Problem 4 In the circuit to the right, & = 1.2kV, C = 6.5 µF, and R₁ = R₂ = R3 = R = 0.73 MN. With C completely uncharged, switch S is sud- denly closed at t = 0. Remember to draw equivalent circuits to help with the analysis! 2 R₁₂ - fε S Ro www R₂ (a) At t = 0, what is the voltage across the capacitor? How are the voltages across R3 and R₂ related? (b) At t= 0, what are the currents in each resistor? (c) For t→∞o, what are the currents in each resistor? (d) For t→ ∞o, what are the voltages across each resistor? (e) For t → ∞, what is the voltage across the capacitor? (f) Once the circuit has nearly reached equilibrium, the switch is reopened. What is the current in each resistor right after the switch is reopened? The equivalent circuit will be super useful here; note that when we change the circuit by opening the switch, the capacitor is no longer in steady state - do not assume its current is zero! (g) How long after the switch is reopened does it take for the current in Re to drop to half of the
Problem 4 In the circuit to the right, & = 1.2kV, C = 6.5 µF, and R₁ = R₂ = R3 = R = 0.73 MN. With C completely uncharged, switch S is sud- denly closed at t = 0. Remember to draw equivalent circuits to help with the analysis! 2 R₁₂ - fε S Ro www R₂ (a) At t = 0, what is the voltage across the capacitor? How are the voltages across R3 and R₂ related? (b) At t= 0, what are the currents in each resistor? (c) For t→∞o, what are the currents in each resistor? (d) For t→ ∞o, what are the voltages across each resistor? (e) For t → ∞, what is the voltage across the capacitor? (f) Once the circuit has nearly reached equilibrium, the switch is reopened. What is the current in each resistor right after the switch is reopened? The equivalent circuit will be super useful here; note that when we change the circuit by opening the switch, the capacitor is no longer in steady state - do not assume its current is zero! (g) How long after the switch is reopened does it take for the current in Re to drop to half of the
Chapter9: Current And Resistance
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 84CP: In this chapter, most examples and problems involved direct current (DC). DC circuits have the...
Related questions
Question
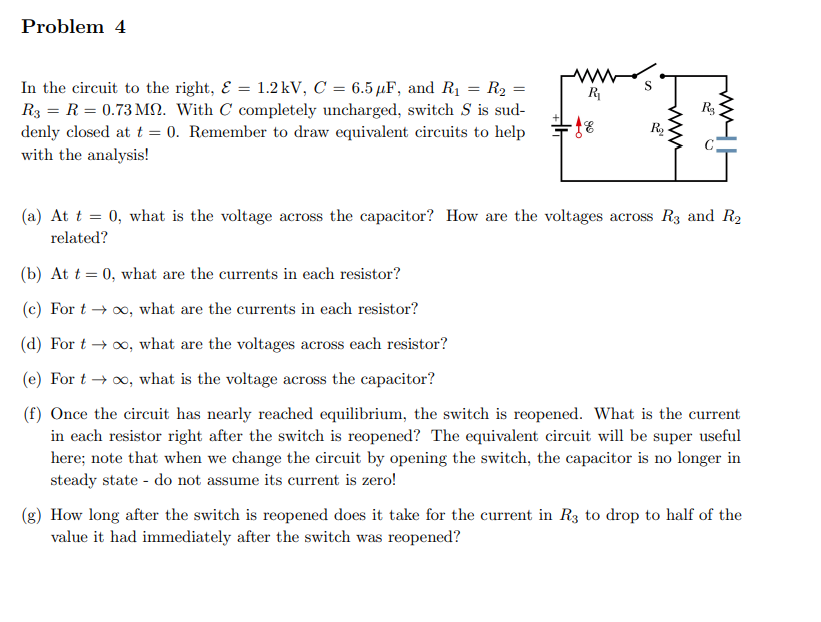
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 4
In the circuit to the right, & = 1.2kV, C = 6.5 µF, and R₁ = R₂
R3 = R = 0.73 M. With C completely uncharged, switch S is sud-
denly closed at t = 0. Remember to draw equivalent circuits to help
with the analysis!
R₁
S
R₂₂
R₂
(a) At t = 0, what is the voltage across the capacitor? How are the voltages across R3 and R₂
related?
(b) At t = 0, what are the currents in each resistor?
(c) For t→∞o, what are the currents in each resistor?
(d) For t→ ∞o, what are the voltages across each resistor?
(e) For t → ∞, what is the voltage across the capacitor?
(f) Once the circuit has nearly reached equilibrium, the switch is reopened. What is the current
in each resistor right after the switch is reopened? The equivalent circuit will be super useful
here; note that when we change the circuit by opening the switch, the capacitor is no longer in
steady state - do not assume its current is zero!
(g) How long after the switch is reopened does it take for the current in R3 to drop to half of the
value it had immediately after the switch was reopened?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

