Q.2. A rectangular foundation of size 2 by 2.5 m is constructed at a depth of D = (1.5 +) m below the ground surface as shown (where X is your group number). The foundation carries a load of 1000 kN. Use 2:1 method to find the stress increment. (2:1 means 2 vertical : 1 horizontal). a) Compute the settlement due to the consolidation of the clay. Assume the clay as one layer. b) Repeat (a) by dividing the clay layer into two equal sublayers (each sublayer 3 m). c) Write comments on your results in (a) and (b).
Q.2. A rectangular foundation of size 2 by 2.5 m is constructed at a depth of D = (1.5 +) m below the ground surface as shown (where X is your group number). The foundation carries a load of 1000 kN. Use 2:1 method to find the stress increment. (2:1 means 2 vertical : 1 horizontal). a) Compute the settlement due to the consolidation of the clay. Assume the clay as one layer. b) Repeat (a) by dividing the clay layer into two equal sublayers (each sublayer 3 m). c) Write comments on your results in (a) and (b).
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Chapter7: Permeability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.22P: Refer to Figure 7.24. The following data were collected during the field permeability measurement of...
Related questions
Question
The value of x is 8
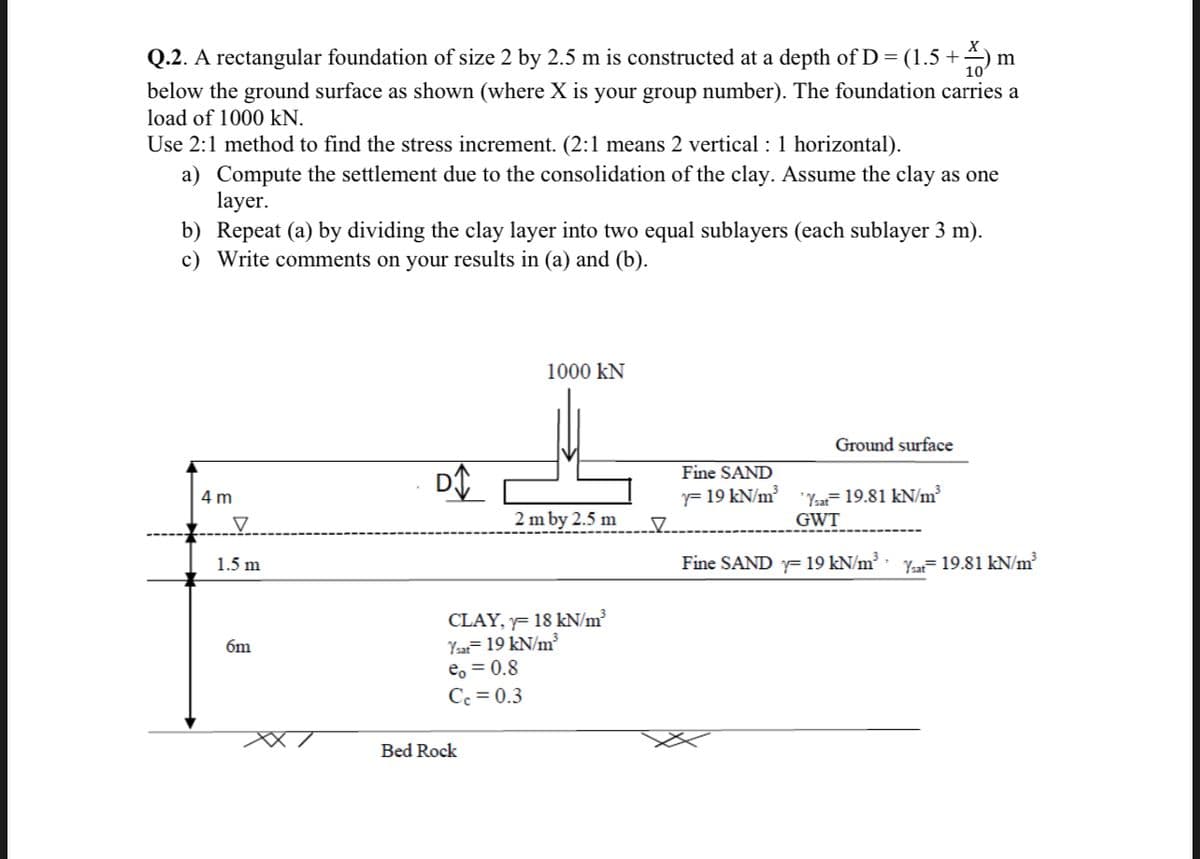
Transcribed Image Text:Q.2. A rectangular foundation of size 2 by 2.5 m is constructed at a depth of D= (1.5 +
below the ground surface as shown (where X is your group number). The foundation carries a
load of 1000 kN.
Use 2:1 method to find the stress increment. (2:1 means 2 vertical : 1 horizontal).
a) Compute the settlement due to the consolidation of the clay. Assume the clay as one
layer.
b) Repeat (a) by dividing the clay layer into two equal sublayers (each sublayer 3 m).
c) Write comments on your results in (a) and (b).
1000 kN
Ground surface
Fine SAND
"Yat= 19.81 kN/m²
GWT
4 m
= 19 kN/m³
2 m by 2.5 m
1.5 m
Fine SAND y= 19 kN/m³ Ye- 19.81 kN/m
CLAY, yF 18 kN/m³
Ysat=19 kN/m³
e, = 0.8
Cc = 0.3
6m
Bed Rock
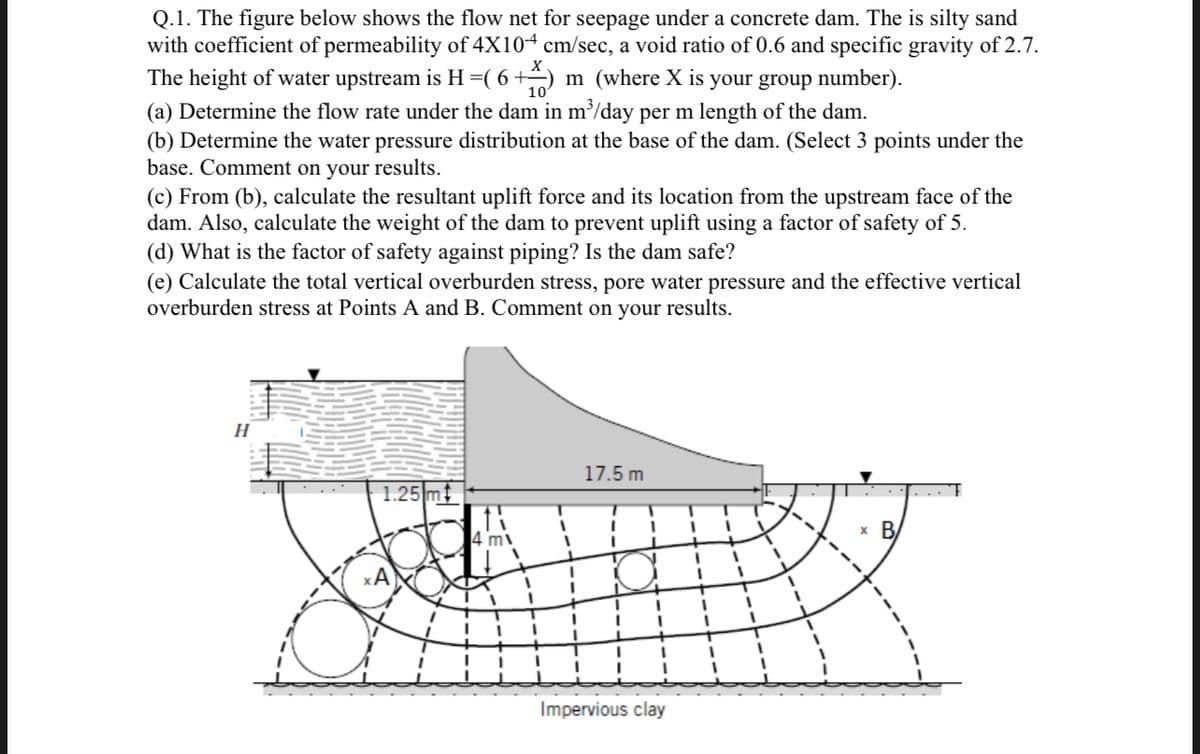
Transcribed Image Text:Q.1. The figure below shows the flow net for seepage under a concrete dam. The is silty sand
with coefficient of permeability of 4X104 cm/sec, a void ratio of 0.6 and specific gravity of 2.7.
The height of water upstream is H=( 6+÷) m (where X is your group number).
(a) Determine the flow rate under the dam in m/day per m length of the dam.
(b) Determine the water pressure distribution at the base of the dam. (Select 3 points under the
base. Comment on your results.
(c) From (b), calculate the resultant uplift force and its location from the upstream face of the
dam. Also, calculate the weight of the dam to prevent uplift using a factor of safety of 5.
(d) What is the factor of safety against piping? Is the dam safe?
(e) Calculate the total vertical overburden stress, pore water pressure and the effective vertical
overburden stress at Points A and B. Comment on your results.
H
17.5 m
1.25 mt
x B
4 m
%3D
3D
Impervious clay
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305635180
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305635180
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning