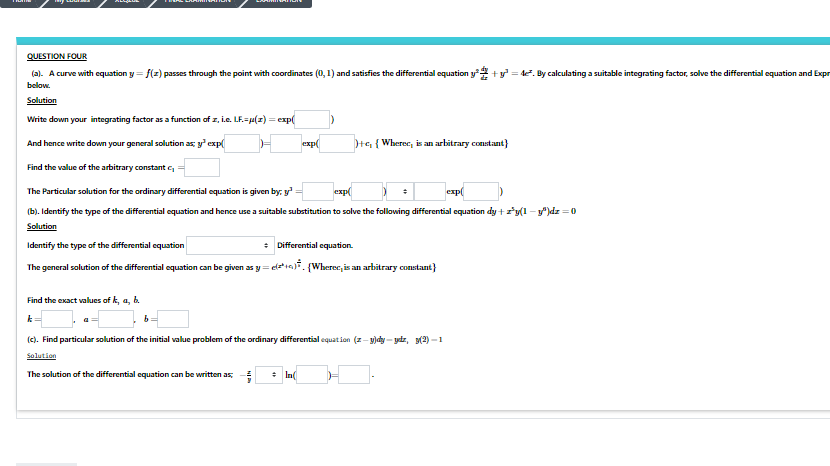
QUESTION FOUR (a). A curve with equation y= f{z) passes through the point with coordinates (0, 1) and satisfies the differental equation y+y =. By cakculating a suitable integrating factoc solve the differential equation and Expr below. Solution Write down your integrating factor as a function of z, ie LE-p(2) = exp( And hence write down your general solution ac y'ap( exp tG { Wherec, is an arbitrary constant} Find the value of the arbitrary costant e, The Particular solution for the ordinary differential equation is given by: y exp
QUESTION FOUR (a). A curve with equation y= f{z) passes through the point with coordinates (0, 1) and satisfies the differental equation y+y =. By cakculating a suitable integrating factoc solve the differential equation and Expr below. Solution Write down your integrating factor as a function of z, ie LE-p(2) = exp( And hence write down your general solution ac y'ap( exp tG { Wherec, is an arbitrary constant} Find the value of the arbitrary costant e, The Particular solution for the ordinary differential equation is given by: y exp
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION FOUR
(a). A curve with equation y= f(z) passes through the point with coordinates (0, 1) and satisfies the differential equation y + y = de. By calculating a suitable integrating factor, solve the differential equation and Expr
below.
Solution
Write down your integrating factor as a function of z, i.e. LF.=p(z) = exp(
And hence write down your general solution as y exp
exp
+4 { Wherec, is an arbitrary constant}
Find the value of the arbitrary constant e,
The Particular solution for the ordinary differential equation is given by: y
exp(
exp
(b). Identify the type of the differential equation and hence use a suitable substitution to solve the following differential equation dy+ry(1 -)dz =0
Solution
Identify the type of the differential equation
: Differential equation.
The general solution of the differential equation can be given as y = el=*ia). {Wherec, is an arbitrary constant}
Find the exact values of k, a, b.
a
(c). Find particular solution of the initial value problem of the ordinary differential equat ion (z – y)dy - ydz, 3(2) -1
Solution
The solution of the differential equation can be written as
: In(
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

