Quinine is a natural product extracted from the bark of the cinchona tree, which is native an antimalarial agent. When 1.90 g of quinine is dissolved in 25.0 g of cyclohexane, the freezing point of the so up the freezing point and Kf constant for cyclohexane in the Colligative Constants table. Calculate the molar mass of quinine. molar mass:
Quinine is a natural product extracted from the bark of the cinchona tree, which is native an antimalarial agent. When 1.90 g of quinine is dissolved in 25.0 g of cyclohexane, the freezing point of the so up the freezing point and Kf constant for cyclohexane in the Colligative Constants table. Calculate the molar mass of quinine. molar mass:
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter15: Principles Of Chemical Reactivity: Equilibria
Section15.6: Disturbing A Chemical Equilibrium
Problem 2.1ACP: Freezing point depression is one means of determining the molar mass of a compound. The freezing...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Quinine is a natural product extracted from the bark of the cinchona tree, which is native to South America. Quinine is used as
an antimalarial agent.
When 1.90 g of quinine is dissolved in 25.0 g of cyclohexane, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 4.88 °C. Look
up the freezing point and Kf constant for cyclohexane in the Colligative Constants table.
Calculate the molar mass of quinine.
molar mass:
g/mol
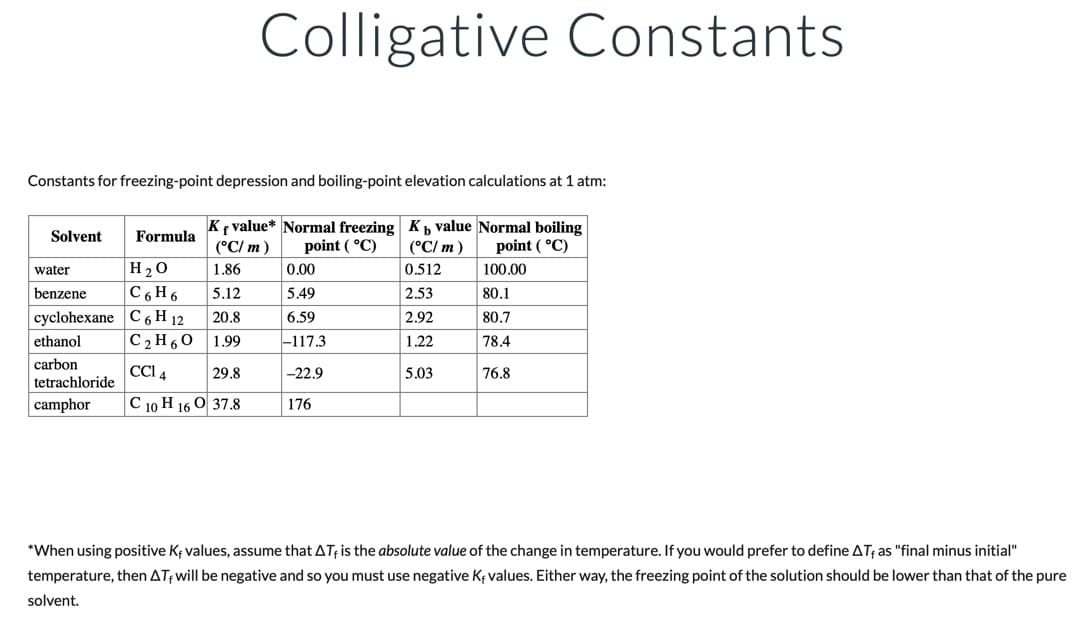
Transcribed Image Text:Colligative Constants
Constants for freezing-point depression and boiling-point elevation calculations at 1 atm:
Kf value* Normal freezing Kb value Normal boiling
(°C/ m)
Solvent
Formula
(°C/ m)
point ( °C)
point ( °C)
H20
1.86
0.00
0.512
100.00
water
benzene
C6H 6
5.12
5.49
2.53
80.1
cyclohexane C 6 H 12
ethanol
20.8
6.59
2.92
80.7
C2 H60
1.99
-117.3
1.22
78.4
carbon
tetrachloride
CCI 4
29.8
-22.9
5.03
76.8
camphor
С 10 Н 160 37.8
176
*When using positive Kf values, assume that ATf is the absolute value of the change in temperature. If you would prefer to define AT; as "final minus initial"
temperature, then ATfwill be negative and so you must use negative Kf values. Either way, the freezing point of the solution should be lower than that of the pure
solvent.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning