Q2. (a) A force of P = 200 N is applied to block A and causes block A to accelerate to the right on a rough surface as shown in Figure Q2(a). Knowing that the mass for block A is (6 + a) kg, where a denotes the last digit of your student ID and the mass for block B is 6 kg. Appendix A shows the examples of identifying the value using student ID. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the surface is 0.15. Pulleys are massless and smooth. (i) With suitable diagram(s), determine the accelerations of block A and B. (ii) (iii) B Determine the tension in the cable attached to block 4. Explain with calculations on the possible way(s) to reduce the acceleration of block B. 6 kg A (6+a) kg 30°
Q2. (a) A force of P = 200 N is applied to block A and causes block A to accelerate to the right on a rough surface as shown in Figure Q2(a). Knowing that the mass for block A is (6 + a) kg, where a denotes the last digit of your student ID and the mass for block B is 6 kg. Appendix A shows the examples of identifying the value using student ID. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the surface is 0.15. Pulleys are massless and smooth. (i) With suitable diagram(s), determine the accelerations of block A and B. (ii) (iii) B Determine the tension in the cable attached to block 4. Explain with calculations on the possible way(s) to reduce the acceleration of block B. 6 kg A (6+a) kg 30°
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Let a = 1
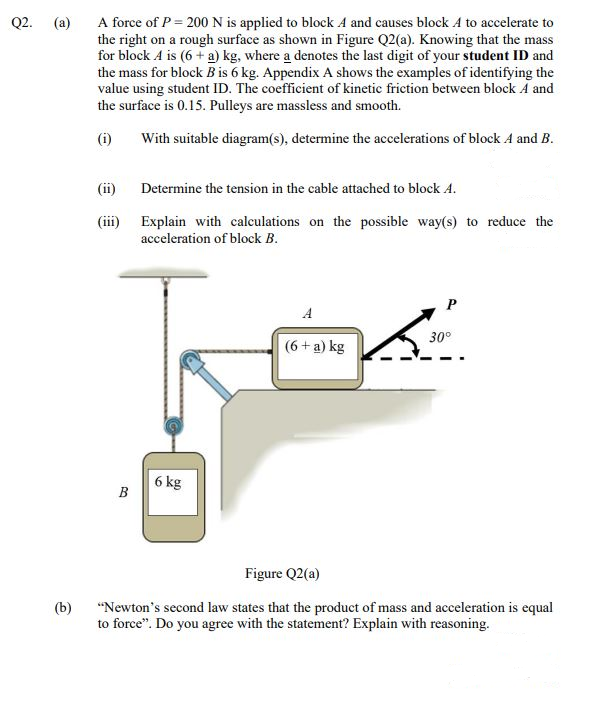
Transcribed Image Text:A force of P = 200N is applied to block A and causes block A to accelerate to
the right on a rough surface as shown in Figure Q2(a). Knowing that the mass
for block A is (6 + a) kg, where a denotes the last digit of your student ID and
the mass for block B is 6 kg. Appendix A shows the examples of identifying the
value using student ID. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and
the surface is 0.15. Pulleys are massless and smooth.
Q2.
(a)
(i)
With suitable diagram(s), determine the accelerations of block A and B.
(ii)
Determine the tension in the cable attached to block A.
(iii) Explain with calculations on the possible way(s) to reduce the
acceleration of block B.
A
30°
(6 + a) kg
6 kg
B
Figure Q2(a)
(b)
"Newton's second law states that the product of mass and acceleration is equal
to force". Do you agree with the statement? Explain with reasoning.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY