Still considering Figure FTR 1, estimate the additional stress- es induced by the footing on the mid thickness of each layer using both 2-1 approximation and graphical method as proposed by Boussinesq. A soil layer consists of 4 meters of sand underlying 5 meters
Still considering Figure FTR 1, estimate the additional stress- es induced by the footing on the mid thickness of each layer using both 2-1 approximation and graphical method as proposed by Boussinesq. A soil layer consists of 4 meters of sand underlying 5 meters
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Chapter17: Subsoil Exploration
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17.14P
Related questions
Question
#2 question only
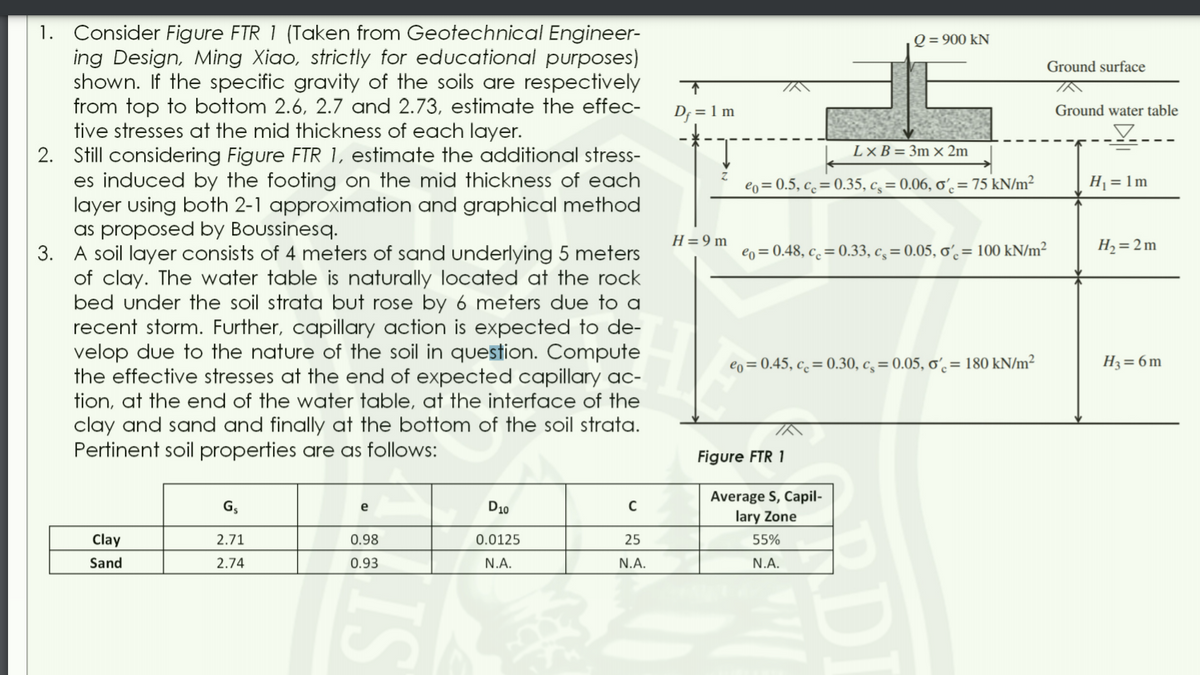
Transcribed Image Text:1. Consider Figure FTR 1 (Taken from Geotechnical Engineer-
ing Design, Ming Xiao, strictly for educational purposes)
shown. If the specific gravity of the soils are respectively
from top to bottom 2.6, 2.7 and 2.73, estimate the effec-
tive stresses at the mid thickness of each layer.
2. Still considering Figure FTR 1, estimate the additional stress-
es induced by the footing on the mid thickness of each
layer using both 2-1 approximation and graphical method
as proposed by Boussinesq.
3. A soil layer consists of 4 meters of sand underlying 5 meters
of clay. The water table is naturally located at the rock
bed under the soil strata but rose by 6 meters due to a
recent storm. Further, capillary action is expected to de-
velop due to the nature of the soil in question. Compute
the effective stresses at the end of expected capillary ac-
Q = 900 kN
Ground surface
D; = 1 m
Ground water table
L× B = 3m × 2m
eo=0.5, cc = 0.35, c, = 0.06, ơʻ,= 75 kN/m²
Cs
Hj = 1m
H=9 m
eo = 0.48, c¸ = 0.33, c¸= 0.05, ơʻ= 100 kN/m²
H2= 2 m
eo=0.45, c. = 0.30, c, = 0.05, o. = 180 kN/m²
H3= 6m
tion, at the end of the water table, at the interface of the
clay and sand and finally at the bottom of the soil strata.
Pertinent soil properties are as follows:
Figure FTR 1
Average S, Capil-
lary Zone
G,
e
D10
Clay
2.71
0.98
0.0125
25
55%
Sand
2.74
0.93
N.A.
N.A.
N.A.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning