Problem Like friction, drag force opposes the motion of a particle in a fluid; however, drag force depends on the particle's velocity. Find the expression for the particle's velocity v(x) as a function of position at any point x in a fluid whose drag force is expressed as Fdrag = kmv where k is a constant, m is the mass of the particle and v is its velocity. Assume that the particle is constrained to move in the x-axis only with an initial velocity vo. Solution: The net force along the x-axis is: EF = -F then: mv = m Since acceleration is the first time derivative of velocity a= dv/dt, mv = m We can eliminate time dt by expressing, the velocity on the left side of the equation as v= dx/dt. Manipulating the variables and simplifying, we arrive at the following expression = -k "Isolating" the infinitesimal velocity dx and integrating with respect to dx, we arrive at the following: = vo - which shows that velocity decreases in a linear manner.
Problem Like friction, drag force opposes the motion of a particle in a fluid; however, drag force depends on the particle's velocity. Find the expression for the particle's velocity v(x) as a function of position at any point x in a fluid whose drag force is expressed as Fdrag = kmv where k is a constant, m is the mass of the particle and v is its velocity. Assume that the particle is constrained to move in the x-axis only with an initial velocity vo. Solution: The net force along the x-axis is: EF = -F then: mv = m Since acceleration is the first time derivative of velocity a= dv/dt, mv = m We can eliminate time dt by expressing, the velocity on the left side of the equation as v= dx/dt. Manipulating the variables and simplifying, we arrive at the following expression = -k "Isolating" the infinitesimal velocity dx and integrating with respect to dx, we arrive at the following: = vo - which shows that velocity decreases in a linear manner.
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter5: Newton's Law Of Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 77AP: (a) Find an equation to determine the magnitude of the net force required to stop a car of mass m,...
Related questions
Question
Kindly add labels and boxes for the final answer. Thank you.
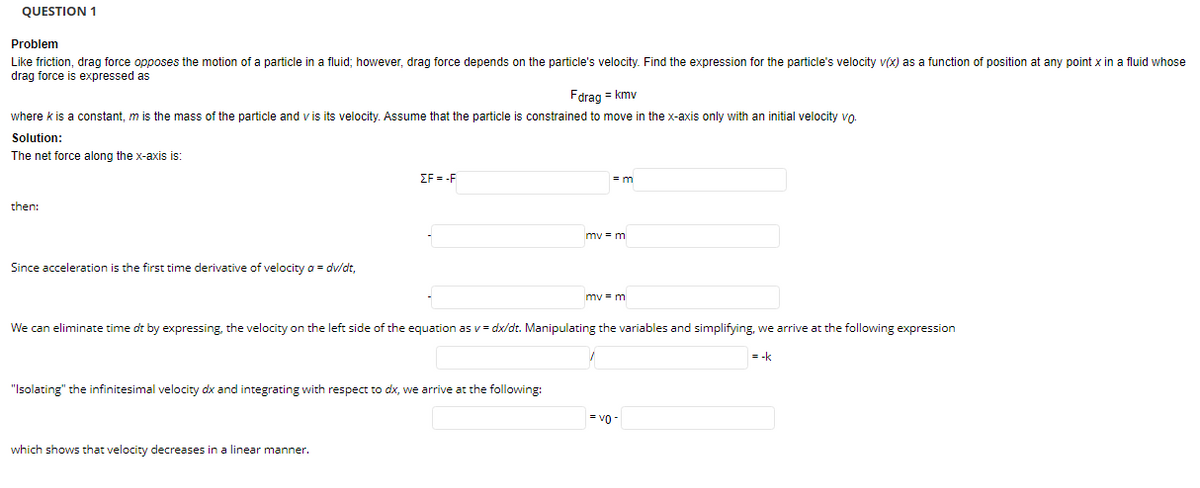
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 1
Problem
Like friction, drag force opposes the motion of a particle in a fluid; however, drag force depends on the particle's velocity. Find the expression for the particle's velocity v(x) as a function of position at any point x in a fluid whose
drag force is expressed as
Fdrag = kmv
where k is a constant, m is the mass of the particle and v is its velocity. Assume that the particle
constrained to move in the x-axis only with an initial velocity vo.
Solution:
The net force along the x-axis is:
ΣF-F
= m
then:
mv - m
Since acceleration is the first time derivative of velocity a = dv/dt,
mv = m
We can eliminate time dt by expressing, the velocity on the left side of the equation as v= dx/dt. Manipulating the variables and simplifying, we arrive at the following expression
= -k
"Isolating" the infinitesimal velocity dx and integrating with respect to dx, we arrive at the following:
= v0
which shows that velocity decreases in a linear manner.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University