Problem 2: The ball is kicked from point A with the initial velocity va = 10m/s at 35° from the horizontal. Determine the height h it reaches and the range the ball covers.
Problem 2: The ball is kicked from point A with the initial velocity va = 10m/s at 35° from the horizontal. Determine the height h it reaches and the range the ball covers.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter4: Motion In Two Dimensions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 49CP: A skier leaves the ramp of a ski jump with a velocity of v = 10.0 m/s at = 15.0 above the...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Answer the following questions. The choices are given below.

Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2: The ball is kicked from point A with the initial velocity vą = 10m/s at 35° from
the horizontal. Determine the height h it reaches and the range the ball covers.
Problem 3: An adventurous archaeologist crosses between two rock cliffs by slowly going
hand over hand along a rope stretched between the cliffs. He stops to rest at the middle of the
rope (as shown in the figure below). The rope will break if the tension in it exceeds
2.50 x 10*N, and our hero's mass is 90.0 kg. (problem 3a) If the angle u is 10.0°, what is the
tension in the rope? (problem 3b) What is the smallest value 0 can have if the rope is not to
break?
にこ
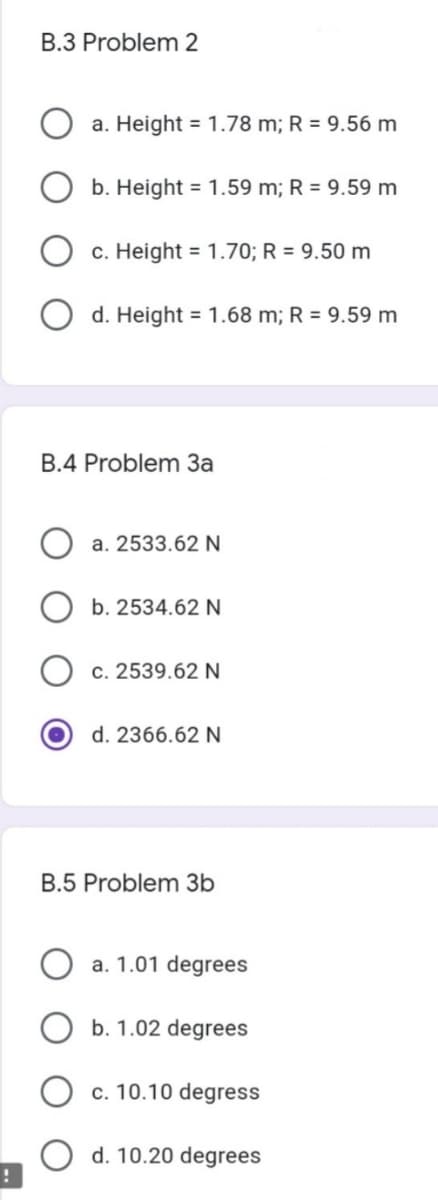
Transcribed Image Text:B.3 Problem 2
a. Height = 1.78 m; R = 9.56 m
b. Height = 1.59 m; R = 9.59 m
c. Height = 1.70; R = 9.50 m
d. Height = 1.68 m; R = 9.59 m
B.4 Problem 3a
a. 2533.62 N
b. 2534.62 N
c. 2539.62 N
d. 2366.62 N
B.5 Problem 3b
a. 1.01 degrees
b. 1.02 degrees
c. 10.10 degress
d. 10.20 degrees
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University