Term policies provide a O death benefit and a savings component. O death benefit only. O savings vehicle only. Whole ife policies provide a: O savings vehicle only. O death benefit and a savings component with variable rate features. O death benefit and a savings component with fixed rate features. Universal policies provide a: O savings vehicle only. O death benefit and a savings component with variable rate features. O death benefit only.
Term policies provide a O death benefit and a savings component. O death benefit only. O savings vehicle only. Whole ife policies provide a: O savings vehicle only. O death benefit and a savings component with variable rate features. O death benefit and a savings component with fixed rate features. Universal policies provide a: O savings vehicle only. O death benefit and a savings component with variable rate features. O death benefit only.
Chapter11: Planning For Health Care Expenses
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4LTAI
Related questions
Question
A Quick Response will be appreciated
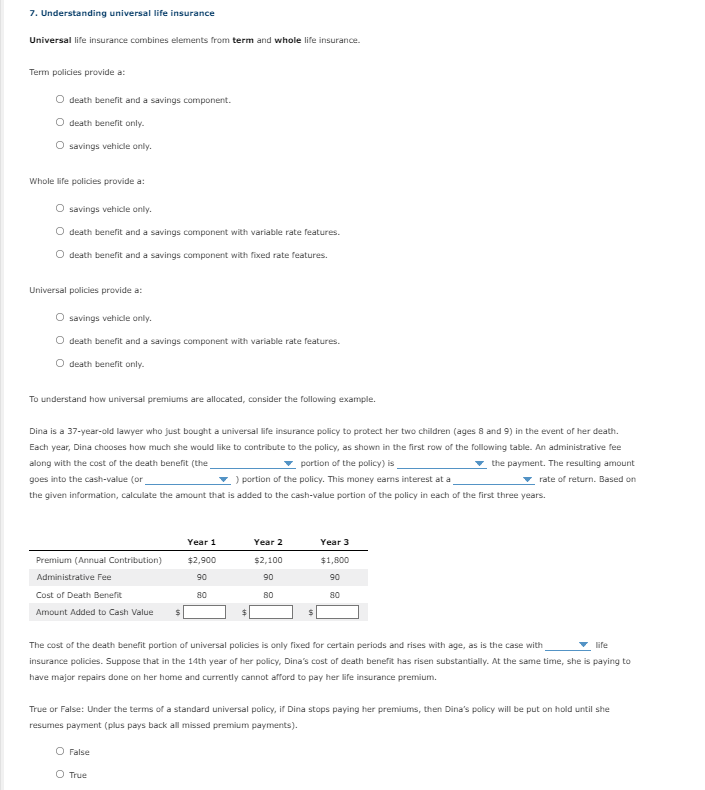
Transcribed Image Text:7. Understanding universal life insurance
Universal life insurance combines elements from term and whole life insurance.
Term policies provide a:
death benefit and a savings component.
death benefit only.
savings vehicle only.
Whole life policies provide a:
savings vehicle only.
O death benefit and a savings component with variable rate features.
death benefit and a savings component with fixed rate features.
Universal policies provide a:
O savings vehicle only.
O death benefit and a savings component with variable rate features.
O death benefit only.
To understand how universal premiums are allocated, consider the following example.
Dina is a 37-year-old lawyer who just bought a universal life insurance policy to protect her two children (ages 8 and 9) in the event of her death.
Each year, Dina chooses how much she would like to contribute to the policy, as shown in the first row of the following table. An administrative fee
along with the cost of the death benefit (the
portion of the policy) is
the payment. The resulting amount
goes into the cash-value (or
) portion of the policy. This money earms interest at a
- rate of return. Based on
the given information, calculate the amount that
added to the cash-value portion of the policy in each of the first three years.
Year 1
Year 2
Year 3
Premium (Annual Contribution)
$2,900
$2,100
$1,800
Administrative Fee
90
90
90
Cost of Death Benefit
80
80
80
Amount Added to Cash Value
The cost of the death benefit portion of universal policies is only fixed for certain periods and rises with age, as is the case with
life
insurance policies. Suppose that in the 14th year of her policy, Dina's cost of death benefit has risen substantially. At the same time, she is paying to
have major repairs done on her home and currently cannot afford to pay her life insurance premium.
True or False: Under the terms of a standard universal policy, if Dina stops paying her premiums, then Dina's policy will be put on hold until she
resumes payment (plus pays back all missed premium payments).
O False
O True
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (…
Finance
ISBN:
9780357033609
Author:
Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. Joehnk
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (…
Finance
ISBN:
9780357033609
Author:
Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. Joehnk
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
