Reaction KspKsp ΔH°ΔH° ΔS°ΔS° FeCO3(s)⇄Fe2+(aq)+CO32−(aq)FeCO3(s)⇄Fe2+(aq)+CO32−(aq) 3×10−113×10−11 <0<0 >0>0 MnCO3(s)⇄Mn2+(aq)+CO32−(aq)MnCO3(s)⇄Mn2+(aq)+CO32−(aq) 2×10−112×10−11 <0<0 >0 The table above lists the equilibrium constants and changes in thermodynamic properties for the dissolution of FeCO3 and MnCO3 at 25°C. The two-particle diagrams below represent saturated solutions of each compound at equilibrium. (see attached image) a.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔH°<0ΔH°<0 because the ions from both compounds are solvated by water molecules. b.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔH°<0ΔH°<0 because both compounds produce about the same amount of CO32−CO32− ions from the dissolution. c.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔS°>0ΔS°>0 because both compounds produce a very small amount of ions from the dissolution. d.) The particle diagrams best represent that the molar solubility is greater for FeCO3 compared to MnCO3.
Reaction KspKsp ΔH°ΔH° ΔS°ΔS° FeCO3(s)⇄Fe2+(aq)+CO32−(aq)FeCO3(s)⇄Fe2+(aq)+CO32−(aq) 3×10−113×10−11 <0<0 >0>0 MnCO3(s)⇄Mn2+(aq)+CO32−(aq)MnCO3(s)⇄Mn2+(aq)+CO32−(aq) 2×10−112×10−11 <0<0 >0 The table above lists the equilibrium constants and changes in thermodynamic properties for the dissolution of FeCO3 and MnCO3 at 25°C. The two-particle diagrams below represent saturated solutions of each compound at equilibrium. (see attached image) a.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔH°<0ΔH°<0 because the ions from both compounds are solvated by water molecules. b.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔH°<0ΔH°<0 because both compounds produce about the same amount of CO32−CO32− ions from the dissolution. c.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔS°>0ΔS°>0 because both compounds produce a very small amount of ions from the dissolution. d.) The particle diagrams best represent that the molar solubility is greater for FeCO3 compared to MnCO3.
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter20: Chemistry Of Selected Transition Elements And Coordination Compounds
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 36QRT
Related questions
Question
| Reaction | KspKsp | ΔH°ΔH° | ΔS°ΔS° |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeCO3(s)⇄Fe2+(aq)+CO32−(aq)FeCO3(s)⇄Fe2+(aq)+CO32−(aq) | 3×10−113×10−11 | <0<0 | >0>0 |
| MnCO3(s)⇄Mn2+(aq)+CO32−(aq)MnCO3(s)⇄Mn2+(aq)+CO32−(aq) | 2×10−112×10−11 | <0<0 | >0 |
The table above lists the equilibrium constants and changes in
a.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔH°<0ΔH°<0 because the ions from both compounds are solvated by water molecules.
b.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔH°<0ΔH°<0 because both compounds produce about the same amount of CO32−CO32− ions from the dissolution.
c.) The particle diagrams best represent that ΔS°>0ΔS°>0 because both compounds produce a very small amount of ions from the dissolution.
d.) The particle diagrams best represent that the molar solubility is greater for FeCO3 compared to MnCO3.
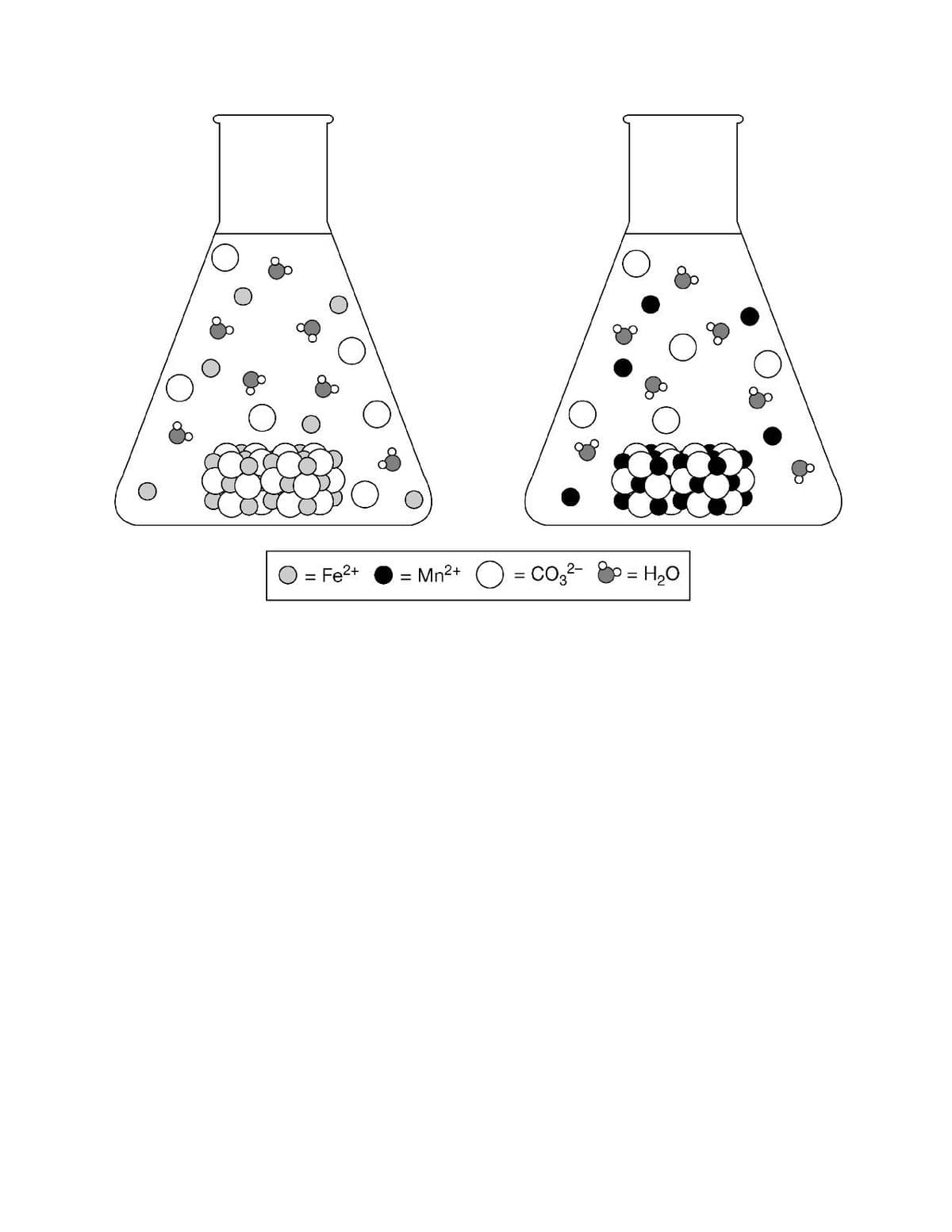
Transcribed Image Text:= Fe2+
Mn2+ O = Co,²-
p= H20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning