Suppose a monopolist faces a market demand that is the first two columns in the table below. Also, in the short run, assume that Total Fixed Cost equals $100 and the monopolist has Total Variable Cost according to the table. Find Total Revenue for each price and quantity combination, and then Marginal Revenue as price falls and quantity increases. Fill in the rest of the costs in the table and find profit at each price and quantity combination as the difference between Total Revenue and Total Cost. If profit is less than zero that indicates a loss. What is the maximum profit you found in this table? At what quantity and price combination is profit maximized for this monopolist? Next, verify this result by using Marginal Analysis to find the profit maximizing price and quantity combination. For each quantity, ask yourself if Marginal Revenue exceeds Marginal Cost. If it does, then profits would be increased by producing that quantity. As you go down the table to higher quantities, stop at the quantity where producing more would cause Marginal Revenue to be less than Marginal Cost. Any quantity where Marginal Revenue is less than Marginal Cost would actually make profit lower and therefore is not profit maximizing. As long as Marginal Revenue exceeds Marginal Cost, producing that quantity adds to profit. What price and quantity combination did you find maximizes the monopolist's profit using Marginal Analysis? Demand and Cost facing Monopolist Total Total Marginal Marginal Total Price Quantity Variable Profit Revenue Revenue Cost Cost Cost $10 10 $30 $9 20 $50 $8 30 $60 $7 40 $80 $6 50 $110 $5 60 $150 $4 70 $210 $3 80 $290
Suppose a monopolist faces a market demand that is the first two columns in the table below. Also, in the short run, assume that Total Fixed Cost equals $100 and the monopolist has Total Variable Cost according to the table. Find Total Revenue for each price and quantity combination, and then Marginal Revenue as price falls and quantity increases. Fill in the rest of the costs in the table and find profit at each price and quantity combination as the difference between Total Revenue and Total Cost. If profit is less than zero that indicates a loss. What is the maximum profit you found in this table? At what quantity and price combination is profit maximized for this monopolist? Next, verify this result by using Marginal Analysis to find the profit maximizing price and quantity combination. For each quantity, ask yourself if Marginal Revenue exceeds Marginal Cost. If it does, then profits would be increased by producing that quantity. As you go down the table to higher quantities, stop at the quantity where producing more would cause Marginal Revenue to be less than Marginal Cost. Any quantity where Marginal Revenue is less than Marginal Cost would actually make profit lower and therefore is not profit maximizing. As long as Marginal Revenue exceeds Marginal Cost, producing that quantity adds to profit. What price and quantity combination did you find maximizes the monopolist's profit using Marginal Analysis? Demand and Cost facing Monopolist Total Total Marginal Marginal Total Price Quantity Variable Profit Revenue Revenue Cost Cost Cost $10 10 $30 $9 20 $50 $8 30 $60 $7 40 $80 $6 50 $110 $5 60 $150 $4 70 $210 $3 80 $290
Chapter14: Monopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14.9P
Related questions
Question
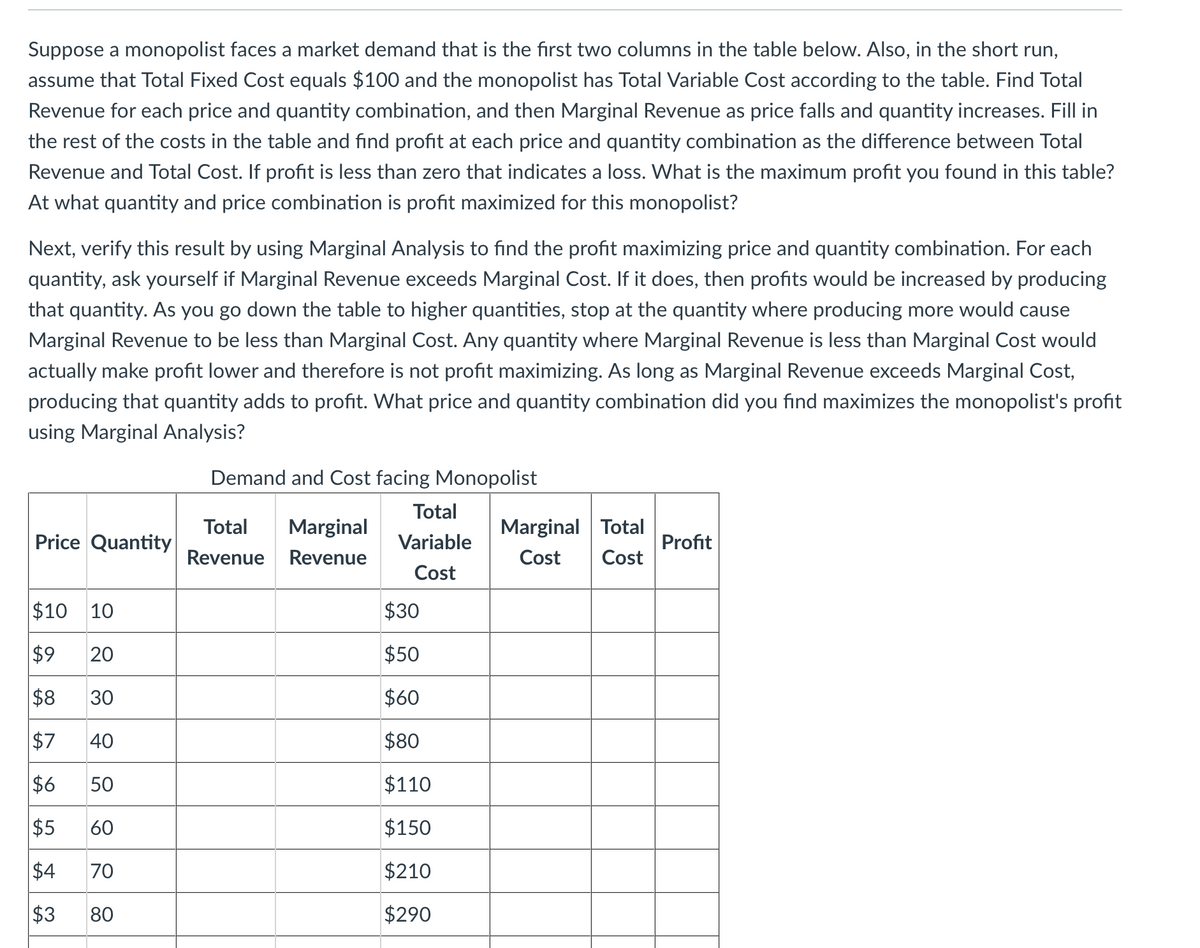
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a monopolist faces a market demand that is the first two columns in the table below. Also, in the short run,
assume that Total Fixed Cost equals $100 and the monopolist has Total Variable Cost according to the table. Find Total
Revenue for each price and quantity combination, and then Marginal Revenue as price falls and quantity increases. Fill in
the rest of the costs in the table and find profit at each price and quantity combination as the difference between Total
Revenue and Total Cost. If profit is less than zero that indicates a loss. What is the maximum profit you found in this table?
At what quantity and price combination is profit maximized for this monopolist?
Next, verify this result by using Marginal Analysis to find the profit maximizing price and quantity combination. For each
quantity, ask yourself if Marginal Revenue exceeds Marginal Cost. If it does, then profits would be increased by producing
that quantity. As you go down the table to higher quantities, stop at the quantity where producing more would cause
Marginal Revenue to be less than Marginal Cost. Any quantity where Marginal Revenue is less than Marginal Cost would
actually make profit lower and therefore is not profit maximizing. As long as Marginal Revenue exceeds Marginal Cost,
producing that quantity adds to profit. What price and quantity combination did you find maximizes the monopolist's profit
using Marginal Analysis?
Demand and Cost facing Monopolist
Total
Total
Marginal
Marginal Total
Price Quantity
Variable
Profit
Revenue
Revenue
Cost
Cost
Cost
$10 10
$30
$9
20
$50
$8
30
$60
$7
40
$80
$6
50
$110
$5
60
$150
$4
70
$210
$3
80
$290
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you








Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
