First Position U C Seconed Position A G code Amino Acid code Amino Acid code Amino Acid code Amino Acid บบบ UCU UAU UGU phe tyr cys UUC UCC UAC UGC U ser UUA UCA UAA STOP UGA STOP leu UUG UCG UAG STOP UGG trp CUU CCU CAU CGU his CUC CCC CAC CGC C leu pro arg CUA CCA CAA CGA gin CUG CCG CAG CGG AUU ACU AAU AGU asn ser AUC ile ACC AAC AGC A thr AUA ACA AAA AGA lys arg AUG met ACG AAG AGG GUU GCU GAU GGU asp GUC GCC GAC GGC G val ala gly GUA GCA GAA GGA glu GUG GCG GAG GGG →CAGUGAGUGAGUGAG с Third Position Snuffle Snork TAC CAA AGA AAT ATT TAC ATG GGT GTT GTC TTC ACT TAC GAG GAT AGC CGC ATC TAC CAA CGA CCC ACT TAC GTA TAA ATT TAC AGA GGC CAA ATC TAC TTG TAT GGT ACC GGT TGC ATC TAC CTA CTA TTG TCC ACT TAC TAC AAA TCA ACT TAC GCT ATG ACA CCT ATT Snapple Snork TAC CAG AGG TTT ATC TAC CAT GGC TGT GGA TTT ACT TAC GAT AAG AAC GGG ATT TAC CGT CAT CAC ATC TAC GTA GTG ATC TAC CAG AAA ATG ACT TAC TTA TAG GAC GAT GGG TGC ATT TAC CAG TTA TTG TCT ATC TAC AAA AAG GTG ACT TAC GCG TAC TGG GGC ACT How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with ten genes on it. Your job is to analyze the genes of its DNA and determine what traits the organism has and then sketch the organism (You can be creative here). For simplicity, the gene sequences are much smaller than *real* gene sequences found in living organisms. Each gene has two versions (alleles) that result in a different trait being expressed in the snork. Genes Amino Acid Sequence met Gene 1 - body covering valser - leu met - valser - lys Gene 2 - body style -- Phenotype Snoopy Snork TAC CAG AGG TTT ATC TAC ATG GGT GTC GTC TTC ACT TAC GAG GAT AGC CGC ATC TAC CGT CAT CAC ATC TAC GTA GTG ATC TAC AGA GGC CAA ATC TAC TTG TAT GGT ACC GGT TGC ATC TAC CAG TTA TTG TCT ATC TAC AAA AAG GTG ACT TAC GCT ATG ACA CCT ATT Gene 3 - legs Gene 4 - head shape Gene 5 - tails Gene 6 - body pigment Gene 7 - eyes ByrdS Gene 8 - mouth Gene 9 - ears Gene 10 - arms met - tyr-pro- gln - gln - lys met-val-pro- thr - pro - lys met - leu - phe - leu - pro met - leu - leu - ser- ala metala - val - val met - val - ala - gly met-his- ile met - his-his met ser - pro - val - met - val - phe - tyr met - asn - - ile - leu - leu - pro - thr met - asn - ile - pro - trp - pro- thr met val - asn - asn arg met asp - asp - asn - arg met - met - phe - ser met - phe - phe - his met- arg - tyr - cys - gly met - arg met - thr - pro hairless hairy plump skinny 3 legged 2 legged round head square head tail no tail blue pigment (hair/skin) red pigment (hair/skin) small slanted eyes large round eyes circular mouth rectangular mouth pointed standing-up ears rounded floppy ears long spaghetti like arms short stumpy arms Each of the DNA samples was taken from volunteer Snorks. Your job is to analyze each DNA sample and determine the phenotype (how the organism looks) based on the sequence. You will do this by (1) transcribing each DNA sequence to mRNA, and then (2) translating the mRNA codons into amino acids. Remember that in mRNA, AUG is a start codon (amino acid = met), an it signifies the beginning of each gene. The stop codons that signify the end of a gene are UAA, UAG and UGA. The genes are in order from Gene 1 to Gene 10. ByrdS
First Position U C Seconed Position A G code Amino Acid code Amino Acid code Amino Acid code Amino Acid บบบ UCU UAU UGU phe tyr cys UUC UCC UAC UGC U ser UUA UCA UAA STOP UGA STOP leu UUG UCG UAG STOP UGG trp CUU CCU CAU CGU his CUC CCC CAC CGC C leu pro arg CUA CCA CAA CGA gin CUG CCG CAG CGG AUU ACU AAU AGU asn ser AUC ile ACC AAC AGC A thr AUA ACA AAA AGA lys arg AUG met ACG AAG AGG GUU GCU GAU GGU asp GUC GCC GAC GGC G val ala gly GUA GCA GAA GGA glu GUG GCG GAG GGG →CAGUGAGUGAGUGAG с Third Position Snuffle Snork TAC CAA AGA AAT ATT TAC ATG GGT GTT GTC TTC ACT TAC GAG GAT AGC CGC ATC TAC CAA CGA CCC ACT TAC GTA TAA ATT TAC AGA GGC CAA ATC TAC TTG TAT GGT ACC GGT TGC ATC TAC CTA CTA TTG TCC ACT TAC TAC AAA TCA ACT TAC GCT ATG ACA CCT ATT Snapple Snork TAC CAG AGG TTT ATC TAC CAT GGC TGT GGA TTT ACT TAC GAT AAG AAC GGG ATT TAC CGT CAT CAC ATC TAC GTA GTG ATC TAC CAG AAA ATG ACT TAC TTA TAG GAC GAT GGG TGC ATT TAC CAG TTA TTG TCT ATC TAC AAA AAG GTG ACT TAC GCG TAC TGG GGC ACT How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with ten genes on it. Your job is to analyze the genes of its DNA and determine what traits the organism has and then sketch the organism (You can be creative here). For simplicity, the gene sequences are much smaller than *real* gene sequences found in living organisms. Each gene has two versions (alleles) that result in a different trait being expressed in the snork. Genes Amino Acid Sequence met Gene 1 - body covering valser - leu met - valser - lys Gene 2 - body style -- Phenotype Snoopy Snork TAC CAG AGG TTT ATC TAC ATG GGT GTC GTC TTC ACT TAC GAG GAT AGC CGC ATC TAC CGT CAT CAC ATC TAC GTA GTG ATC TAC AGA GGC CAA ATC TAC TTG TAT GGT ACC GGT TGC ATC TAC CAG TTA TTG TCT ATC TAC AAA AAG GTG ACT TAC GCT ATG ACA CCT ATT Gene 3 - legs Gene 4 - head shape Gene 5 - tails Gene 6 - body pigment Gene 7 - eyes ByrdS Gene 8 - mouth Gene 9 - ears Gene 10 - arms met - tyr-pro- gln - gln - lys met-val-pro- thr - pro - lys met - leu - phe - leu - pro met - leu - leu - ser- ala metala - val - val met - val - ala - gly met-his- ile met - his-his met ser - pro - val - met - val - phe - tyr met - asn - - ile - leu - leu - pro - thr met - asn - ile - pro - trp - pro- thr met val - asn - asn arg met asp - asp - asn - arg met - met - phe - ser met - phe - phe - his met- arg - tyr - cys - gly met - arg met - thr - pro hairless hairy plump skinny 3 legged 2 legged round head square head tail no tail blue pigment (hair/skin) red pigment (hair/skin) small slanted eyes large round eyes circular mouth rectangular mouth pointed standing-up ears rounded floppy ears long spaghetti like arms short stumpy arms Each of the DNA samples was taken from volunteer Snorks. Your job is to analyze each DNA sample and determine the phenotype (how the organism looks) based on the sequence. You will do this by (1) transcribing each DNA sequence to mRNA, and then (2) translating the mRNA codons into amino acids. Remember that in mRNA, AUG is a start codon (amino acid = met), an it signifies the beginning of each gene. The stop codons that signify the end of a gene are UAA, UAG and UGA. The genes are in order from Gene 1 to Gene 10. ByrdS
Chapter23: All The Rest
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6MC
Related questions
Question
100%
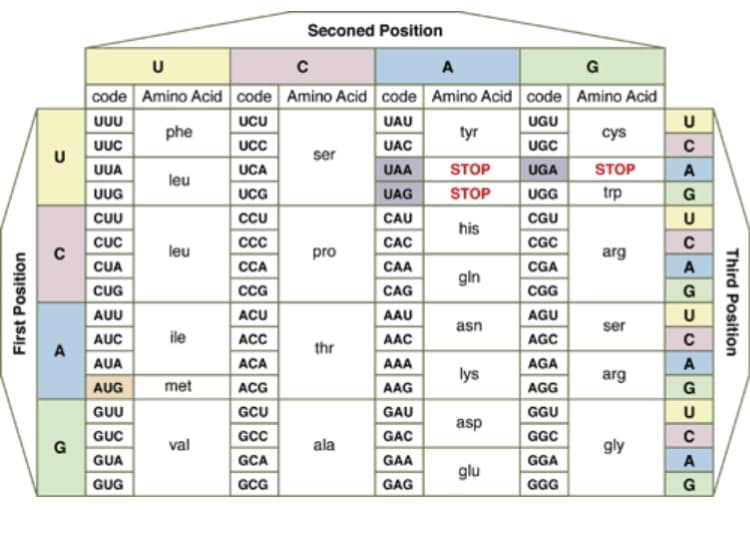
Transcribed Image Text:First Position
U
C
Seconed Position
A
G
code Amino Acid code Amino Acid code Amino Acid code Amino Acid
บบบ
UCU
UAU
UGU
phe
tyr
cys
UUC
UCC
UAC
UGC
U
ser
UUA
UCA
UAA
STOP
UGA
STOP
leu
UUG
UCG
UAG
STOP
UGG
trp
CUU
CCU
CAU
CGU
his
CUC
CCC
CAC
CGC
C
leu
pro
arg
CUA
CCA
CAA
CGA
gin
CUG
CCG
CAG
CGG
AUU
ACU
AAU
AGU
asn
ser
AUC
ile
ACC
AAC
AGC
A
thr
AUA
ACA
AAA
AGA
lys
arg
AUG
met
ACG
AAG
AGG
GUU
GCU
GAU
GGU
asp
GUC
GCC
GAC
GGC
G
val
ala
gly
GUA
GCA
GAA
GGA
glu
GUG
GCG
GAG
GGG
→CAGUGAGUGAGUGAG
с
Third Position

Transcribed Image Text:Snuffle Snork
TAC CAA AGA AAT ATT TAC ATG GGT GTT GTC TTC ACT TAC GAG GAT
AGC CGC ATC TAC CAA CGA CCC ACT TAC GTA TAA ATT TAC AGA GGC
CAA ATC TAC TTG TAT GGT ACC GGT TGC ATC TAC CTA CTA TTG TCC ACT
TAC TAC AAA TCA ACT TAC GCT ATG ACA CCT ATT
Snapple Snork
TAC CAG AGG TTT ATC TAC CAT GGC TGT GGA TTT ACT TAC GAT AAG
AAC GGG ATT TAC CGT CAT CAC ATC TAC GTA GTG ATC TAC CAG AAA
ATG ACT TAC TTA TAG GAC GAT GGG TGC ATT TAC CAG TTA TTG TCT ATC
TAC AAA AAG GTG ACT TAC GCG TAC TGG GGC ACT
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism?
Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism -
the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only
have one chromosome with ten genes on it. Your job is to analyze the genes of its DNA and
determine what traits the organism has and then sketch the organism (You can be creative here).
For simplicity, the gene sequences are much smaller than *real* gene sequences found in living
organisms. Each gene has two versions (alleles) that result in a different trait being expressed in
the snork.
Genes
Amino Acid Sequence
met
Gene 1 - body covering
valser - leu
met - valser - lys
Gene 2 - body style
--
Phenotype
Snoopy Snork
TAC CAG AGG TTT ATC TAC ATG GGT GTC GTC TTC ACT TAC GAG GAT
AGC CGC ATC TAC CGT CAT CAC ATC TAC GTA GTG ATC TAC AGA GGC
CAA ATC TAC TTG TAT GGT ACC GGT TGC ATC TAC CAG TTA TTG TCT ATC
TAC AAA AAG GTG ACT TAC GCT ATG ACA CCT ATT
Gene 3 - legs
Gene 4 - head shape
Gene 5 - tails
Gene 6 - body pigment
Gene 7 - eyes
ByrdS
Gene 8 - mouth
Gene 9 - ears
Gene 10 - arms
met - tyr-pro- gln - gln - lys
met-val-pro- thr - pro - lys
met - leu - phe - leu - pro
met - leu - leu - ser- ala
metala - val - val
met - val - ala - gly
met-his- ile
met - his-his
met ser - pro - val
-
met - val - phe - tyr
met - asn - - ile - leu - leu - pro - thr
met - asn - ile - pro - trp - pro- thr
met val - asn - asn arg
met asp - asp - asn - arg
met - met - phe - ser
met - phe - phe - his
met- arg - tyr - cys - gly
met - arg met - thr - pro
hairless
hairy
plump
skinny
3 legged
2 legged
round head
square head
tail
no tail
blue pigment (hair/skin)
red pigment (hair/skin)
small slanted eyes
large round eyes
circular mouth
rectangular mouth
pointed standing-up ears
rounded floppy ears
long spaghetti like arms
short stumpy arms
Each of the DNA samples was taken from volunteer Snorks. Your job is to analyze each DNA
sample and determine the phenotype (how the organism looks) based on the sequence. You will
do this by (1) transcribing each DNA sequence to mRNA, and then (2) translating the mRNA
codons into amino acids. Remember that in mRNA, AUG is a start codon (amino acid = met), an
it signifies the beginning of each gene. The stop codons that signify the end of a gene are UAA,
UAG and UGA. The genes are in order from Gene 1 to Gene 10.
ByrdS
AI-Generated Solution
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
Recommended textbooks for you


Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning