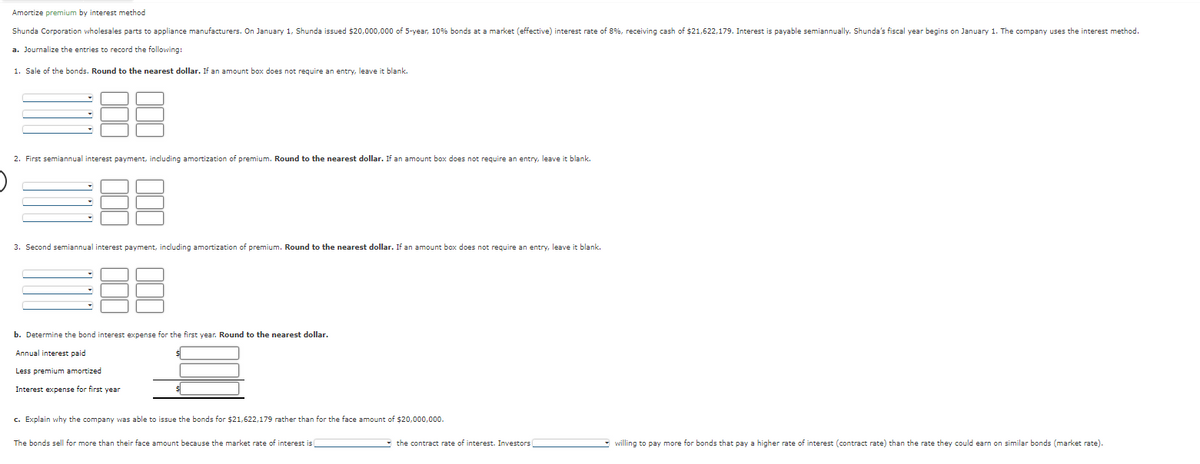
Shunda Corporation wholesales parts to appliance manufacturers. On January 1, Shunda issued $20.000.000 of 5-year, 10% bonds at a market (effective) interest rate of 8%, receiving cash of $21.622.179. Interest is payable semiannually. Shunda's fiscal year begins on January 1. The company uses the inter a. Journalize the entries to record the following: 1. Sale of the bonds. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. 188 2. First semiannual interest payment, including amortization of premium. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. 188 3. Second semiannual interest payment, including amortization of premium. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. b. Determine the bond interest expense for the first year. Round to the nearest dollar. Annual interest paid Less premium amortized 른 Interest expense for first year c. Explain why the company was able to issue the bonds for $21,622,179 rather than for the face amount of $20,000,000.
Shunda Corporation wholesales parts to appliance manufacturers. On January 1, Shunda issued $20.000.000 of 5-year, 10% bonds at a market (effective) interest rate of 8%, receiving cash of $21.622.179. Interest is payable semiannually. Shunda's fiscal year begins on January 1. The company uses the inter a. Journalize the entries to record the following: 1. Sale of the bonds. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. 188 2. First semiannual interest payment, including amortization of premium. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. 188 3. Second semiannual interest payment, including amortization of premium. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. b. Determine the bond interest expense for the first year. Round to the nearest dollar. Annual interest paid Less premium amortized 른 Interest expense for first year c. Explain why the company was able to issue the bonds for $21,622,179 rather than for the face amount of $20,000,000.
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337690881
Author:Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Chapter9: Long-term Liabilities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 79E
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Amortize premium by interest method
Shunda Corporation wholesales parts to appliance manufacturers. On January 1, Shunda issued $20,000,000 of 5-year, 10% bonds at a market (effective) interest rate of 8%, receiving cash of $21,622,179. Interest is payable semiannually. Shunda's fiscal year begins on January 1. The company uses the interest method.
a. Journalize the entries to record the following:
1. Sale of the bonds. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
€88
2. First semiannual interest payment, including amortization of premium. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
3. Second semiannual interest payment, including amortization of premium. Round to the nearest dollar. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
b. Determine the bond interest expense for the first year. Round to the nearest dollar.
Annual interest paid
Less premium amortized
Interest expense for first year
c. Explain why the company was able to issue the bonds for $21,622,179 rather than for the face amount of $20,000,000.
The bonds sell for more than their face amount because the market rate of interest is
the contract rate of interest. Investors
willing to pay more for bonds that pay a higher rate of interest (contract rate) than the rate they could earn on similar bonds (market rate).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:
9781111581565
Author:
Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:
9781111581565
Author:
Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,