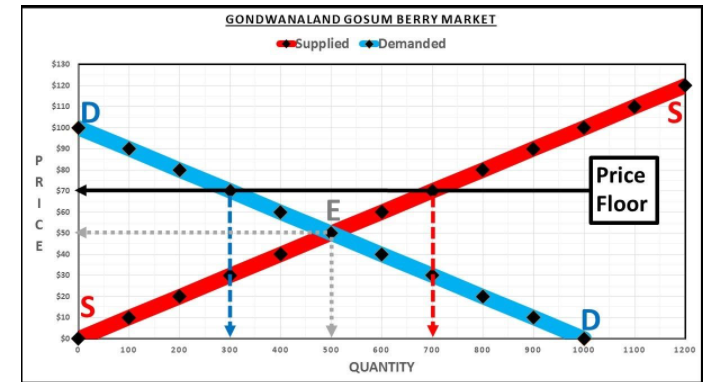
Suppose that the Gondwanaland Chairman of Production, who sets the governmental price floor for gosum berries, in an effort to assist the gosum berry producers to have a higher income, set the price floor at $70 per barrel. In that particular year, the amount of gosum berries produced at the $70 price floor was 700 barrels per month. To support the price of gosum berries, the Chairman of Production’s Office had to purchase 400 barrels per month. The accompanying chart and diagram shows supply and demand curves illustrating the market for Gondwanaland gosum berries. Price Quantity Supplied Quantity Demanded $120 1,200 $110 1,100 $100 1,000 0 $90 900 100 $80 800 200 $70 700 300 $60 600 400 $50 500 500 $40 400 600 $30 300 700 $20 200 800 $10 100 900 $0 0 1,000 The accompanying diagram shows supply and demand curves illustrating the market for Gondwanaland gosum berries. Utilizing this information, answer the following questions. In the absence of a price floor, the maximum price that a few of the consumers are willing to pay up to $100 per barrel of gosum berries. The market equilibrium (E) price is $50 per barrel. How much consumer surplus is created when there is no price floor? Show your calculations. How much producer surplus is created when there is no price floor? Show your calculations. What is the total surplus when there is no price floor? Show your calculations. After the price floor is instituted, the legal minimum price that can be charged by suppliers is $70 per barrel. The maximum price that a few of the consumers are still willing to pay is $100 per barrel of gosum berries. With the price floor at $70 per barrel, consumers buy 300 barrels of gosum berries per month. How much consumer surplus is created with the price floor? Show your calculations. After the price floor is instituted, the Chairman of Productions Office buys up any barrels of gosum berries that the producers are not able to sell. With the price floor, the producers sell 300 barrels per month to consumers, but the producers, at this high price floor, produce 700 barrels per month. How much producer surplus is created with the price floor? Show your calculations. The Chairman of Production’s Office buys any barrels of gosum berries that the producers are not able to sell. With the price floor, the producers sell 300 barrels per month to consumers, but the producers, at this high price floor, produce 700 barrels per month. How much money does the Chairman of Production’s Office spend on buying up surplus gosum berries? Show your calculations. The Emperor of Gondwanaland must collect taxes from the people to pay for the purchases of surplus gosum berries by the Chairman of Production’s Office. As a result, total surplus (producer plus consumer) is reduced by the amount the Chairman of Production’s Office spent on buying surplus gosum berries. Using your answers for problems 4, 5, and 6 above, what is the total surplus when there is a price floor? Show your calculations. How does this compare to the total surplus without a price floor from problem 3 above? Is it more, or less, and by how much?
Suppose that the Gondwanaland Chairman of Production, who sets the governmental
|
Price |
Quantity Supplied |
Quantity Demanded |
|---|---|---|
|
$120 |
1,200 |
|
|
$110 |
1,100 |
|
|
$100 |
1,000 |
0 |
|
$90 |
900 |
100 |
|
$80 |
800 |
200 |
|
$70 |
700 |
300 |
|
$60 |
600 |
400 |
|
$50 |
500 |
500 |
|
$40 |
400 |
600 |
|
$30 |
300 |
700 |
|
$20 |
200 |
800 |
|
$10 |
100 |
900 |
|
$0 |
0 |
1,000 |
The accompanying diagram shows supply and demand curves illustrating the market for Gondwanaland gosum berries. Utilizing this information, answer the following questions.
- In the absence of a price floor, the maximum price that a few of the consumers are willing to pay up to $100 per barrel of gosum berries. The market
equilibrium (E) price is $50 per barrel. How much consumer surplus is created when there is no price floor? Show your calculations.
- How much
producer surplus is created when there is no price floor? Show your calculations.
- What is the total surplus when there is no price floor? Show your calculations.
- After the price floor is instituted, the legal minimum price that can be charged by suppliers is $70 per barrel. The maximum price that a few of the consumers are still willing to pay is $100 per barrel of gosum berries. With the price floor at $70 per barrel, consumers buy 300 barrels of gosum berries per month. How much consumer surplus is created with the price floor? Show your calculations.
- After the price floor is instituted, the Chairman of Productions Office buys up any barrels of gosum berries that the producers are not able to sell. With the price floor, the producers sell 300 barrels per month to consumers, but the producers, at this high price floor, produce 700 barrels per month. How much producer surplus is created with the price floor? Show your calculations.
- The Chairman of Production’s Office buys any barrels of gosum berries that the producers are not able to sell. With the price floor, the producers sell 300 barrels per month to consumers, but the producers, at this high price floor, produce 700 barrels per month. How much money does the Chairman of Production’s Office spend on buying up surplus gosum berries? Show your calculations.
- The Emperor of Gondwanaland must collect taxes from the people to pay for the purchases of surplus gosum berries by the Chairman of Production’s Office. As a result, total surplus (producer plus consumer) is reduced by the amount the Chairman of Production’s Office spent on buying surplus gosum berries. Using your answers for problems 4, 5, and 6 above, what is the total surplus when there is a price floor? Show your calculations.
- How does this compare to the total surplus without a price floor from problem 3 above? Is it more, or less, and by how much?
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









