Step 4: Fill in the relative half-cell reduction potentials with zinc as the reference electrode using data from the previous steps (Steps 1-3 in Video 2). Zn²+/Zn: vols Cu²+/Cu: Mg2+/Mg: Fe²+/Fe: Step 5: Calculate the expected potentials for the following cells using the half-cell potentials in the table above. Compare them with the measured values (from Video 2) and determine the percent error. Assume that the expected potential is the accepted value. Cell Mg Mg²+||Fe²+ Fe Mg|Mg2+||Cu²+ Cu Fe|Fe²+||Cu²+|Cu CALCULATIONS: Expected Potential Measured Potential Percent Error
Step 4: Fill in the relative half-cell reduction potentials with zinc as the reference electrode using data from the previous steps (Steps 1-3 in Video 2). Zn²+/Zn: vols Cu²+/Cu: Mg2+/Mg: Fe²+/Fe: Step 5: Calculate the expected potentials for the following cells using the half-cell potentials in the table above. Compare them with the measured values (from Video 2) and determine the percent error. Assume that the expected potential is the accepted value. Cell Mg Mg²+||Fe²+ Fe Mg|Mg2+||Cu²+ Cu Fe|Fe²+||Cu²+|Cu CALCULATIONS: Expected Potential Measured Potential Percent Error
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter17: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 83AP
Related questions
Question
Step 4 and Step 5. Use the tabel I filled out to find out.
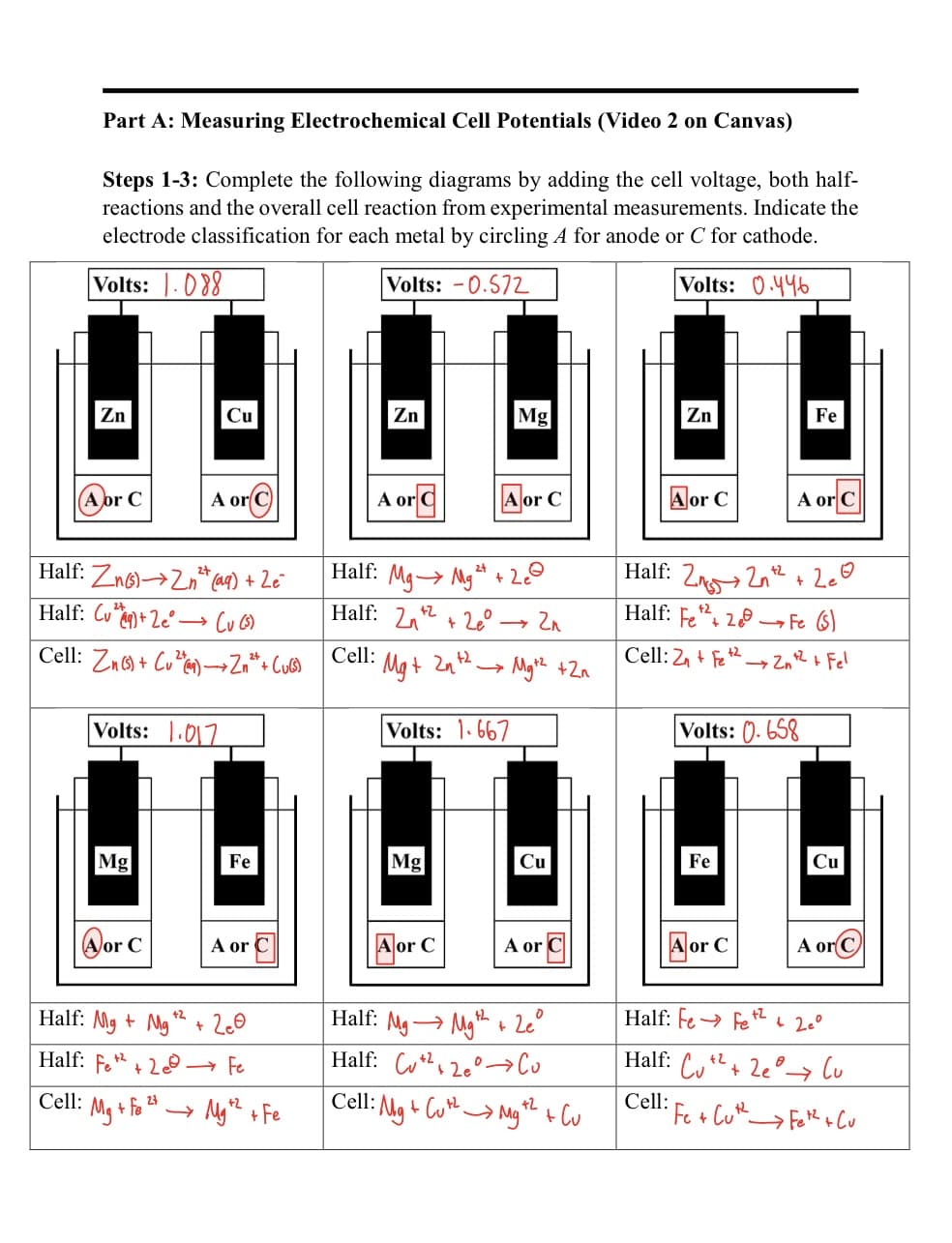
Transcribed Image Text:Part A: Measuring Electrochemical Cell Potentials (Video 2 on Canvas)
Steps 1-3: Complete the following diagrams by adding the cell voltage, both half-
reactions and the overall cell reaction from experimental measurements. Indicate the
electrode classification for each metal by circling A for anode or C for cathode.
Volts: 088
Volts: -0.572
Volts: 0.446
Zn
A or C
Cell:
Half: Zn(s)→2
(aq) + Ze
Half: Cu+ 2e
(u (5)
Cell: Zn(s) + Cu)→→ Zn²+ + (u(s)
Volts: 1.017
Mg
or C
Cu
A or C
• Mg + fe ²7.
+2
Half: Mg + Mg
Half: Fe2+2 → Fe
Fe
A or
+ 2e0
+2
Муж + Fe
Zn
A or C
Cell: Mg + 2n
2+
Half: Mg→ Mg ¹ + 2
Half: 2+²+2
Mg
+2
A or C
Mg
A or C
Volts: 1.667
→ 2n
- Mg +² +2n
Cu
A or
Half: Mg Mg+Leº
Half: C220 Co
Cell: Mg + Cut Mg2+ Cu
Zn
A or C
Half: 22n+² +2e
Half: Fe2+ 2Fe (S)
Cell: 2+ Fe22n+²+ Fel
Volts: 0.658
Fe
A or C
Fe
A or C
Fe + Cut_
Cu
A or C
Half: Fe→ +Z + 20°
Half: +² +2e
+2
Cell:
lu
→ Fet² + Cu

Transcribed Image Text:Step 4: Fill in the relative half-cell reduction potentials with zinc as the reference
electrode using data from the previous steps (Steps 1-3 in Video 2).
Zn²+/Zn: 0volts Cu²+/Cu:
Mg2+/Mg:
Fe²+/Fe:
Step 5: Calculate the expected potentials for the following cells using the half-cell
potentials in the table above. Compare them with the measured values (from Video
2) and determine the percent error. Assume that the expected potential is the
accepted value.
Cell
Mg Mg2+||Fe²+ Fe
Mg Mg2+|| Cu²+|Cu
Fe|Fe²+||Cu²+|Cu
CALCULATIONS:
Expected Potential Measured Potential Percent Error
Step 6: Rank the reduction potentials of the metal ions (Zn²+, Cu²+, Mg²+, Fe²+).
smallest
greatest
Cutz
Fe +2
ढककर
Mg +2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning