Suppose that General Motors Acceptance Corporation issued a bond with 10 years until maturity, a face value of $1,000, and a coupon rate of 7% (annual payments). The yield to maturity on this bond when it was issued was 6%. Assuming the yield to maturity remains constant, what is the price of the bond immediately after it makes its first coupon payment? Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. Maturity (years) Face value Coupon rate Yield to maturity Coupon Remaining Maturity (years) Bond price =quirements 1 2 3 $ 10 1,000 7% 6% In cell D11, by using cell references, calculate the coupon payment of the bond In cell D12, by using cell references, calculate the number of periods left on the bond In cell D13, by using cell references, calculate the price of the bond or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. Note: The output of the expression
Suppose that General Motors Acceptance Corporation issued a bond with 10 years until maturity, a face value of $1,000, and a coupon rate of 7% (annual payments). The yield to maturity on this bond when it was issued was 6%. Assuming the yield to maturity remains constant, what is the price of the bond immediately after it makes its first coupon payment? Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. Maturity (years) Face value Coupon rate Yield to maturity Coupon Remaining Maturity (years) Bond price =quirements 1 2 3 $ 10 1,000 7% 6% In cell D11, by using cell references, calculate the coupon payment of the bond In cell D12, by using cell references, calculate the number of periods left on the bond In cell D13, by using cell references, calculate the price of the bond or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. Note: The output of the expression
Chapter8: Analysis Of Risk And Return
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9P
Related questions
Question
please show hoe to complete using excel formulas
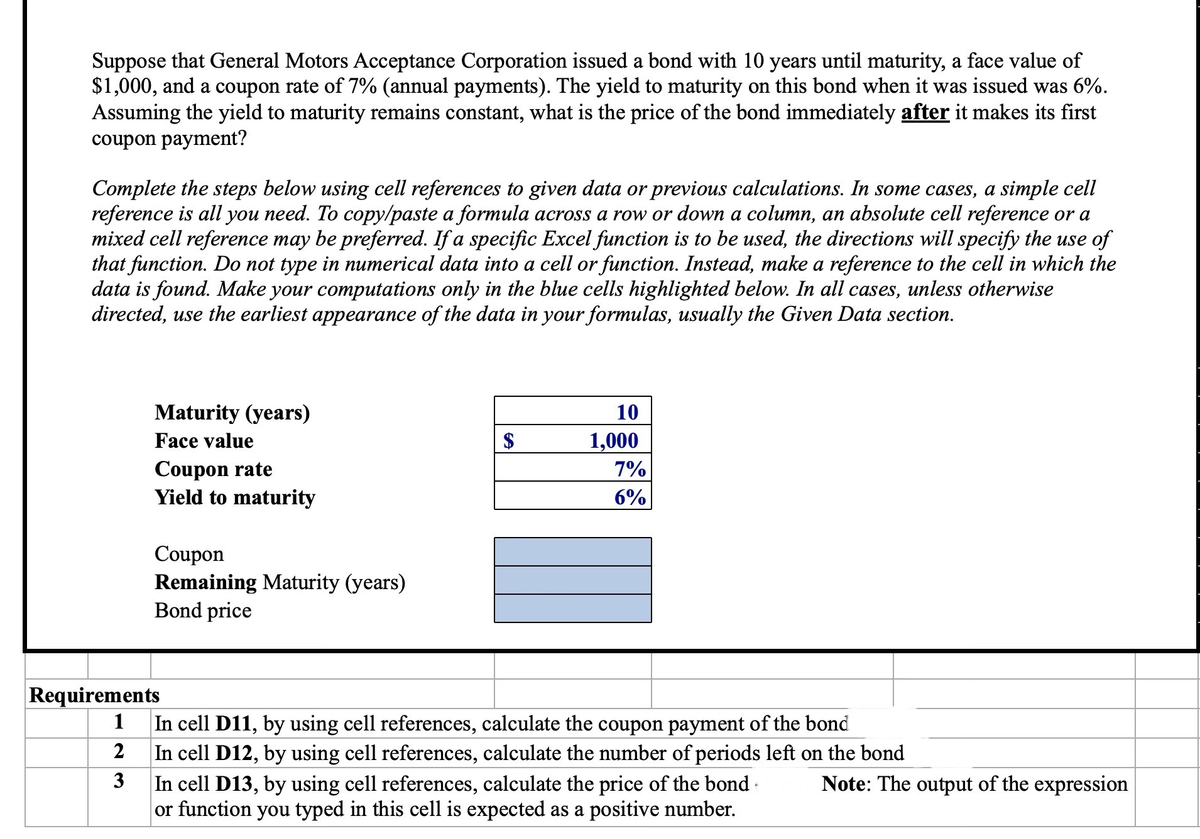
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that General Motors Acceptance Corporation issued a bond with 10 years until maturity, a face value of
$1,000, and a coupon rate of 7% (annual payments). The yield to maturity on this bond when it was issued was 6%.
Assuming the yield to maturity remains constant, what is the price of the bond immediately after it makes its first
coupon payment?
Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell
reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a
mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of
that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the
data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise
directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section.
Maturity (years)
Face value
Coupon rate
Yield to maturity
Coupon
Remaining Maturity (years)
Bond price
Requirements
1
2
3
10
1,000
7%
6%
In cell D11, by using cell references, calculate the coupon payment of the bond
In cell D12, by using cell references, calculate the number of periods left on the bond
In cell D13, by using cell references, calculate the price of the bond
or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number.
Note: The output of the expression
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
