*Problem 3.17 The 2 x 2 matrix representing a rotation of the xy-plane is cos 0 - sin 0 cos e T = sin 0 Show that (except for certain special angles-what are they?) this matrix has no real eigenvalues. (This reflects the geometrical fact that no vector in the plane is carried into itself under such a rotation; contrast rotations in three dimensions.) This matrix does, however, have complex eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Find them. Construct a matrix S which diagonalizes T. Perform the similarity transformation (STS-) explicitly, and show that it reduces T to diagonal form.
*Problem 3.17 The 2 x 2 matrix representing a rotation of the xy-plane is cos 0 - sin 0 cos e T = sin 0 Show that (except for certain special angles-what are they?) this matrix has no real eigenvalues. (This reflects the geometrical fact that no vector in the plane is carried into itself under such a rotation; contrast rotations in three dimensions.) This matrix does, however, have complex eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Find them. Construct a matrix S which diagonalizes T. Perform the similarity transformation (STS-) explicitly, and show that it reduces T to diagonal form.
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter2: Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 59P: At one point in space, the direction of the electric field vector Is given In the Cartesian system...
Related questions
Question
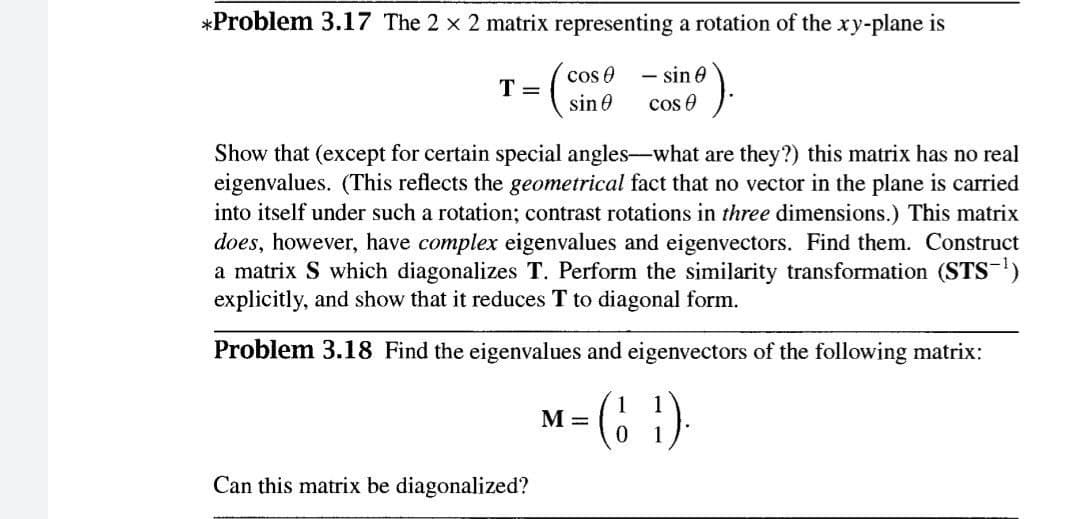
Transcribed Image Text:*Problem 3.17 The 2 x 2 matrix representing a rotation of the xy-plane is
- sin 0
cos e
cos e
T =
sin 0
Show that (except for certain special angles-what are they?) this matrix has no real
eigenvalues. (This reflects the geometrical fact that no vector in the plane is carried
into itself under such a rotation; contrast rotations in three dimensions.) This matrix
does, however, have complex eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Find them. Construct
a matrix S which diagonalizes T. Perform the similarity transformation (STS-)
explicitly, and show that it reduces T to diagonal form.
Problem 3.18 Find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the following matrix:
M =
Can this matrix be diagonalized?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning