Suppose we have a formula for the titration function P(x). What calculation would we want to do to find the equivalence point? What is our mathematical name for that type of point?
Suppose we have a formula for the titration function P(x). What calculation would we want to do to find the equivalence point? What is our mathematical name for that type of point?
Chapter16: Applications Of Neutralization Titrations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16.48QAP
Related questions
Question
Suppose we have a formula for the titration function P(x). What calculation would we want to do to find the equivalence point? What is our mathematical name for that type of point?

Transcribed Image Text:Titration is a method of chemical analysis in which a reactive substance is slowly added to another
substance, and some property of the combined substance is measured. This procedure is taught in
CHM 116, General Chemistry II.
We will be looking at an example of acid-base titration. Specifically, 25 mL of an unknown
monoprotic weak acid is titrated against 0.105M NaOH (which is a strong base). This means we
are adding the base to the acid using a burette in a slow and precisely controlled manner. We
measure the pH after each addition. (A pH of less than 7 is an acid, and a pH of more than 7 is a
base.)
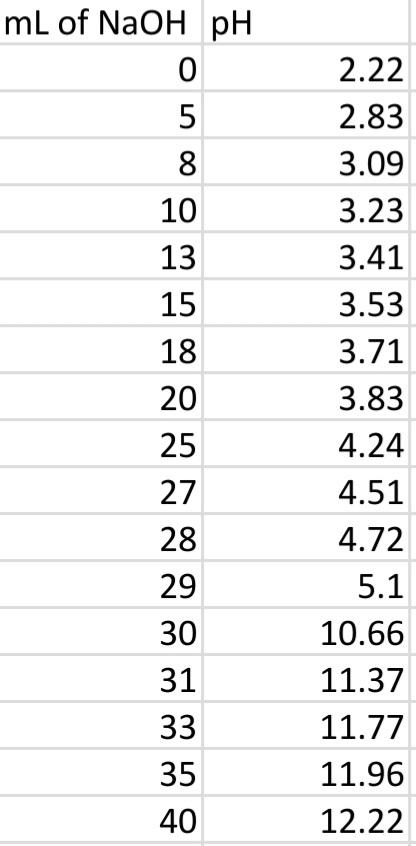
Transcribed Image Text:mL of NaOH pH
2.22
5
2.83
3.09
10
3.23
13
3.41
15
3.53
18
3.71
20
3.83
25
4.24
27
4.51
28
4.72
29
5.1
30
10.66
31
11.37
33
11.77
35
11.96
40
12.22
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning