The Beck 550 Spyder described below has manual hydraulic brakes with a single master cylinder. The car is traveling on level ground at sea-level where g = 9.81 m/s². Find the values for the front and rear brake gains that will make this car decelerate at 8.829 m/s², or 0.90g, on a road surface where the peak coefficient of friction is 0.90 when the pedal force is Fp = 250 N. Neglect the aerodynamic drag and the rolling resistance, but this time include the rotational inertia of the tires and wheels. Answer: G₁ =166.1 N-m/MPa for each front wheel and G₁ =114.5 N-m/MPa for each rear wheel. Pedal Assembly The diameter of the master cylinder is DMC = 19.05 mm. The pedal length is L₂ = 225 mm. The pushrod for the master cylinder is located at LR = 50 mm. Pushrod LR Tire rolling radius: r = 0.31 m Wheelbase: L = 2.16 m Lip Masses, Tire Radius, Wheelbase and Location of the CG Mass of the car with driver, passenger and some stuff: m = 780 kg Inertia of each tire and wheel: I = 0.7 kg-m² The center of gravity is located at distance b=1.18 m behind the front axle and h = 0.34 m above the ground.
The Beck 550 Spyder described below has manual hydraulic brakes with a single master cylinder. The car is traveling on level ground at sea-level where g = 9.81 m/s². Find the values for the front and rear brake gains that will make this car decelerate at 8.829 m/s², or 0.90g, on a road surface where the peak coefficient of friction is 0.90 when the pedal force is Fp = 250 N. Neglect the aerodynamic drag and the rolling resistance, but this time include the rotational inertia of the tires and wheels. Answer: G₁ =166.1 N-m/MPa for each front wheel and G₁ =114.5 N-m/MPa for each rear wheel. Pedal Assembly The diameter of the master cylinder is DMC = 19.05 mm. The pedal length is L₂ = 225 mm. The pushrod for the master cylinder is located at LR = 50 mm. Pushrod LR Tire rolling radius: r = 0.31 m Wheelbase: L = 2.16 m Lip Masses, Tire Radius, Wheelbase and Location of the CG Mass of the car with driver, passenger and some stuff: m = 780 kg Inertia of each tire and wheel: I = 0.7 kg-m² The center of gravity is located at distance b=1.18 m behind the front axle and h = 0.34 m above the ground.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
100%
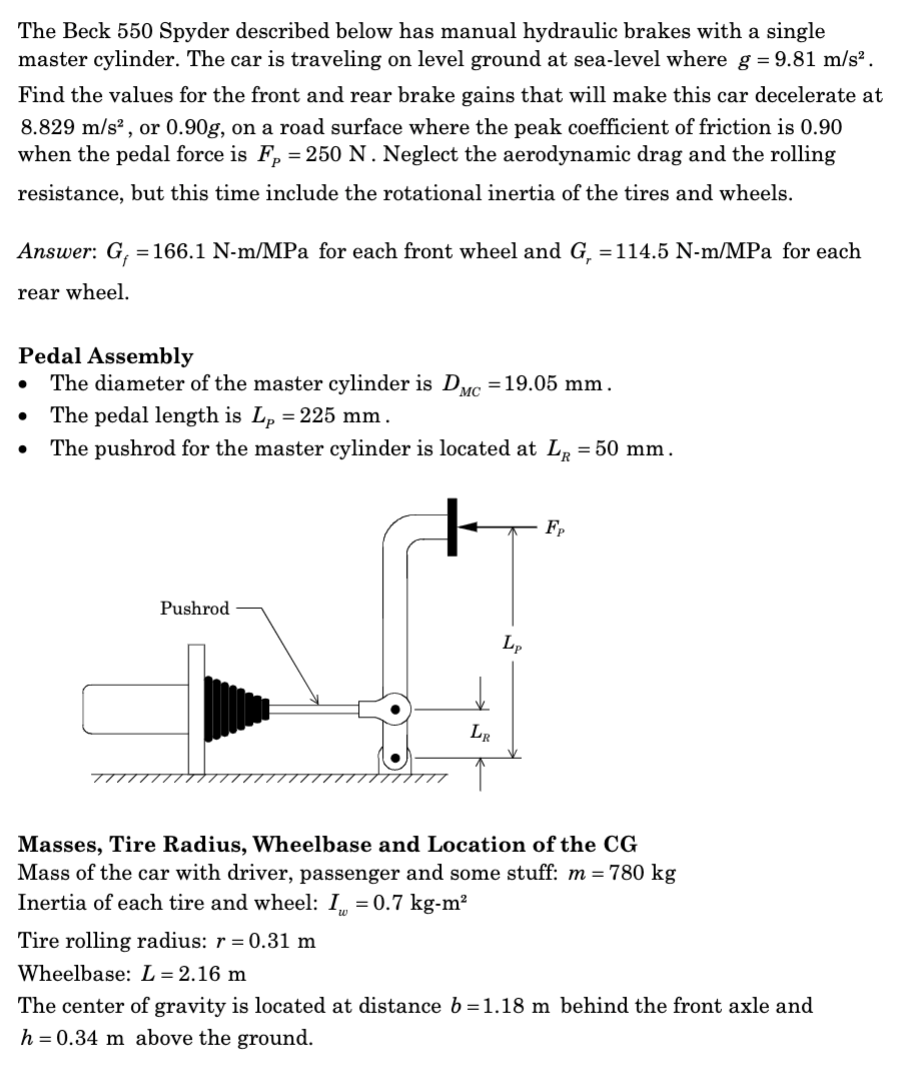
Transcribed Image Text:The Beck 550 Spyder described below has manual hydraulic brakes with a single
master cylinder. The car is traveling on level ground at sea-level where g = 9.81 m/s².
Find the values for the front and rear brake gains that will make this car decelerate at
8.829 m/s², or 0.90g, on a road surface where the peak coefficient of friction is 0.90
when the pedal force is F₂ = 250 N. Neglect the aerodynamic drag and the rolling
resistance, but this time include the rotational inertia of the tires and wheels.
Answer: G₁ =166.1 N-m/MPa for each front wheel and G, = 114.5 N-m/MPa for each
rear wheel.
Pedal Assembly
The diameter of the master cylinder is DMC = 19.05 mm.
The pedal length is Lp = 225 mm.
The pushrod for the master cylinder is located at LR = 50 mm.
●
●
Pushrod
LR
Lp
Fp
Masses, Tire Radius, Wheelbase and Location of the CG
Mass of the car with driver, passenger and some stuff: m = 780 kg
Inertia of each tire and wheel: I = 0.7 kg-m²
Tire rolling radius: r = 0.31 m
Wheelbase: L = 2.16 m
The center of gravity is located at distance b=1.18 m behind the front axle and
h = 0.34 m above the ground.
Expert Solution
Step 1
The front and rear brake gains can be calculated using the following formulas:
Gf = (2μf(b / L)mg)/(DmAf)
Gr = (2μr((L - b)/L)m g)/(DmAr)
where:
μf and μr are the peak coefficients of friction for the front and rear wheels, respectively
b is the distance from the center of gravity to the front axle
L is the wheelbase
m is the mass of the car
g is the acceleration due to gravity
Dm is the diameter of the master cylinder
Af and Ar are the effective piston areas for the front and rear brakes, respectively
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY