Refer to the table below and assume that the Fed's reserve ratio is 10 percent and the economy is in a severe recession. Also suppose that the commercial banks are hoarding all excess reserves (not lending them out) because of their fear of loan defaults. Finally suppose that the Fed is highly concerned that the banks will suddenly lend out these excess reserves and possibly contribute to inflation once the economy begins to recover and confidence is restored (1) (2) Checkable Deposits $20,000 (3) Actual Reserves (4) Required Reserves (5) (6) (7) Reserve Ratio, Money-Creating Potential of Money-Creating Potential Single Bank,-(5) Excess Reserves of Banking System (1) 10 $5,000 $2,000 $3,000 $3,000 $30,000 (2) 20 20,000 5,000 4,000 1,000 1,000 5,000 (3) 25 20,000 5,000 5,000 0 0 (4) 30 20,000 5,000 6,000 -1,000 -1,000 -3.333 a. By how many percentage points would the Fed need to increase the reserve ratio to eliminate one-third of the excess reserves? b. What would be the size of the monetary multiplier before the change in the reserve ratio? Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places. b. What would be the size of the monetary multiplier before the change in the reserve ratio? Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places What would be the size after the change? c. By how much would the lending potential of the banks decline as a result of the increase in the reserve ratio? Instructions: Enter your answer as an absolute value.
Refer to the table below and assume that the Fed's reserve ratio is 10 percent and the economy is in a severe recession. Also suppose that the commercial banks are hoarding all excess reserves (not lending them out) because of their fear of loan defaults. Finally suppose that the Fed is highly concerned that the banks will suddenly lend out these excess reserves and possibly contribute to inflation once the economy begins to recover and confidence is restored (1) (2) Checkable Deposits $20,000 (3) Actual Reserves (4) Required Reserves (5) (6) (7) Reserve Ratio, Money-Creating Potential of Money-Creating Potential Single Bank,-(5) Excess Reserves of Banking System (1) 10 $5,000 $2,000 $3,000 $3,000 $30,000 (2) 20 20,000 5,000 4,000 1,000 1,000 5,000 (3) 25 20,000 5,000 5,000 0 0 (4) 30 20,000 5,000 6,000 -1,000 -1,000 -3.333 a. By how many percentage points would the Fed need to increase the reserve ratio to eliminate one-third of the excess reserves? b. What would be the size of the monetary multiplier before the change in the reserve ratio? Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places. b. What would be the size of the monetary multiplier before the change in the reserve ratio? Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places What would be the size after the change? c. By how much would the lending potential of the banks decline as a result of the increase in the reserve ratio? Instructions: Enter your answer as an absolute value.
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Course List)
7th Edition
ISBN:9781285165875
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter29: The Monetary System
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10PA
Related questions
Question
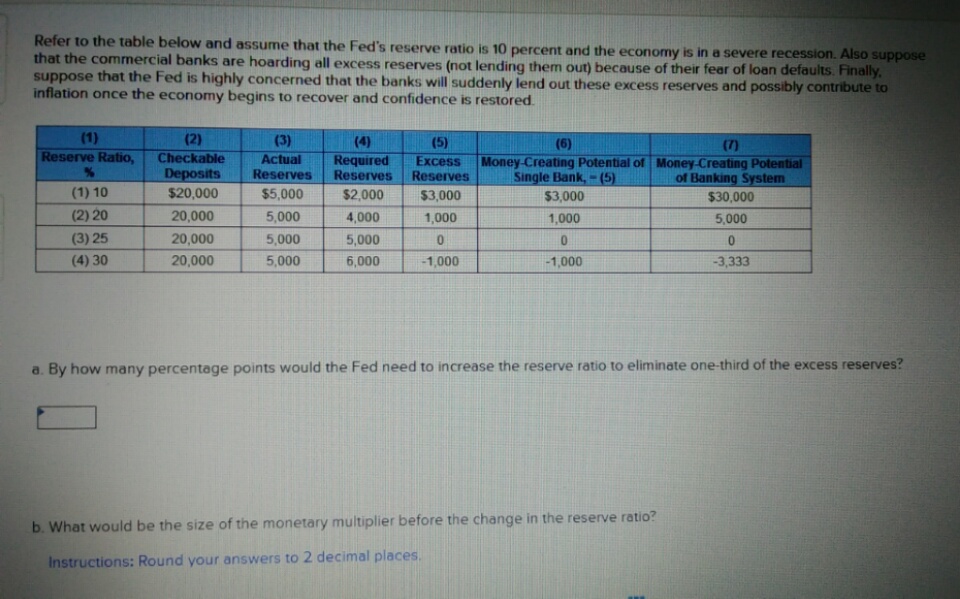
Transcribed Image Text:Refer to the table below and assume that the Fed's reserve ratio is 10 percent and the economy is in a severe recession. Also suppose
that the commercial banks are hoarding all excess reserves (not lending them out) because of their fear of loan defaults. Finally
suppose that the Fed is highly concerned that the banks will suddenly lend out these excess reserves and possibly contribute to
inflation once the economy begins to recover and confidence is restored
(1)
(2)
Checkable
Deposits
$20,000
(3)
Actual
Reserves
(4)
Required
Reserves
(5)
(6)
(7)
Reserve Ratio,
Money-Creating Potential of Money-Creating Potential
Single Bank,-(5)
Excess
Reserves
of Banking System
(1) 10
$5,000
$2,000
$3,000
$3,000
$30,000
(2) 20
20,000
5,000
4,000
1,000
1,000
5,000
(3) 25
20,000
5,000
5,000
0
0
(4) 30
20,000
5,000
6,000
-1,000
-1,000
-3.333
a. By how many percentage points would the Fed need to increase the reserve ratio to eliminate one-third of the excess reserves?
b. What would be the size of the monetary multiplier before the change in the reserve ratio?
Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places.
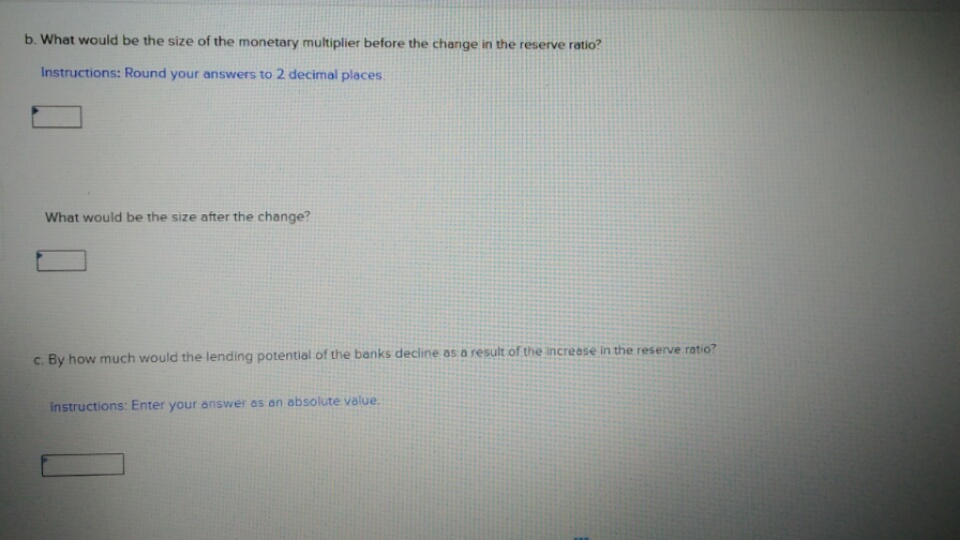
Transcribed Image Text:b. What would be the size of the monetary multiplier before the change in the reserve ratio?
Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places
What would be the size after the change?
c. By how much would the lending potential of the banks decline as a result of the increase in the reserve ratio?
Instructions: Enter your answer as an absolute value.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning