Projectile Motion The position of a projectile fired with an initial velocity vo feet per second and at an angle 0 to the horizontal at the end of t seconds is given by the parametric equations x = (vo cos 0)t y = (vo sin 0)t – 16r2 See the illustration. R- (a) Obtain the rectangular equation of the trajectory and identify the curve. (b) Show that the projectile hits the ground (y = 0) when Vo sin 0. 16 (c) How far has the projectile traveled (horizontally) when it strikes the ground? In other words, find the range R. (d) Find the time t when x = y. Then find the horizontal distance x and the vertical distance y traveled by the projectile in this time. Then compute Vx + y. This is the distance R, the range, that the projectile travels up a plane inclined at 45° to the horizontal (x = y). See the following illustration. (See also Problem 97 in Section 7.6.) 45°
Projectile Motion The position of a projectile fired with an initial velocity vo feet per second and at an angle 0 to the horizontal at the end of t seconds is given by the parametric equations x = (vo cos 0)t y = (vo sin 0)t – 16r2 See the illustration. R- (a) Obtain the rectangular equation of the trajectory and identify the curve. (b) Show that the projectile hits the ground (y = 0) when Vo sin 0. 16 (c) How far has the projectile traveled (horizontally) when it strikes the ground? In other words, find the range R. (d) Find the time t when x = y. Then find the horizontal distance x and the vertical distance y traveled by the projectile in this time. Then compute Vx + y. This is the distance R, the range, that the projectile travels up a plane inclined at 45° to the horizontal (x = y). See the following illustration. (See also Problem 97 in Section 7.6.) 45°
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter6: Motion In Two Dimensions
Section6.1: Projectile Motion
Problem 9SSC
Related questions
Question
snip
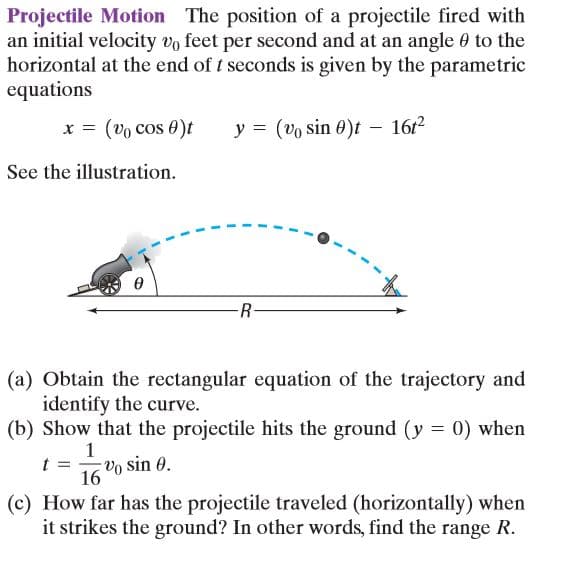
Transcribed Image Text:Projectile Motion The position of a projectile fired with
an initial velocity vo feet per second and at an angle 0 to the
horizontal at the end of t seconds is given by the parametric
equations
x = (vo cos 0)t
y = (vo sin 0)t – 16r2
See the illustration.
R-
(a) Obtain the rectangular equation of the trajectory and
identify the curve.
(b) Show that the projectile hits the ground (y = 0) when
Vo sin 0.
16
(c) How far has the projectile traveled (horizontally) when
it strikes the ground? In other words, find the range R.
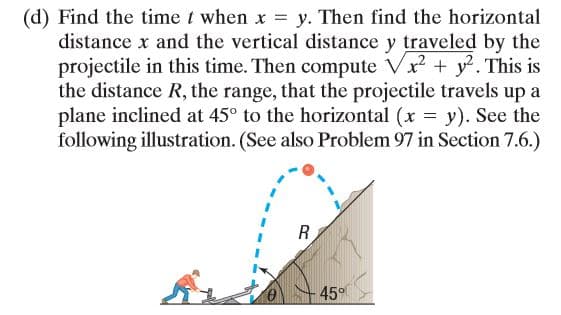
Transcribed Image Text:(d) Find the time t when x = y. Then find the horizontal
distance x and the vertical distance y traveled by the
projectile in this time. Then compute Vx + y. This is
the distance R, the range, that the projectile travels up a
plane inclined at 45° to the horizontal (x = y). See the
following illustration. (See also Problem 97 in Section 7.6.)
45°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning