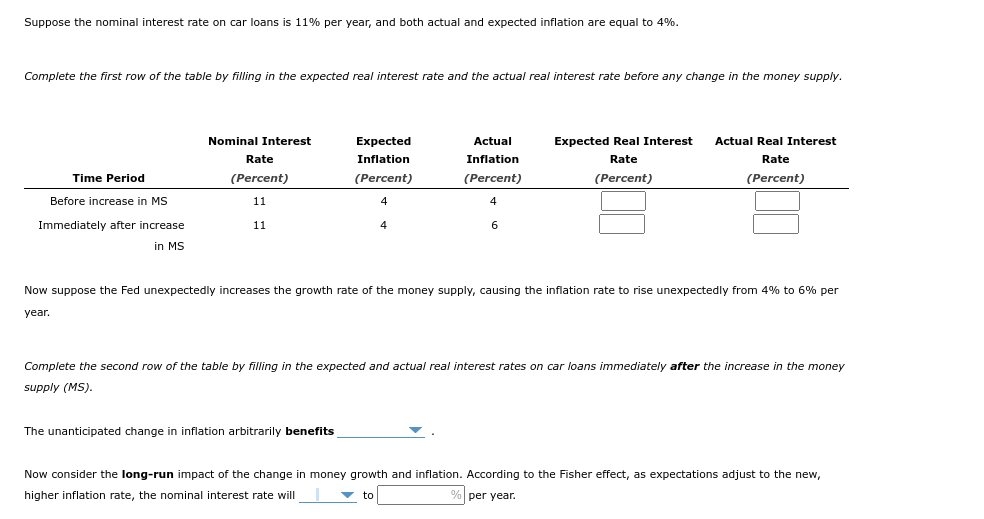
Suppose the nominal interest rate on car loans is 11% per year, and both actual and expected inflation are equal to 4%. Complete the first row of the table by filling in the expected real interest rate and the actual real interest rate before any change in the money supply. Time Period Nominal Interest Rate (Percent) Expected Inflation (Percent) Actual Inflation (Percent) Expected Real Interest Rate (Percent) Actual Real Interest Rate (Percent) Before increase in MS 11 4 4 Immediately after increase in MS 11 4 6 Now suppose the Fed unexpectedly increases the growth rate of the money supply, causing the inflation rate to rise unexpectedly from 4% to 6% per year. Complete the second row of the table by filling in the expected and actual real interest rates on car loans immediately after the increase in the money supply (MS). The unanticipated change in inflation arbitrarily benefits (a. borrows, b. lenders). Now consider the long-run impact of the change in money growth and inflation. According to the Fisher effect, as expectations adjust to the new, higher inflation rate, the nominal interest rate will (a. rise, b. fall) to ___% per year
Suppose the nominal interest rate on car loans is 11% per year, and both actual and expected inflation are equal to 4%. Complete the first row of the table by filling in the expected real interest rate and the actual real interest rate before any change in the money supply. Time Period Nominal Interest Rate (Percent) Expected Inflation (Percent) Actual Inflation (Percent) Expected Real Interest Rate (Percent) Actual Real Interest Rate (Percent) Before increase in MS 11 4 4 Immediately after increase in MS 11 4 6 Now suppose the Fed unexpectedly increases the growth rate of the money supply, causing the inflation rate to rise unexpectedly from 4% to 6% per year. Complete the second row of the table by filling in the expected and actual real interest rates on car loans immediately after the increase in the money supply (MS). The unanticipated change in inflation arbitrarily benefits (a. borrows, b. lenders). Now consider the long-run impact of the change in money growth and inflation. According to the Fisher effect, as expectations adjust to the new, higher inflation rate, the nominal interest rate will (a. rise, b. fall) to ___% per year
Chapter18: Introduction To Macroeconomics: Unemployment, Inflation, And Economic Fluctuations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13P
Related questions
Question
Suppose the nominal interest rate on car loans is 11% per year, and both actual and expected inflation are equal to 4%.
Complete the first row of the table by filling in the expected real interest rate and the actual real interest rate before any change in the money supply.
|
Time Period
|
Nominal Interest Rate (Percent)
|
Expected Inflation (Percent)
|
Actual Inflation (Percent)
|
Expected Real Interest Rate (Percent)
|
Actual Real Interest Rate (Percent)
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before increase in MS | 11 | 4 | 4 |
|
|
| Immediately after increase in MS | 11 | 4 | 6 |
|
|
Now suppose the Fed unexpectedly increases the growth rate of the money supply, causing the inflation rate to rise unexpectedly from 4% to 6% per year.
Complete the second row of the table by filling in the expected and actual real interest rates on car loans immediately after the increase in the money supply (MS).
The unanticipated change in inflation arbitrarily benefits (a. borrows, b. lenders).
Now consider the long-run impact of the change in money growth and inflation. According to the Fisher effect, as expectations adjust to the new, higher inflation rate, the nominal interest rate will (a. rise, b. fall) to ___% per year.
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the nominal interest rate on car loans is 11% per year, and both actual and expected inflation are equal to 4%.
Complete the first row of the table by filling in the expected real interest rate and the actual real interest rate before any change in the money supply.
Time Period
Before increase in MS
Immediately after increase
in MS
Nominal Interest
Rate
(Percent)
11
11
Expected
Inflation
(Percent)
Actual
Inflation
(Percent)
The unanticipated change in inflation arbitrarily benefits
6
Expected Real Interest
Rate
(Percent)
Actual Real Interest
Rate
(Percent)
Now suppose the Fed unexpectedly increases the growth rate of the money supply, causing the inflation rate to rise unexpectedly from 4% to 6% per
year.
Complete the second row of the table by filling in the expected and actual real interest rates on car loans immediately after the increase in the money
supply (MS).
Now consider the long-run impact of the change in money growth and inflation. According to the Fisher effect, as expectations adjust to the new,
higher inflation rate, the nominal interest rate will
% per year.
▼ to
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax