Seneca Hill Winery recently purchased land for the purpose of establishing a new vineyard. Management is considering two varieties of white grapes for the new vineyard: Chardonnay and Riesling. The Chardonnay grapes would be used to produce a dry Chardonnay wine, and the Riesling grapes would be used to produce a semidry Riesling wine. It takes approximately four years from the time of planting before new grapes can be harvested. This length of time creates a great deal of uncertainty concerning future demand and makes the decision concerning the type of grapes to plant difficult. Three possibilities are being considered: Chardonnay grapes only; Riesling grapes only; and both Chardonnay and Riesling grapes. Seneca management decided that for planning purposes it would be adequate to consider only two demand possibilities for each type of wine: strong or weak. With two possibilities for each type of wine it was necessary to assess four probabilities. With the help of some forecasts in industry publications management made the following probability assessments. Chardonnay Demand Riesling Demand Weak Strong 0.05 0.50 0.25 0.20 Weak Strong Revenue projections show an annual contribution to profit of $40,000 if Seneca Hill only plants Chardonnay grapes and demand is weak for Chardonnay wine, and $90,000 if the company only plants Chardonnay grapes and demand is strong for Chardonnay wine. If Seneca Hill only plants Riesling grapes, the annual profit projection is $45,000 if demand is weak for Riesling grapes and $65,000 if demand is strong for Riesling grapes. If Seneca plants both types of grapes, the annual profit projections are as shown in the following table. Riesling Demand Chardonnay Demand Weak Strong $42,000 $60,000 $46,000 $80,000 Weak Strong (a) What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence? The decision to be made is to choose what type of grapes to plant . The chance event is demand for the wine The consequence is the expected annual profit contribution Identify the alternatives for the decisions and the possible outcomes for the chance events. The alternatives for the decisions are Chardonnay, Riesling, and both . The possible outcomes for the chance events are (W,W), (W,S), (S,W), (S,S) ▼ (b) Develop a decision tree. (Enter monetary values in thousands and percentages in decimal form.) Decision Tree Plant Chardonnay 2 Plant both grapes 1 3 Plant Riesling 4 Description Weak for Chardonnay 40,000 40,000 × Strong for Chardonnay 90,000 Weak Chardonnay, Weak Riesling 42,000 Weak Chardonnay, Strong Riesling 60,000 × 90,000 42,000 60,000 Strong Chardonnay, Weak Riesling 46,000 46,000 × Strong Chardonnay, Strong Riesling 80,000 80,000 × Weak for Riesling 45,000 45,000 ☑ Strong for Riesling 65,000 65,000 ×
Seneca Hill Winery recently purchased land for the purpose of establishing a new vineyard. Management is considering two varieties of white grapes for the new vineyard: Chardonnay and Riesling. The Chardonnay grapes would be used to produce a dry Chardonnay wine, and the Riesling grapes would be used to produce a semidry Riesling wine. It takes approximately four years from the time of planting before new grapes can be harvested. This length of time creates a great deal of uncertainty concerning future demand and makes the decision concerning the type of grapes to plant difficult. Three possibilities are being considered: Chardonnay grapes only; Riesling grapes only; and both Chardonnay and Riesling grapes. Seneca management decided that for planning purposes it would be adequate to consider only two demand possibilities for each type of wine: strong or weak. With two possibilities for each type of wine it was necessary to assess four probabilities. With the help of some forecasts in industry publications management made the following probability assessments. Chardonnay Demand Riesling Demand Weak Strong 0.05 0.50 0.25 0.20 Weak Strong Revenue projections show an annual contribution to profit of $40,000 if Seneca Hill only plants Chardonnay grapes and demand is weak for Chardonnay wine, and $90,000 if the company only plants Chardonnay grapes and demand is strong for Chardonnay wine. If Seneca Hill only plants Riesling grapes, the annual profit projection is $45,000 if demand is weak for Riesling grapes and $65,000 if demand is strong for Riesling grapes. If Seneca plants both types of grapes, the annual profit projections are as shown in the following table. Riesling Demand Chardonnay Demand Weak Strong $42,000 $60,000 $46,000 $80,000 Weak Strong (a) What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence? The decision to be made is to choose what type of grapes to plant . The chance event is demand for the wine The consequence is the expected annual profit contribution Identify the alternatives for the decisions and the possible outcomes for the chance events. The alternatives for the decisions are Chardonnay, Riesling, and both . The possible outcomes for the chance events are (W,W), (W,S), (S,W), (S,S) ▼ (b) Develop a decision tree. (Enter monetary values in thousands and percentages in decimal form.) Decision Tree Plant Chardonnay 2 Plant both grapes 1 3 Plant Riesling 4 Description Weak for Chardonnay 40,000 40,000 × Strong for Chardonnay 90,000 Weak Chardonnay, Weak Riesling 42,000 Weak Chardonnay, Strong Riesling 60,000 × 90,000 42,000 60,000 Strong Chardonnay, Weak Riesling 46,000 46,000 × Strong Chardonnay, Strong Riesling 80,000 80,000 × Weak for Riesling 45,000 45,000 ☑ Strong for Riesling 65,000 65,000 ×
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter4: Linear Programming Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 107P
Related questions
Question
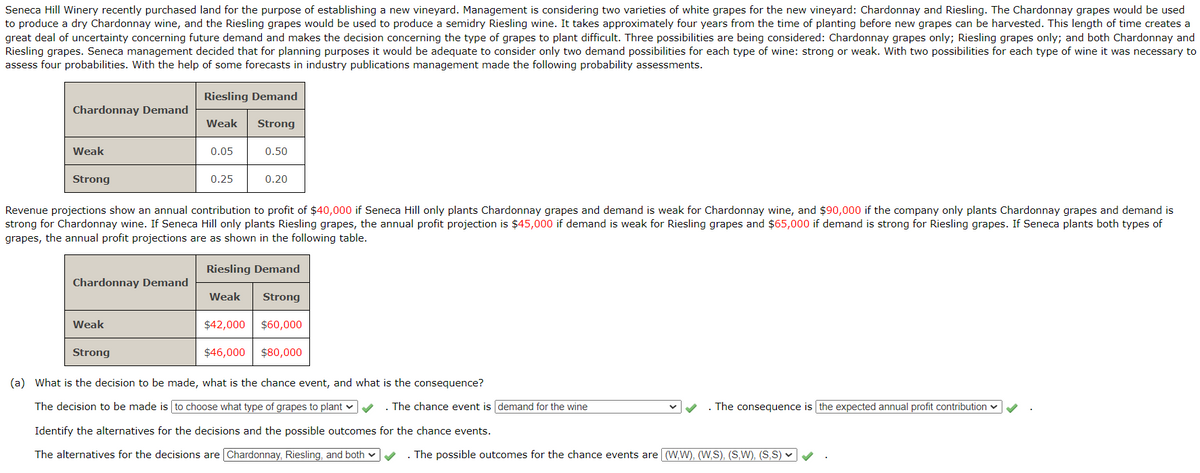
Transcribed Image Text:Seneca Hill Winery recently purchased land for the purpose of establishing a new vineyard. Management is considering two varieties of white grapes for the new vineyard: Chardonnay and Riesling. The Chardonnay grapes would be used
to produce a dry Chardonnay wine, and the Riesling grapes would be used to produce a semidry Riesling wine. It takes approximately four years from the time of planting before new grapes can be harvested. This length of time creates a
great deal of uncertainty concerning future demand and makes the decision concerning the type of grapes to plant difficult. Three possibilities are being considered: Chardonnay grapes only; Riesling grapes only; and both Chardonnay and
Riesling grapes. Seneca management decided that for planning purposes it would be adequate to consider only two demand possibilities for each type of wine: strong or weak. With two possibilities for each type of wine it was necessary to
assess four probabilities. With the help of some forecasts in industry publications management made the following probability assessments.
Chardonnay Demand
Riesling Demand
Weak
Strong
0.05
0.50
0.25
0.20
Weak
Strong
Revenue projections show an annual contribution to profit of $40,000 if Seneca Hill only plants Chardonnay grapes and demand is weak for Chardonnay wine, and $90,000 if the company only plants Chardonnay grapes and demand is
strong for Chardonnay wine. If Seneca Hill only plants Riesling grapes, the annual profit projection is $45,000 if demand is weak for Riesling grapes and $65,000 if demand is strong for Riesling grapes. If Seneca plants both types of
grapes, the annual profit projections are as shown in the following table.
Riesling Demand
Chardonnay Demand
Weak Strong
$42,000 $60,000
$46,000 $80,000
Weak
Strong
(a) What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence?
The decision to be made is to choose what type of grapes to plant
. The chance event is demand for the wine
The consequence is the expected annual profit contribution
Identify the alternatives for the decisions and the possible outcomes for the chance events.
The alternatives for the decisions are Chardonnay, Riesling, and both
. The possible outcomes for the chance events are (W,W), (W,S), (S,W), (S,S) ▼
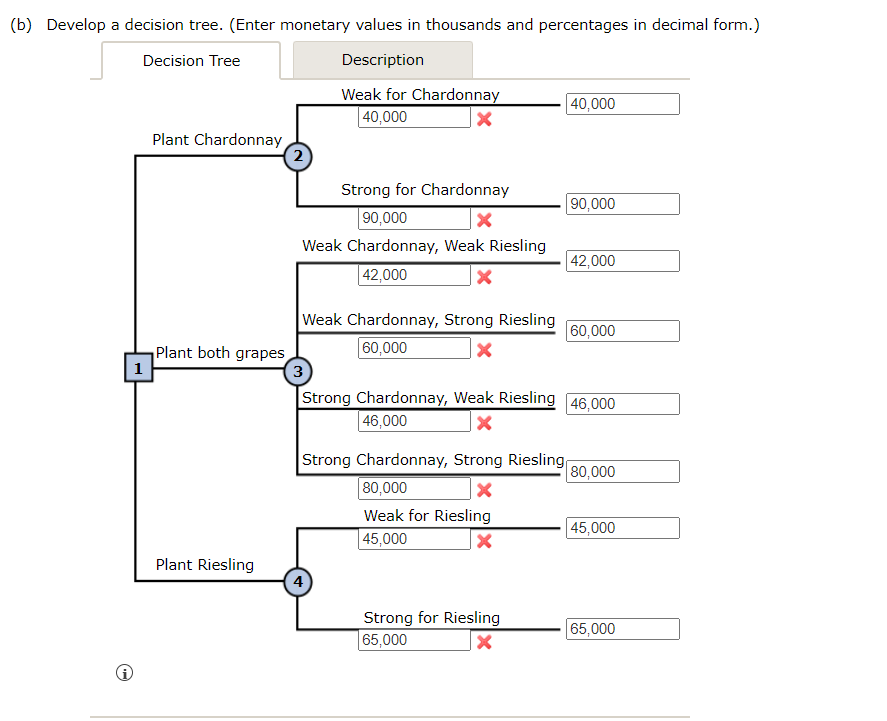
Transcribed Image Text:(b) Develop a decision tree. (Enter monetary values in thousands and percentages in decimal form.)
Decision Tree
Plant Chardonnay
2
Plant both grapes
1
3
Plant Riesling
4
Description
Weak for Chardonnay
40,000
40,000
×
Strong for Chardonnay
90,000
Weak Chardonnay, Weak Riesling
42,000
Weak Chardonnay, Strong Riesling
60,000
×
90,000
42,000
60,000
Strong Chardonnay, Weak Riesling 46,000
46,000
×
Strong Chardonnay, Strong Riesling
80,000
80,000
×
Weak for Riesling
45,000
45,000
☑
Strong for Riesling
65,000
65,000
×
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,