Problem #4
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
100%
Problem #4
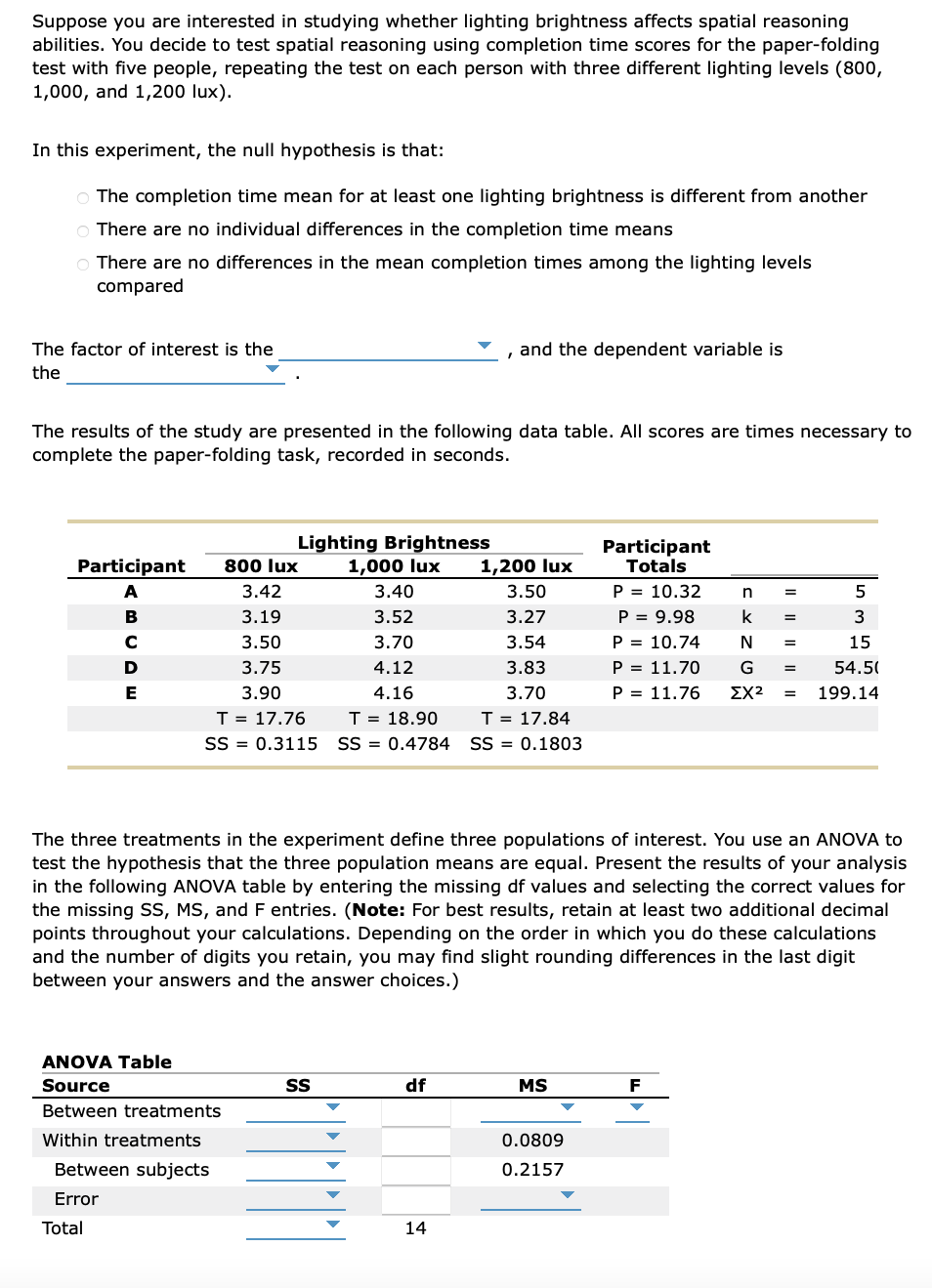
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose you are interested in studying whether lighting brightness affects spatial reasoning
abilities. You decide to test spatial reasoning using completion time scores for the paper-folding
test with five people, repeating the test on each person with three different lighting levels (800,
1,000, and 1,200 lux).
In this experiment, the null hypothesis is that:
O The completion time mean for at least one lighting brightness is different from another
o There are no individual differences in the completion time means
o There are no differences in the mean completion times among the lighting levels
compared
The factor of interest is the
the
The results of the study are presented in the following data table. All scores are times necessary to
complete the paper-folding task, recorded in seconds.
Participant 800 lux
A
B
с
D
E
Lighting Brightness
1,000 lux
3.42
3.19
3.50
3.75
3.90
T = 17.76
SS=0.3115
ANOVA Table
Source
Between treatments
Within treatments
Between subjects
Error
Total
SS
3.40
3.52
3.70
4.12
4.16
▼
I
and the dependent variable is
T = 18.90
T = 17.84
SS = 0.4784 SS = 0.1803
df
14
1,200 lux
3.50
3.27
3.54
3.83
3.70
The three treatments in the experiment define three populations of interest. You use an ANOVA to
test the hypothesis that the three population means are equal. Present the results of your analysis
in the following ANOVA table by entering the missing df values and selecting the correct values for
the missing SS, MS, and F entries. (Note: For best results, retain at least two additional decimal
points throughout your calculations. Depending on the order in which you do these calculations
and the number of digits you retain, you may find slight rounding differences in the last digit
between your answers and the answer choices.)
MS
Participant
Totals
0.0809
0.2157
P = 10.32
P = 9.98
P = 10.74
P = 11.70
P = 11.76
n =
k =
N
G
ΣΧ2 =
F
=
=
5
3
15
54.5(
199.14
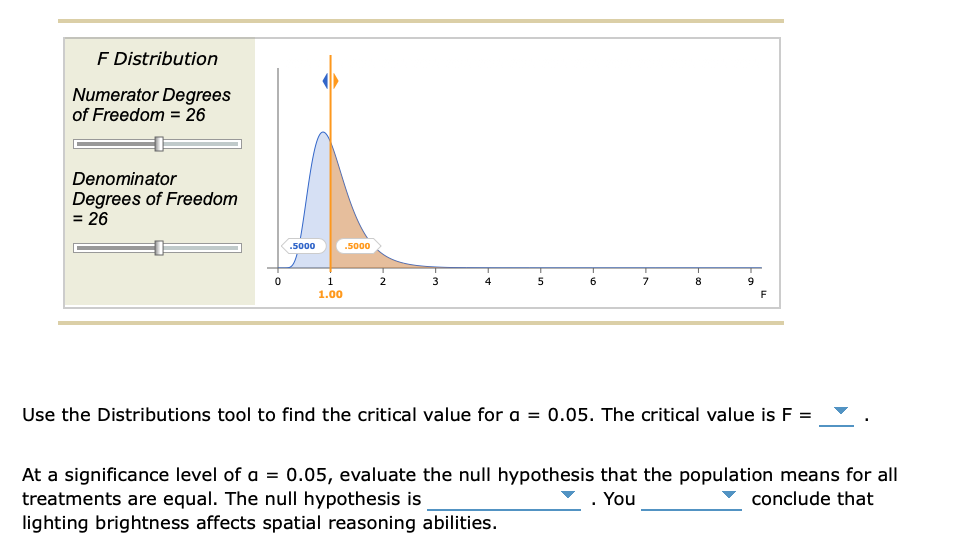
Transcribed Image Text:F Distribution
Numerator Degrees
of Freedom = 26
Denominator
Degrees of Freedom
= 26
0
.5000
1
1.00
.5000
2
3
4
6
8
F
Use the Distributions tool to find the critical value for a = 0.05. The critical value is F =
At a significance level of a = 0.05, evaluate the null hypothesis that the population means for all
treatments are equal. The null hypothesis is
You
conclude that
lighting brightness affects spatial reasoning abilities.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage