Q4) Draw a supply curve for the tables on the same diagram as the demand curve you have drawn for Q3. Q5) On the supplyldemand diagram find the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantities sold/bought Q6) Would you make a loss or profit by selling the equilibrium quantity and charging the equilibrium price?
Q4) Draw a supply curve for the tables on the same diagram as the demand curve you have drawn for Q3. Q5) On the supplyldemand diagram find the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantities sold/bought Q6) Would you make a loss or profit by selling the equilibrium quantity and charging the equilibrium price?
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter14: Pricing Techniques And Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1E
Related questions
Question
Answer 4, 5 and 6.
Thank You!
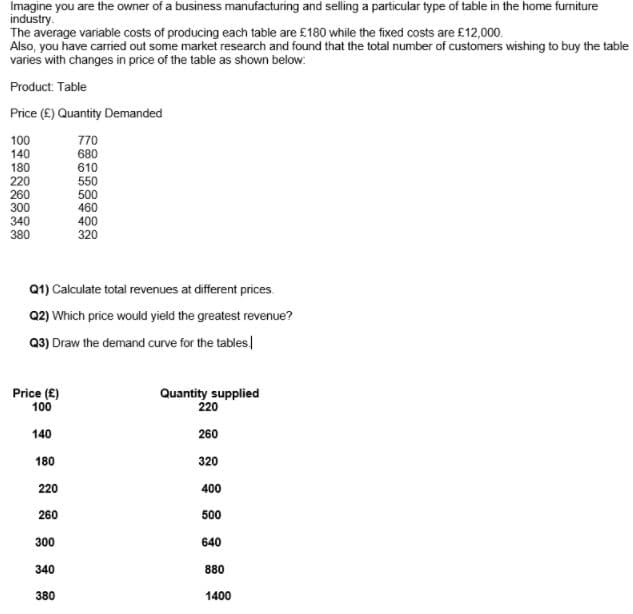
Transcribed Image Text:Imagine you are the owner of a business manufacturing and selling a particular type of table in the home furniture
industry.
The average variable costs of producing each table are £180 while the fixed costs are £12,000.
Also, you have carried out some market research and found that the total number of customers wishing to buy the table
varies with changes in price of the table as shown below:
Product. Table
Price (E) Quantity Demanded
100
140
770
680
610
180
220
260
300
550
500
460
340
380
400
320
Q1) Calculate total revenues at different prices.
Q2) Which price would yield the greatest revenue?
Q3) Draw the demand curve for the tables
Price (E)
100
Quantity supplied
220
140
260
180
320
220
400
260
500
300
640
340
880
380
1400
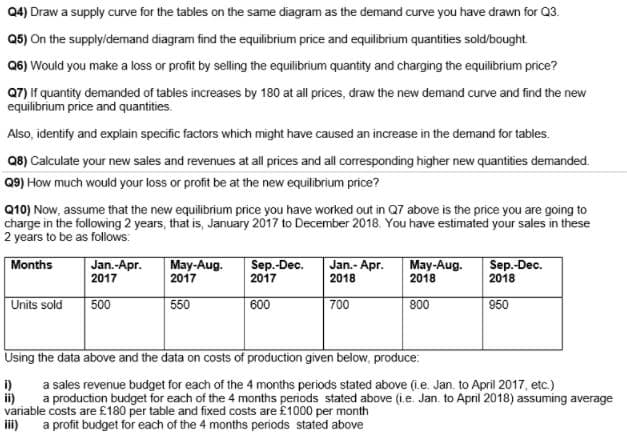
Transcribed Image Text:Q4) Draw a supply curve for the tables on the same diagram as the demand curve you have drawn for Q3.
Q5) On the supplyldemand diagram find the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantities sold/bought.
Q6) Would you make a loss or profit by selling the equilibrium quantity and charging the equilibrium price?
Q7) If quantity demanded of tables increases by 180 at all prices, draw the new demand curve and find the new
equilibrium price and quantities.
Also, identify and explain specific factors which might have caused an increase in the demand for tables.
Q8) Calculate your new sales and revenues at all prices and all corresponding higher new quantities demanded.
Q9) How much would your loss or profit be at the new equilibrium price?
Q10) Now, assume that the new equilibrium price you have worked out in Q7 above is the price you are going to
charge in the following 2 years, that is, January 2017 to December 2018. You have estimated your sales in these
2 years to be as follows:
Months
Jan.-Apr.
May-Aug.
2017
Sep.-Dec.
Jan.- Apr.
2018
May-Aug.
2018
Sep.-Dec.
2018
2017
2017
Units sold
500
550
600
800
950
700
Using the data above and the data on costs of production given below, produce:
i)
a sales revenue budget for each of the 4 months periods stated above (i.e. Jan. to April 2017, etc.)
ii)
a production budget for each of the 4 months periods stated above (i.e. Jan. to April 2018) assuming average
variable costs are £180 per table and fixed costs are £1000 per month
a profit budget for each of the 4 months periods stated above
iii)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning