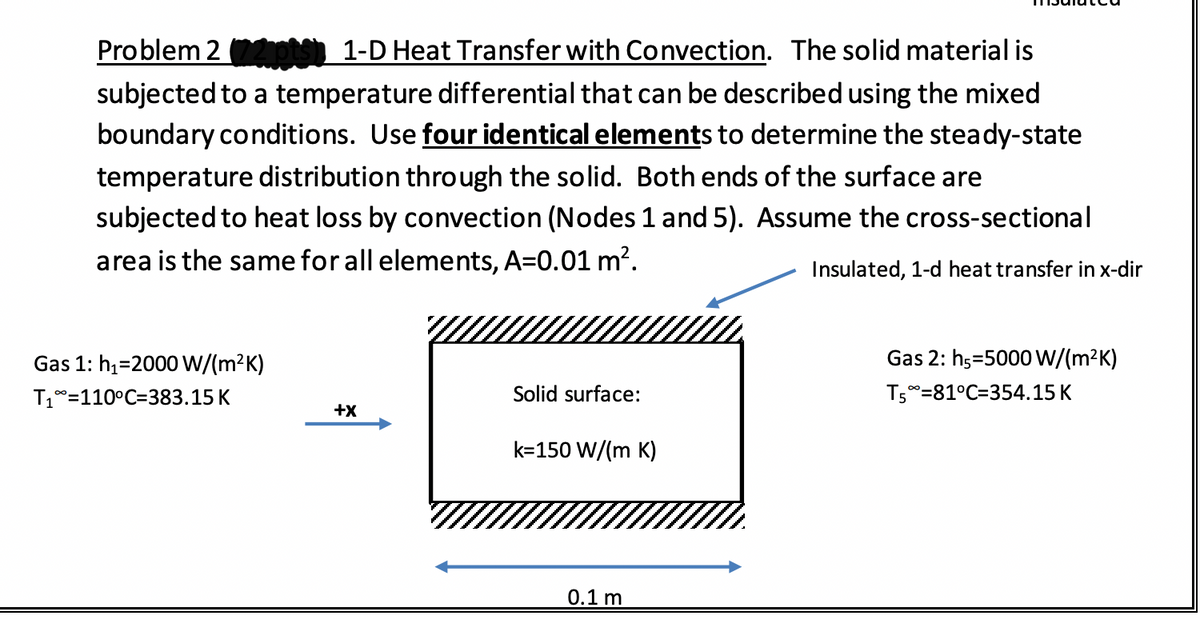
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2 pts 1-D Heat Transfer with Convection. The solid material is
subjected to a temperature differential that can be described using the mixed
boundary conditions. Use four identical elements to determine the steady-state
temperature distribution through the solid. Both ends of the surface are
subjected to heat loss by convection (Nodes 1 and 5). Assume the cross-sectional
area is the same for all elements, A=0.01 m?.
Insulated, 1-d heat transfer in x-dir
Gas 1: h1=2000 W/(m?K)
Gas 2: h5=5000 W/(m²K)
T1°=110°C=383.15 K
Solid surface:
T50=81°C=354.15 K
+x
k=150 W/(m K)
0.1 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning